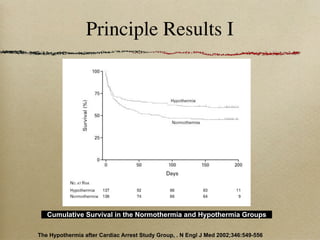
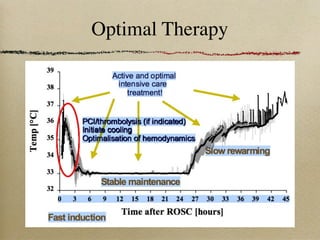
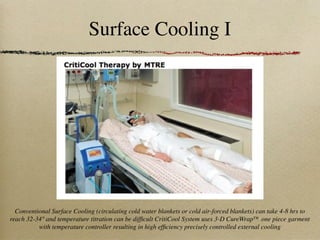
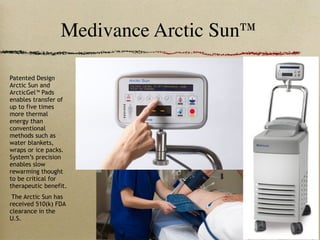
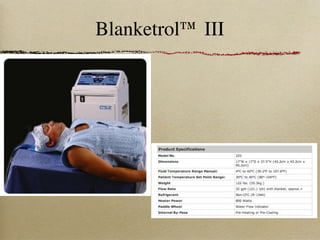
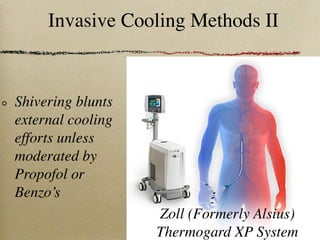
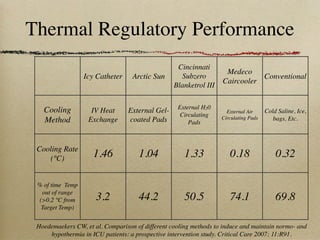
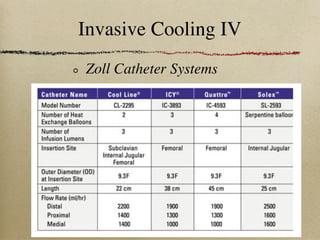
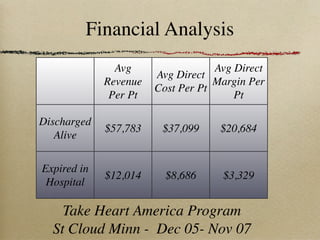
This document discusses therapeutic hypothermia for patients who experience cardiac arrest. Lowering a patient's core body temperature to 32-34°C for 12-24 hours after resuscitation can improve outcomes by reducing neurological injury from reperfusion. Clinical studies show increased survival rates and neurological function for patients who receive therapeutic hypothermia. The document reviews different methods for inducing and maintaining therapeutic hypothermia, as well as barriers to implementing these protocols more widely. It advocates for the establishment of specialized cardiac arrest centers to optimize post-cardiac arrest care.