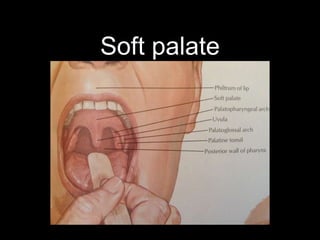
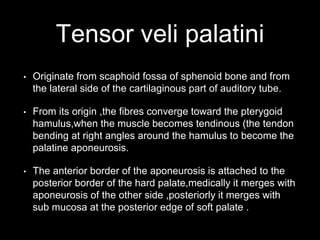
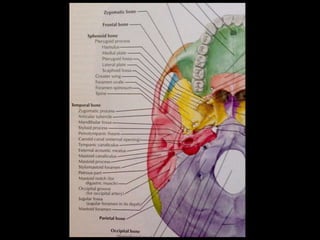
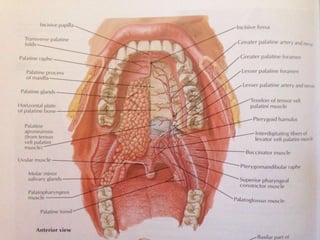
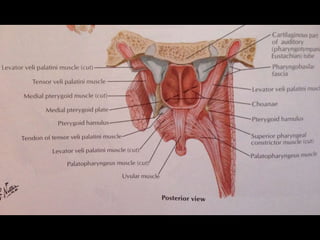
The soft palate contains five muscles that are important for swallowing and breathing. The muscles are the tensor veli palatini, levator veli palatini, palatoglossus, palatopharyngeus, and musculus uvulae. Each muscle has a specific origin, insertion point, and action. For example, the levator veli palatini originates from the base of the skull and curves downward and forward to enter the palate, contracting to lift the soft palate upwards and backwards during swallowing. The muscles receive their nerve supply from either the trigeminal or accessory cranial nerves and are supplied by arteries including the facial and maxillary arteries.