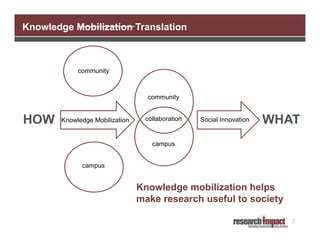
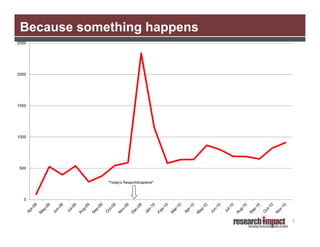
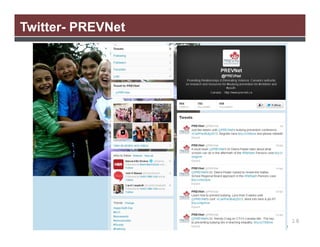
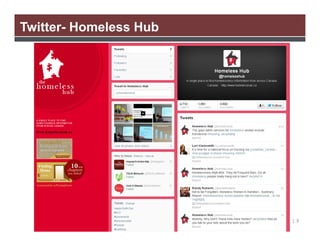
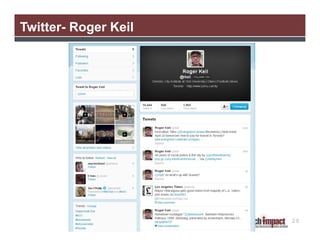
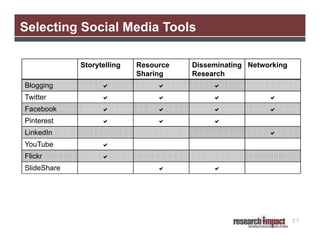
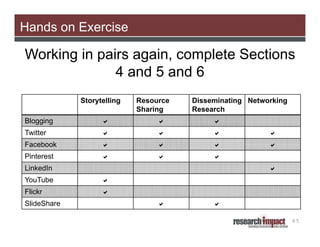
The document discusses the importance of using social media for knowledge mobilization in research, highlighting the need for a strategic approach to engage with communities and disseminate research findings effectively. It outlines different social media tools such as blogging, Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn, and provides guidance on developing a social media strategy that includes setting goals, identifying audiences, and measuring success. Additionally, it emphasizes the integration of social media strategies into grant proposals to enhance research impact.