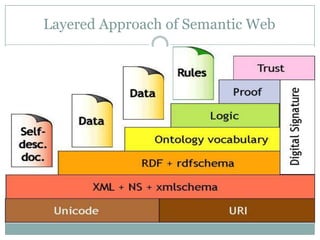
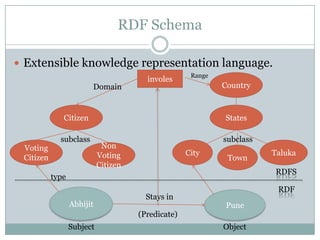
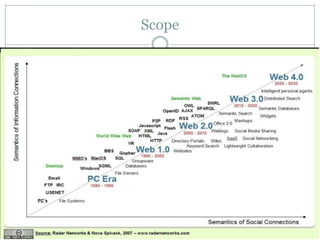
The document discusses the semantic web, including its history and key components. It describes how the semantic web aims to make web content machine-readable through technologies like XML, URIs, RDF, RDFS, and OWL. This will allow computers to better understand web resources and their relationships, enabling more intelligent searching and use of web data than is possible on the traditional web. However, developing the semantic web also faces challenges such as complexity, lack of industry adoption, and needing further consensus on technical standards.