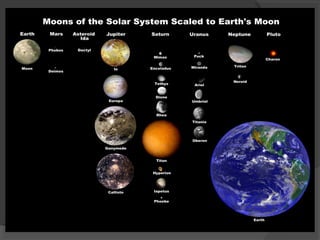
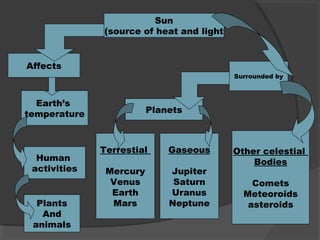
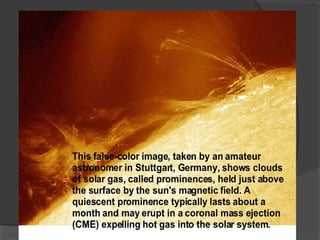
The document provides information about the solar system. It begins by stating the objectives are to infer that the sun is the center of the solar system, name the planets and other heavenly bodies, describe the sun, and thank God for the sun. It then provides information about the formation of the sun and solar system from a giant cloud of gas and dust approximately 4.6 billion years ago. Key details are provided about the sun being at the center and a giant ball of hot glowing gas that gives off light and heat. The major planets and other objects in the solar system like asteroids, meteoroids, and comets are also named.