Tissue typing is the process of determining compatibility between donor and recipient tissues by identifying their Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) types. HLA acts as a barcode to distinguish self from nonself. Tissue typing ensures a transplanted organ will be compatible with the recipient to reduce rejection. It is done by testing the donor and recipient's blood or tissue to identify their unique HLA antigens. Close matching of HLA antigens between donor and recipient increases the likelihood the recipient's body will accept the transplant. Molecular methods like sequence-based typing now allow highly accurate HLA typing.




![TISSUE TYPING
➔ Tissue typing ensures that an organ from a donor will be compatible
with its recipient.The process starts with identifying the unique Human
Leukocyte Antigens[HLA] for the organ donor and recipient, either
from blood or tissue.
➔ This test is also called Human Leukocyte Antigen [HLA] typing.
➔ The genetic loci involved in the rejection of foreign organs are known
as the Major Histocompatibility Complex-MHC. The Human MHC is
called the HLA system because these antigens were first identified and
characterized using alloantibodies against leukocytes.
➔ The Human MHC maps to short arm of chromosome and spans
approximately 3,600 Kilobases of DNA.
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-5-2048.jpg)

![SNEAK PEEK OF TISSUE TYPING HISTORY…
➔ Tissue matching was first suggested by Alexis Carrel and was
studied in animals by George Snell [Snell 1948].
➔ It began to emerge as a reality for human transplants in 1958,
when Jean Dausset discovered the first Human Leukocyte
Antigen[HLA][Dausset 1958].
➔ Antibodies against this antigen were identified in transfused
patients and multiparous women by Rose Payne [1957] and Jon
Van Rood [Van Rood et al. 1958].
➔ In 1960s,UCLA professor Paul Terasaki invented a tissue typing
test that became an international standard for matching
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-7-2048.jpg)
![➔ He developed a microcytotoxicity assay in
1964 [Terasaki 1964].
➔ His test, which mixed recipient serum and
donor lymphocytes in tiny wells quickly
became standard.
➔ For several years, Terasaki did the typing for
most U.S. transplant centres.
➔ Histocompatibility matching remains
crucial in bone marrow transplantation and
important in selection of family
donors.Unless their is perfect match it is less
Paul Terasaki
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-8-2048.jpg)



