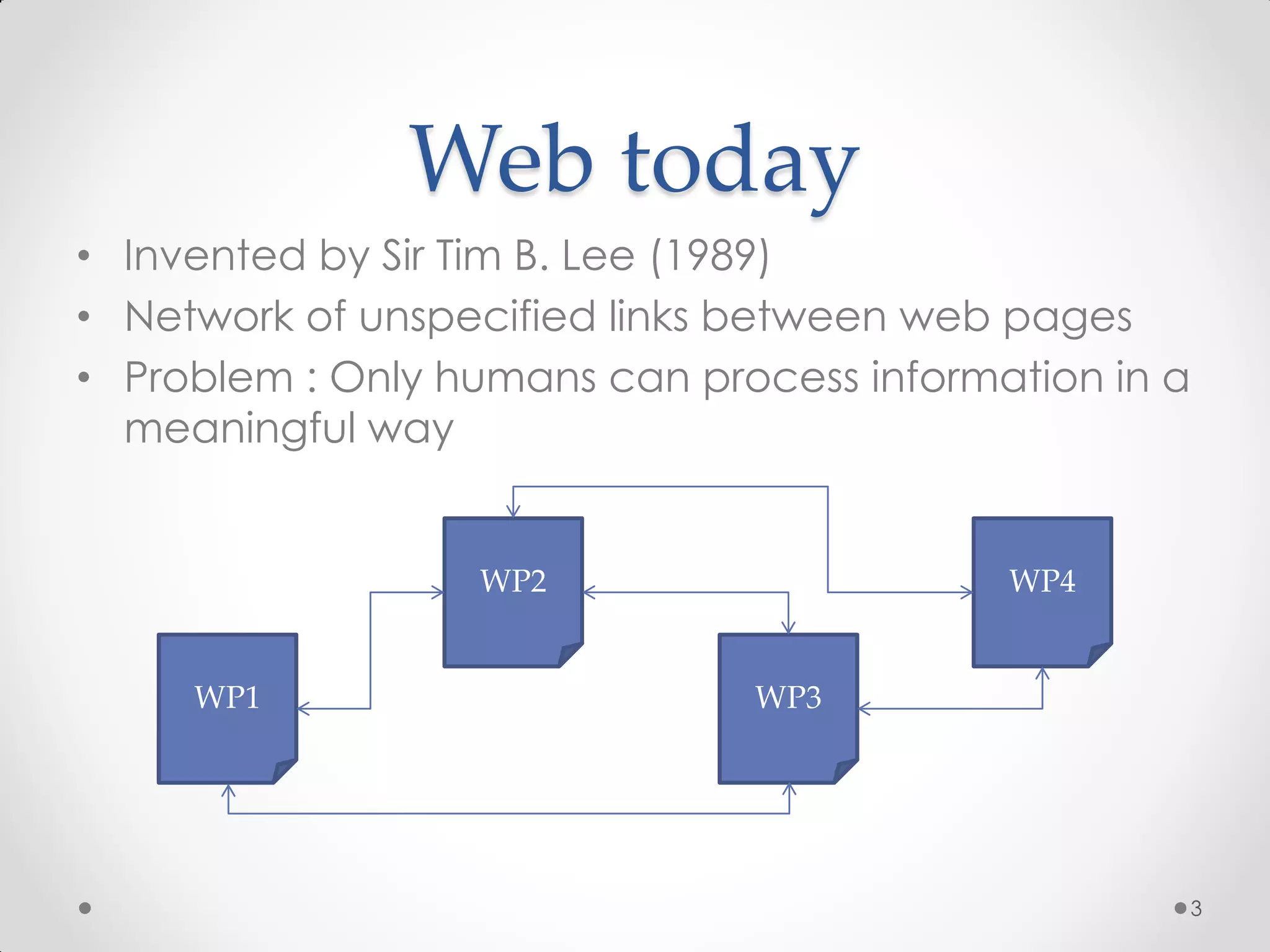
