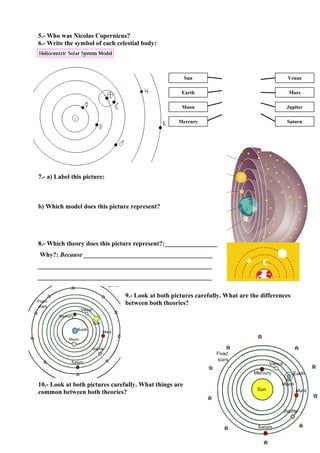
The document provides information about the universe, what composes the universe, constellations, units of measurement used by astronomers, and details about the solar system. It explains that the universe is made up of galaxies, nebulas, stars, planets, and other celestial bodies. It describes the geocentric and heliocentric models of the solar system and notes that Galileo proved the heliocentric model. It provides details about the sun, planets, dwarf planets, comets, asteroids, and satellites that make up the solar system. Finally, it discusses the difference between natural and artificial satellites and defines key terms.