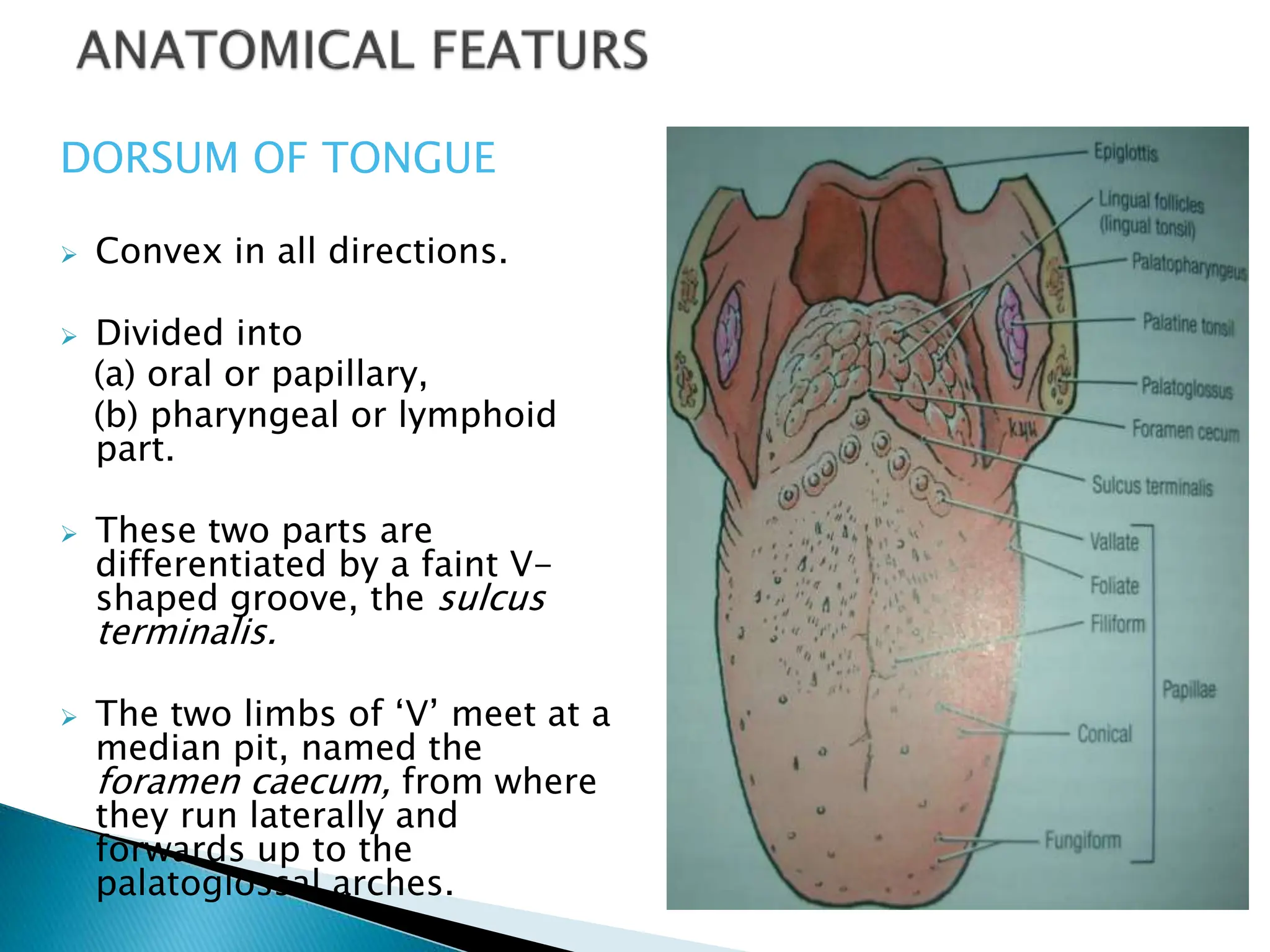
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth that aids in tasting, speaking, chewing, and swallowing. It has intrinsic and extrinsic muscles that allow it to move and change shape. The tongue's surface contains papillae that give it a rough texture and help with taste. The root of the tongue attaches to bones in the mouth, while the tip is free. Sensory nerves allow the tongue to detect different tastes across its surface.