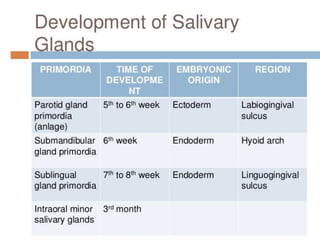
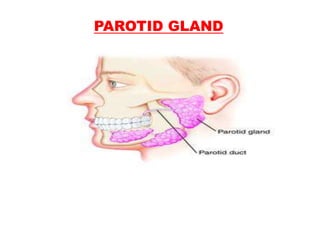
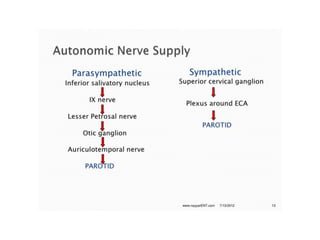
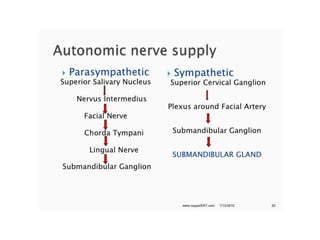
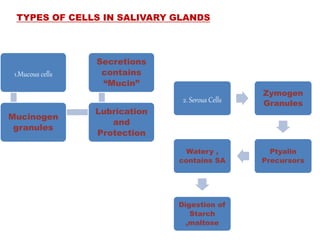
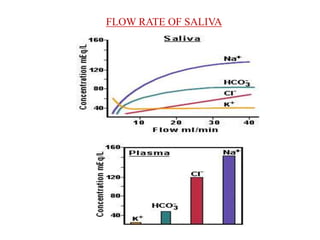
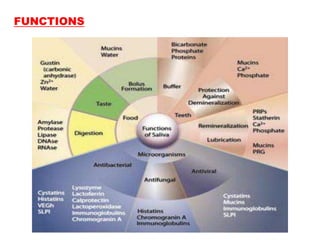
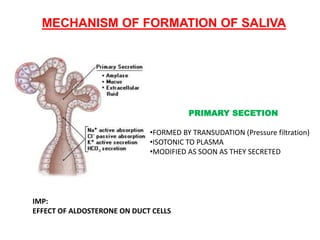
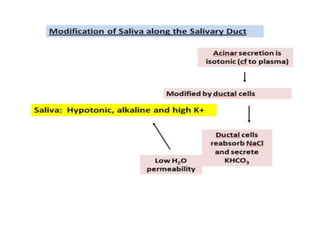
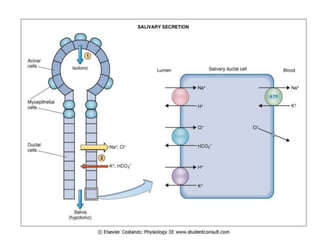
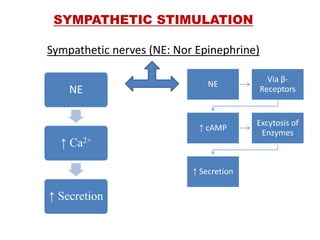
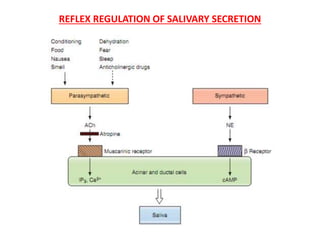
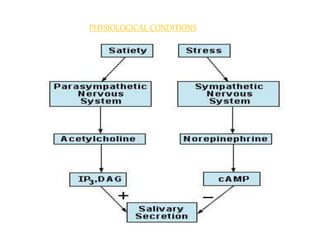
The document discusses the salivary glands and their secretions. It describes the three major salivary glands - the parotid gland, submandibular gland, and sublingual gland - and their locations and contributions to saliva production. It also outlines the major cell types in salivary glands, the composition and flow rate of saliva, and its functions. Furthermore, it explains the mechanisms of saliva formation, including primary secretion, modification in the ducts, and reflex regulation in response to physiological conditions like the cephalic, buccal, esophageal, gastric, and intestinal phases. In summary, the document provides an overview of the anatomy, physiology and functions of the sal






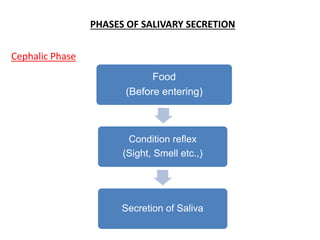
![CEPHALIC PHASE SECRETION OF SALIVA BEFORE
ENTRY OF FOOD
CONDITIONAL REFLEX
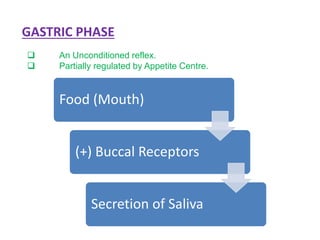
BUCCAL PHASE PRESENCE OF FOOD IN THE
MOUTH [(+) BUCCAL
RECEPTORS]
UNCONDITIONAL REFLEX&
PARTIALLY REGULATED BY
APETITE CENTRE
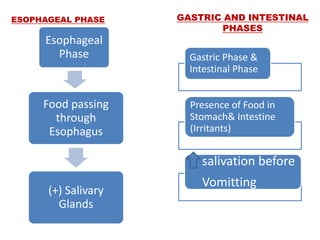
OESOPHAGEAL PHASE PASSING OF FOOD THROUGH
OESOPHAGUS
STIMULATION OF SALIVARY
GLANDS
GASTRIC PHASE PRESENCE OF FOOD IN
STOMACH
IRRITANT FOODS IN
STOMACH (VOMITING)
INTESTINAL PHASE FOOD IN INTESTINE IRRITANT FOOD IN UPPER
INTESTINE
PHASES OF SALIVARY SECRETION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/salivarysecretion-190808031842/85/Salivary-secretion-20-320.jpg)