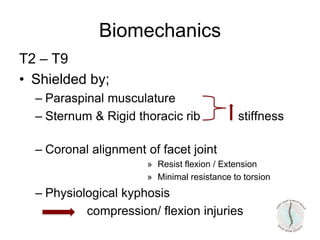
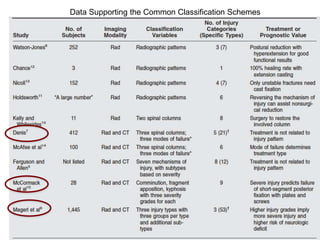
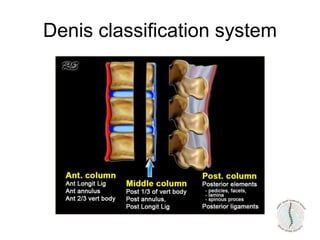
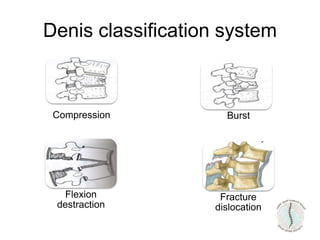
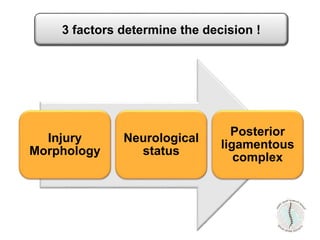
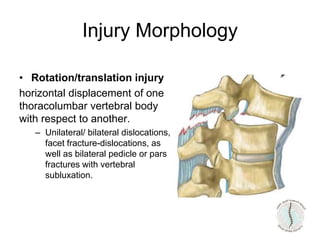
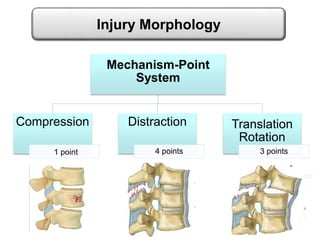
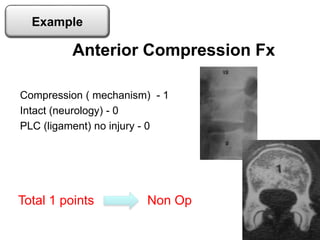
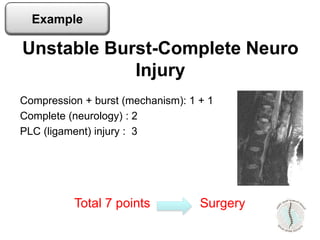
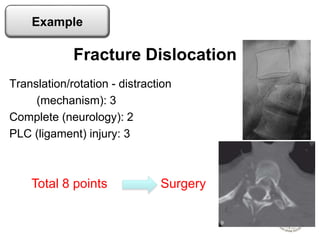
Thoraco-lumbar fractures are common injuries that occur primarily from motor vehicle accidents. Several classification systems exist to characterize the injuries including the commonly used Denis classification, Load Sharing classification, and AO classification system. The Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Score (TLICS) system incorporates injury morphology, neurological status, and posterior ligamentous complex integrity to determine a score to guide treatment decisions. A score of 4 or less generally indicates non-surgical management while a score of 5 or more indicates surgery is needed. The timing of surgery remains unclear but early decompression may improve outcomes in neurologically incomplete injuries. Treatment is based on fracture stability, deformity, and neurological status.