This document defines key thermodynamic terms and concepts:
- A system is the part of the universe being studied, with the surroundings making up the rest. Systems can be open, closed, or isolated depending on energy/matter exchange.
- State functions like internal energy (U), enthalpy (H), and temperature (T) depend only on the current state and not the path to get there.
- The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved, expressed as a change in internal energy (ΔU) equals heat (q) plus work (w).
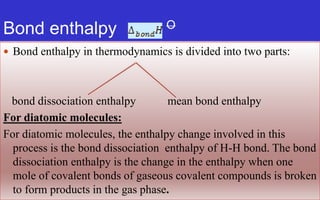
- Enthalpy (H) includes pressure-volume work and is useful for constant pressure processes, where the heat of reaction

















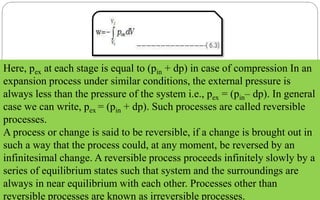





![ We can rewrite the above equation as:
On rearranging we get:
qp=(U2+pV2)-(U1+pV1)
Now we can define another thermodynamic function the enthalpy H [Greek word enthalpien, to warm
or heat content] as:
H = u+pV
So the equation becomes:
qp=H2-H1=∆H
Although q is a path dependent function, H is a state function because it depends on U, p and V, all of
which are state functions. Therefore, ∆H is independent of path. Hence, qp is also independent of
path.
For finite changes at constant pressure,
∆H=∆U+∆pV
Since p is constant , we can write
∆H=∆U+p∆V
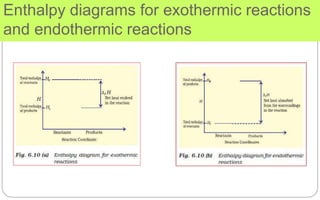
∆H is negative for exothermic reactions which evolve heat during the reaction and ∆H is positive for
endothermic reactions which absorb heat from the surroundings.
U2-U1=qp-p(V2-V1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-thermodynamics-150702042902-lva1-app6891/85/Chapter-6-thermodynamics-class-11-cbse-25-320.jpg)