This document provides an overview of thyrotoxicosis, including its epidemiology, pathophysiology, causes, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. Some key points:
- Thyrotoxicosis is defined as thyroid hormone excess and can be caused by hyperthyroidism, thyroiditis, or excess hormone ingestion. The major causes of hyperthyroidism are Graves' disease, toxic multinodular goiter, and toxic adenomas.
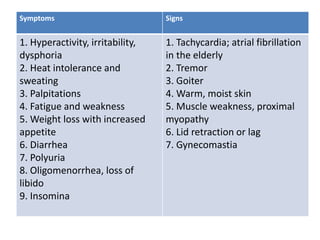
- Clinical manifestations depend on severity and duration of thyrotoxicosis, and include symptoms like palpitations, sweating, weight loss as well as signs like goiter, tremor, eye changes. Diagnosis involves testing thyroid function through TSH,





























































![REFERENCE
• Blick C, Jialal I. Thyroid, Thyrotoxicosis. 2018 Jan. [Medline]. [Full Text].
• Doubleday AR, Sippel RS. Hyperthyroidism. Gland Surg. 2020 Feb. 9 (1):124-35. [Medline].
[Full Text].
• Frost L, Vestergaard P, Mosekilde L. Hyperthyroidism and risk of atrial fibrillation or flutter: a
population-based study. Arch Intern Med. 2004 Aug 9-23. 164(15):1675-8. [Medline].
• [Guideline] Bahn Chair RS, Burch HB, Cooper DS, et al. Hyperthyroidism and other causes of
thyrotoxicosis: management guidelines of the American Thyroid Association and American
Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. Thyroid. 2011 Jun. 21(6):593-646. [Medline].
• [Guideline] Ross DS, Burch HB, Cooper DS, et al. 2016 American Thyroid Association
Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of
Thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid. 2016 Oct. 26 (10):1343-1421. [Medline]. [Full Text].
• Simmonds MJ, Brand OJ, Barrett JC, Newby PR, Franklyn JA, Gough SC. Association of Fc
receptor-like 5 (FCRL5) with Graves' disease is secondary to the effect of FCRL3. Clin
Endocrinology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thyrotoxicosis-210613094752/85/Thyrotoxicosis-63-320.jpg)