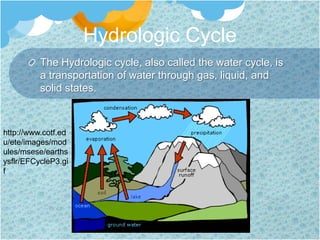
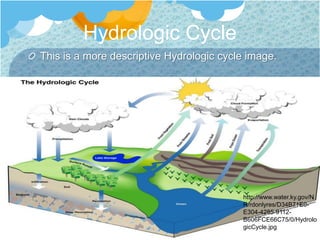
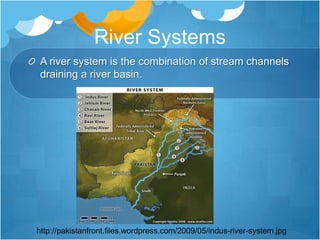
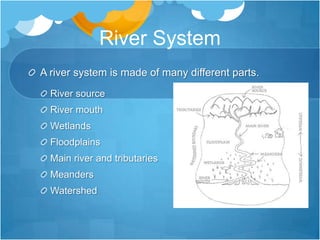
The document discusses the global water cycle and distribution of water on Earth. It explains that 97% of water is ocean water and 3% is fresh water. Fresh water is found primarily as ice caps and glaciers (68.7%), groundwater (30.1%), and other fresh surface water sources. The hydrologic cycle describes the continuous movement of water through evaporation, precipitation, and runoff between oceans, atmosphere, and land. River systems are made up of river sources, mouths, floodplains, tributaries, and watersheds that drain into larger bodies of water. Groundwater is fresh water stored underground in aquifers and contributes to drinking water and irrigation needs.