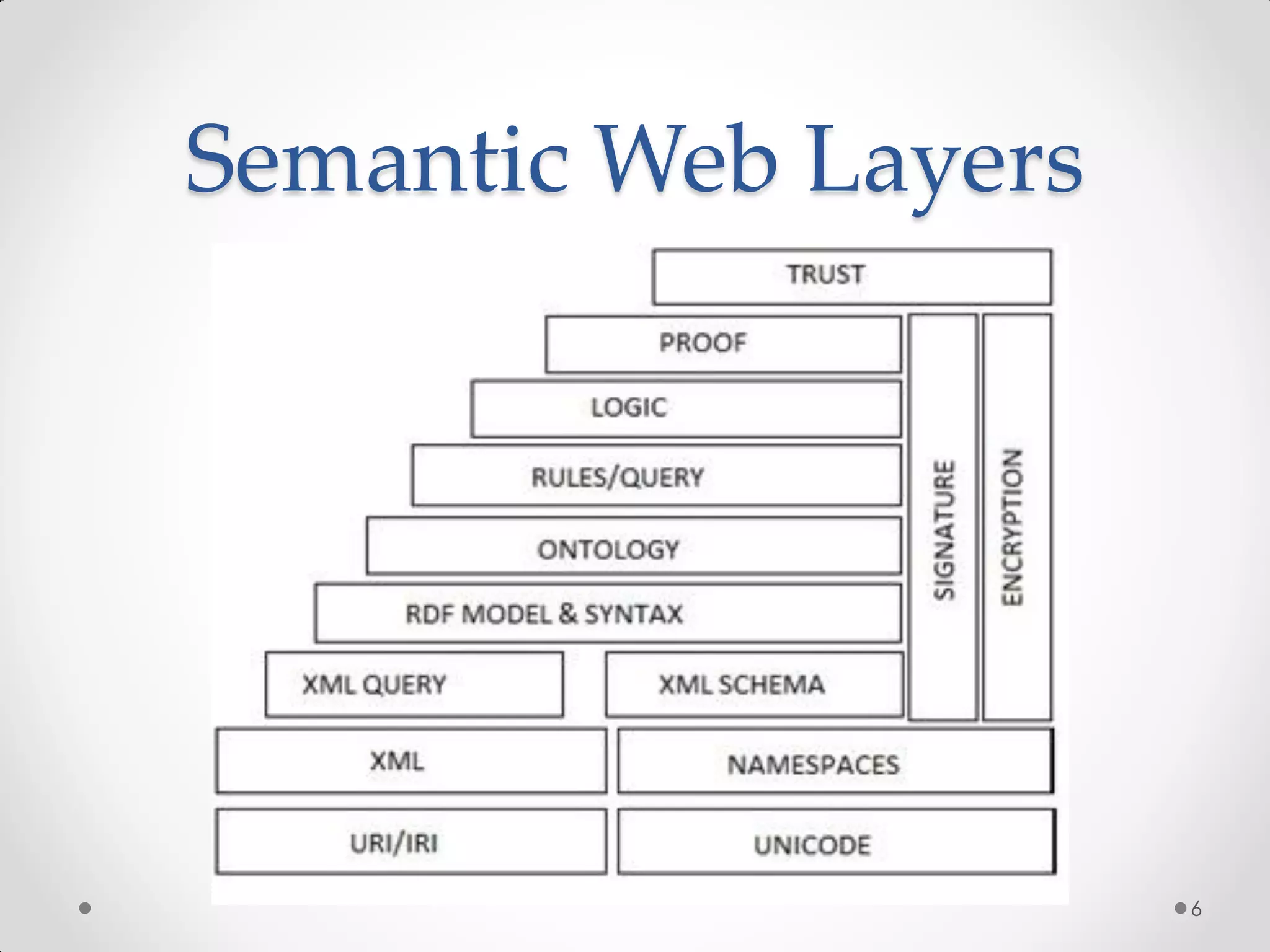
