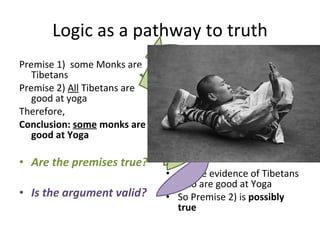
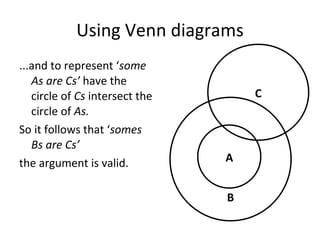
The document discusses different types of logic, including deductive and inductive reasoning. It notes that deductive reasoning is more certain but less informative than inductive reasoning. It also discusses what distinguishes good generalizations from bad ones, including considering number and variety of examples, exceptions, coherence, and subject area. The document describes how logic can help get closer to truth when premises are true and arguments are valid, but gives examples of when conclusions could be tentatively accepted. It also discusses common fallacies in reasoning such as post hoc, ad hominem, circular reasoning, equivocation, and false dilemmas.