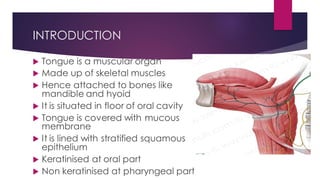
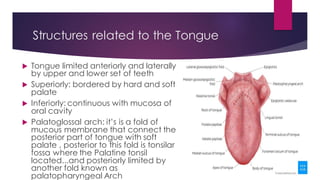
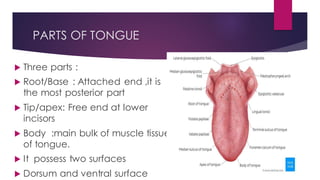
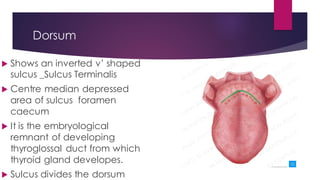
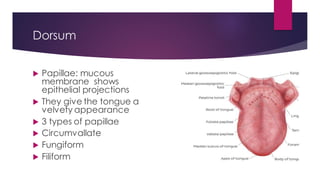
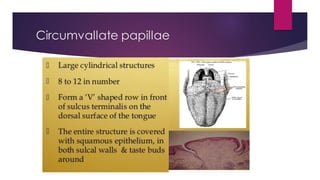
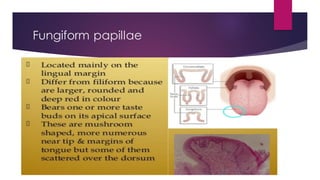
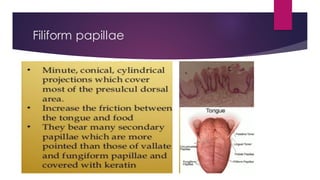
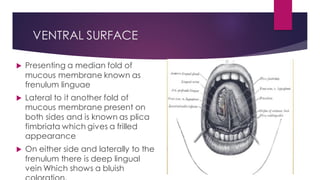
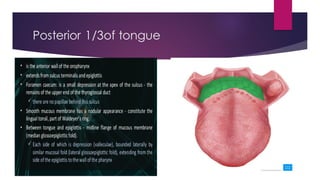
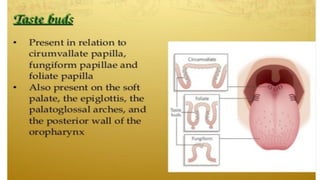
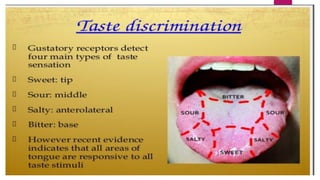
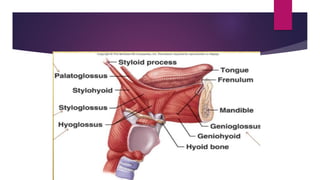
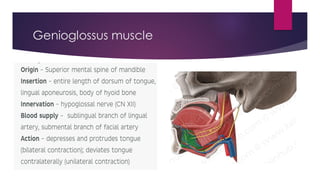
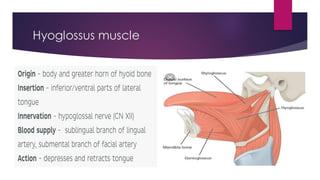
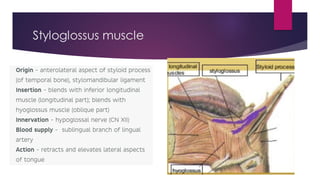
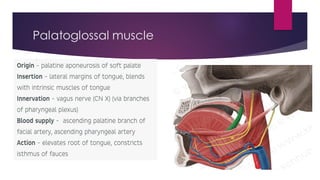
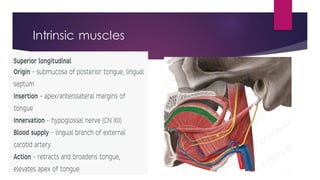
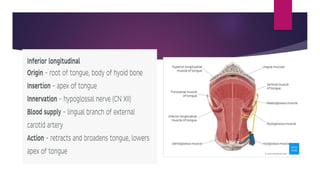
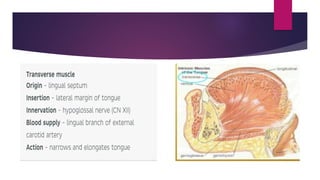
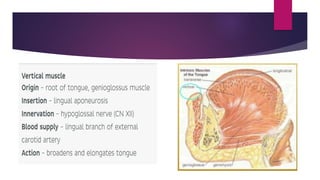
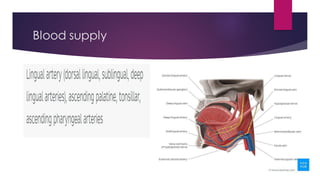
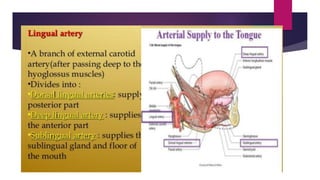
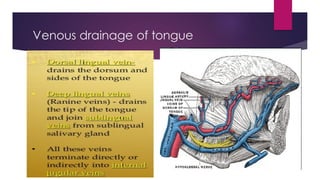
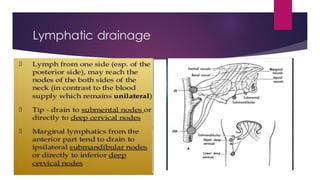
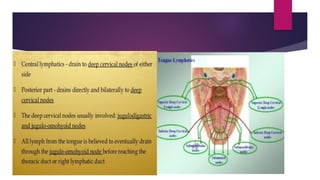
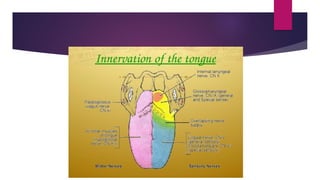
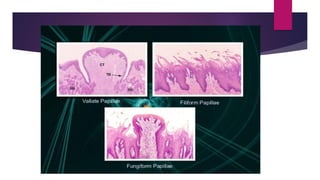
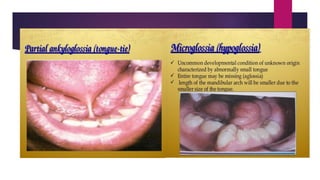
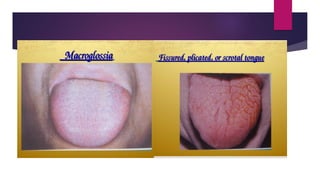
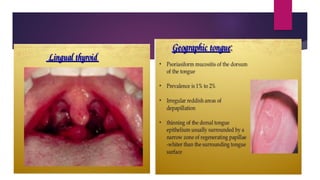
The tongue is a muscular organ located in the oral cavity that is covered by mucous membrane. It has three parts - the root, body, and tip. The dorsal surface features papillae like circumvallate, fungiform, and filiform that give the tongue a velvety texture. The ventral surface has a median frenulum linguae fold. Intrinsic muscles inside the tongue regulate its shape while extrinsic muscles like genioglossus anchor it to surrounding bones. The tongue receives blood supply from lingual arteries and drains into deep lingual veins. Sensory innervation comes from cranial nerves like the lingual nerve while motor function is controlled by the hypoglossal nerve.