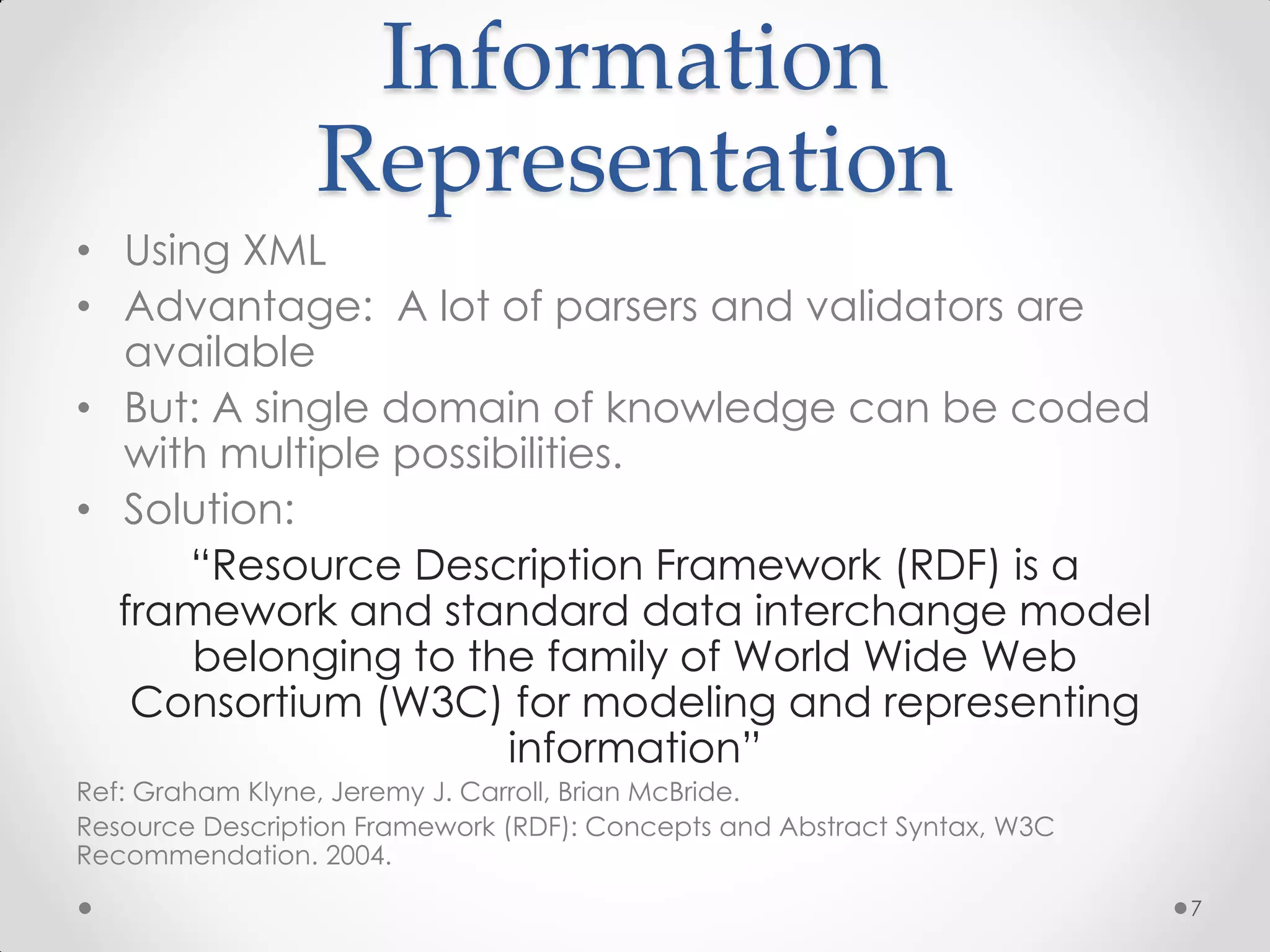