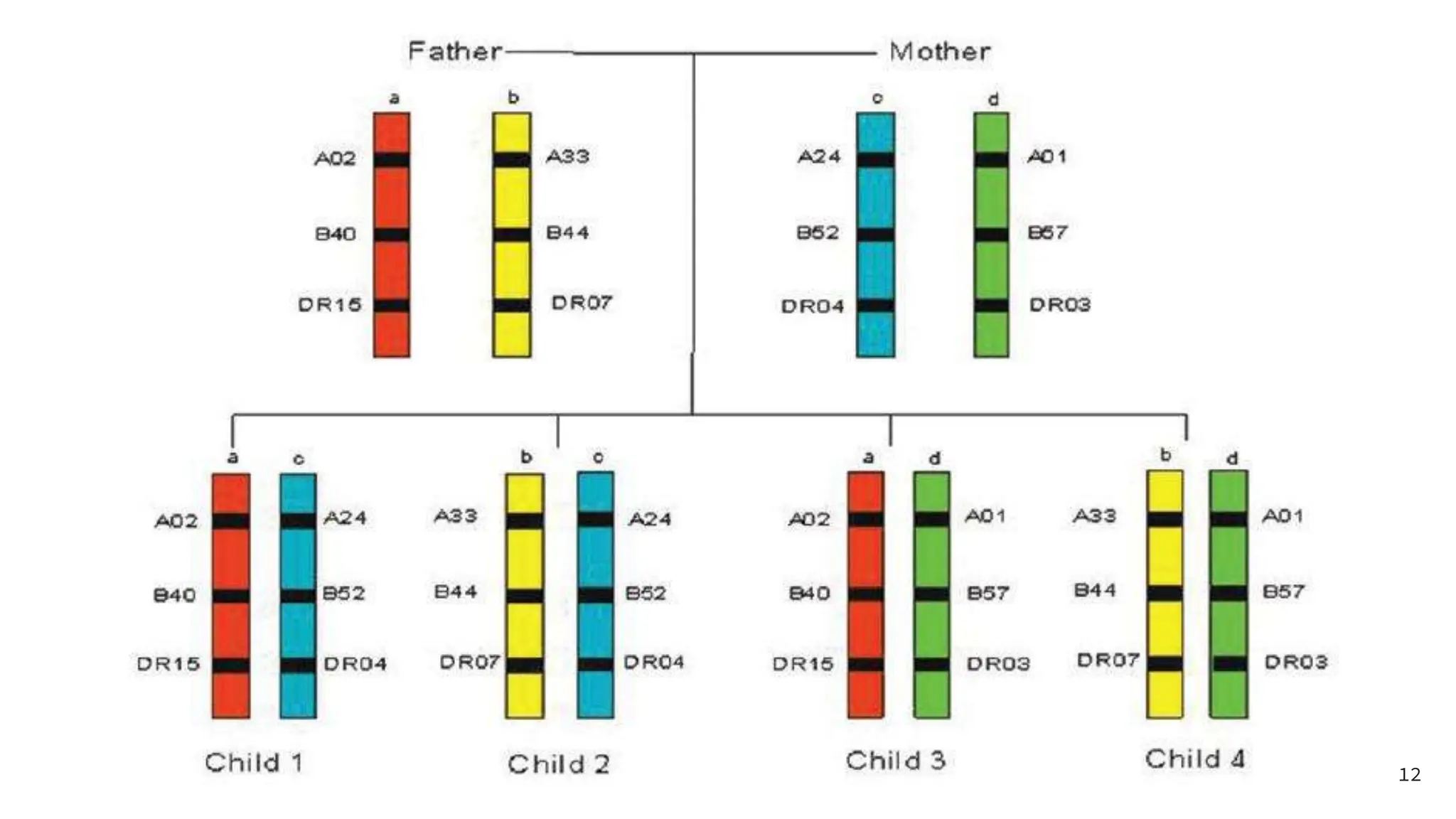




![2. MIXED LYMPHOCYTE CULTURE (MLC)-
➔ It has been observed that lymphocytes from one donor,when
cultured with lymphocytes from unrelated donor stimulates
proliferation.
➔ This is due to a disparity in class II MHC [DR] antigens and T cells of
one individual interacts with allogenic class II MHC antigen bearing
cells [B cells, dendritic cells, langerhans cells, etc] of another.
➔ This reactivity is also known as Mixed Leukocyte Reaction[ MLR].
➔ In this test, lymphocytes [responder cells] of donor are mixed with
irradiated or mitomycin C which is treated leukocytes from the
recipient, containing B-lymphocytes and monocytes [stimulator cells].17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-17-2048.jpg)
![➔ Cells are cultured for 4-6 days.
➔ Responder cell will recognise the foreign class II antigens found
on the donor and undergoes transformation and proliferation
[mitogenesis].
➔ The T cells that respond to foreign class II antigens are typically
CD4+ TH-1 type cells.
➔ These changes are recorded by addition of radioactive (tritiated,
3H) thymidine into the culture and monitoring its incorporation
into DNA.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-18-2048.jpg)


![The types are :-
➔ Hybridization with Sequence Specific Oligonucleotide Probes
[SSOP]
➔ Sequence Specific primers [SSP]
➔ Sequence Based Typing [SBT]
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-21-2048.jpg)
![1. SEQUENCE SPECIFIC OLIGONUCLEOTIDE PROBES [SSOP]:-
➔ Method involves selective amplification of target followed by
hybridization to a panel of oligonucleotide probes.
➔ Specificity for a particular HLA locus is achieved by selecting PCR
primers specific for a sequence in conserved region of the second
exon.
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-22-2048.jpg)

![2. SEQUENCE SPECIFIC PRIMING [SSP]:-
➔ It's a rapid method of HLA typing that uses sets of primer pairs to
amplify region of genomic DNA.
➔ The efficiency of the amplification reaction is controlled by the
primers that amplify conserved sequences of a selected gene.
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-24-2048.jpg)

![3. SEQUENCE BASED HLA TYPING:-
➔ Involves determining the nucleotide sequence of an amplified
segment of an HLA gene.
➔ It is advantageous over other procedures because of relatively fast [
in 24-48 hrs] with high level resolution.
➔ It is more reliable and specific method.
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tissuetypingkr-240404161519-44d12379/75/TISSUE-TYPING-pptx-26-2048.jpg)