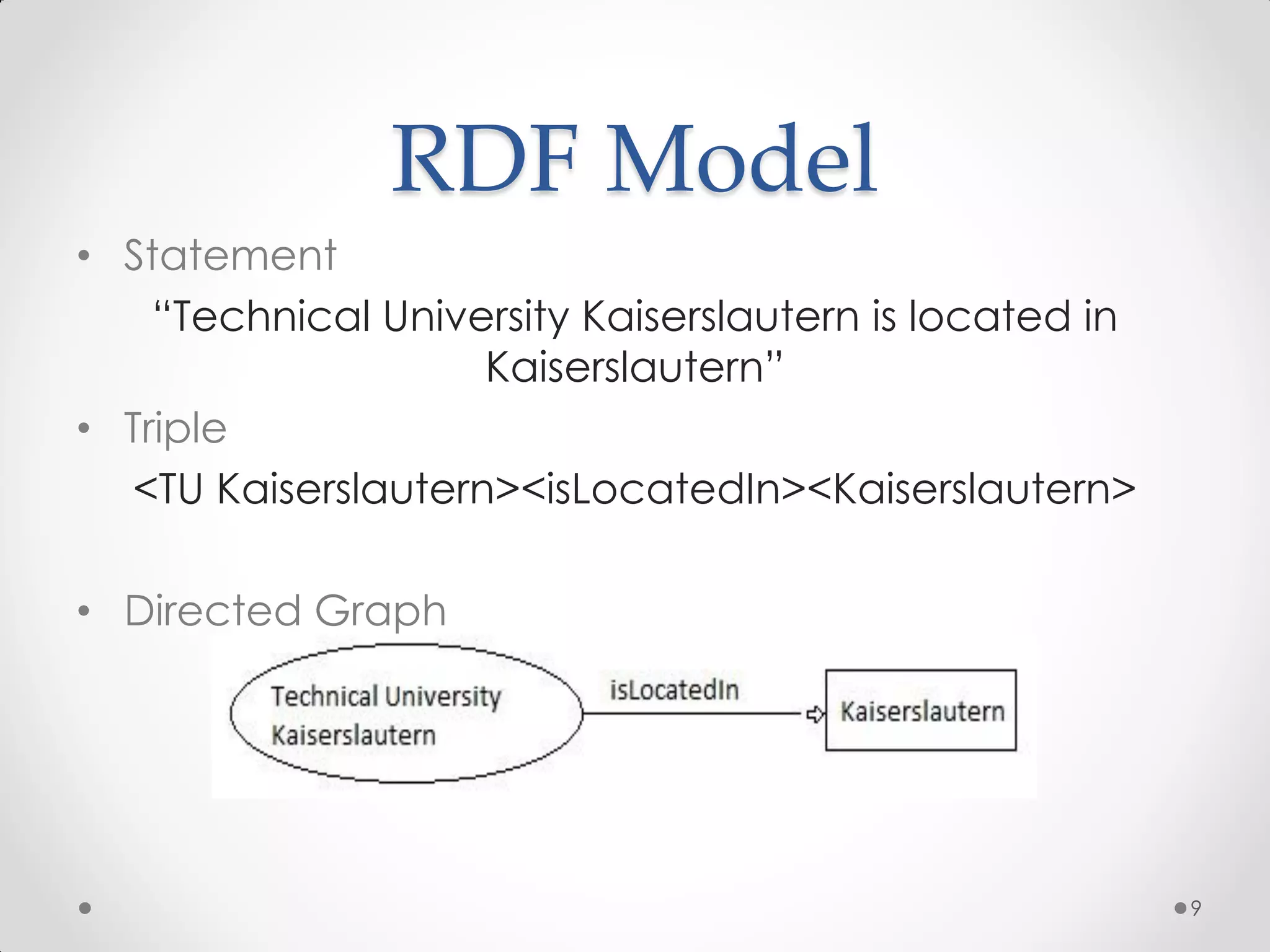
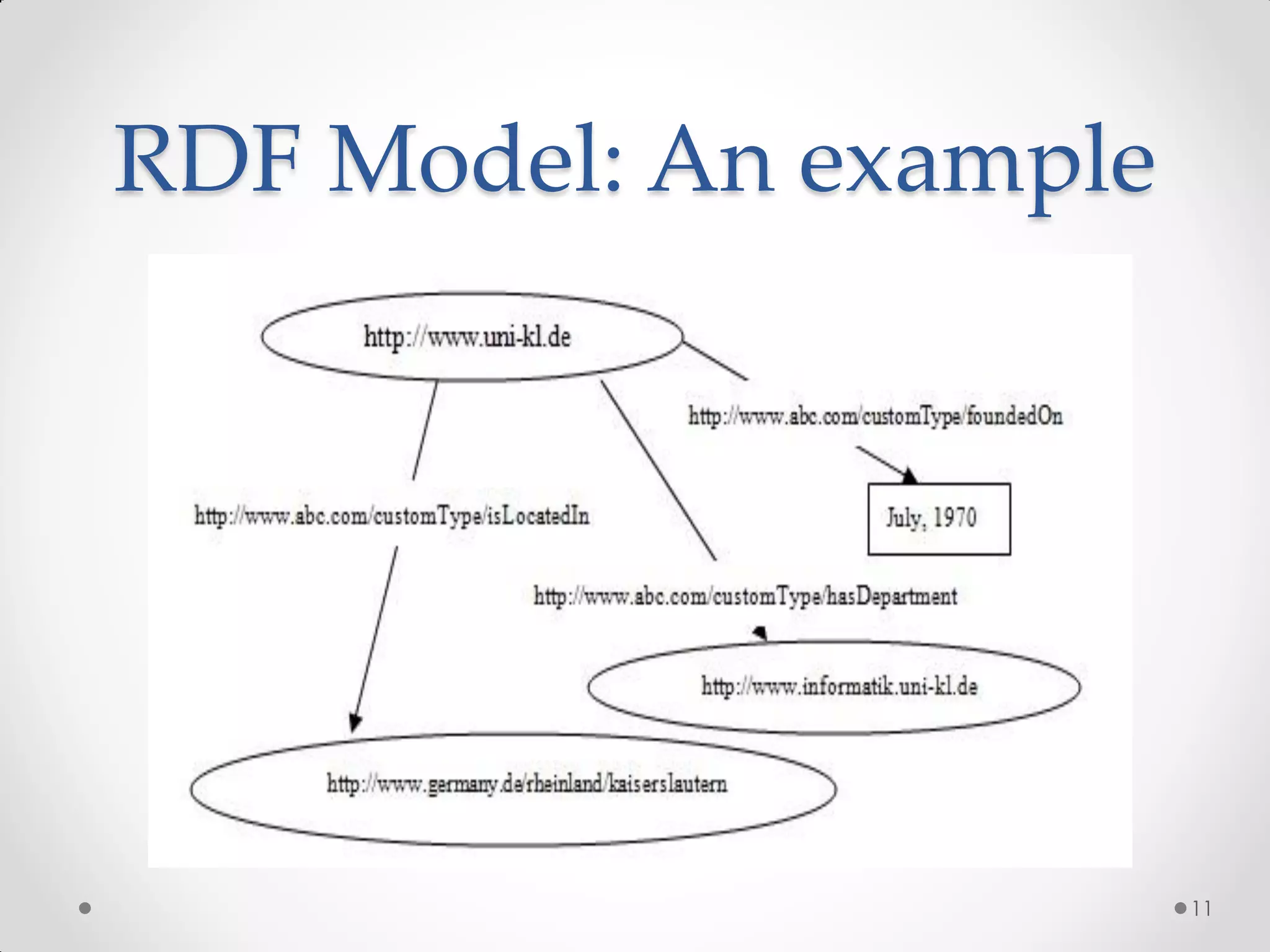
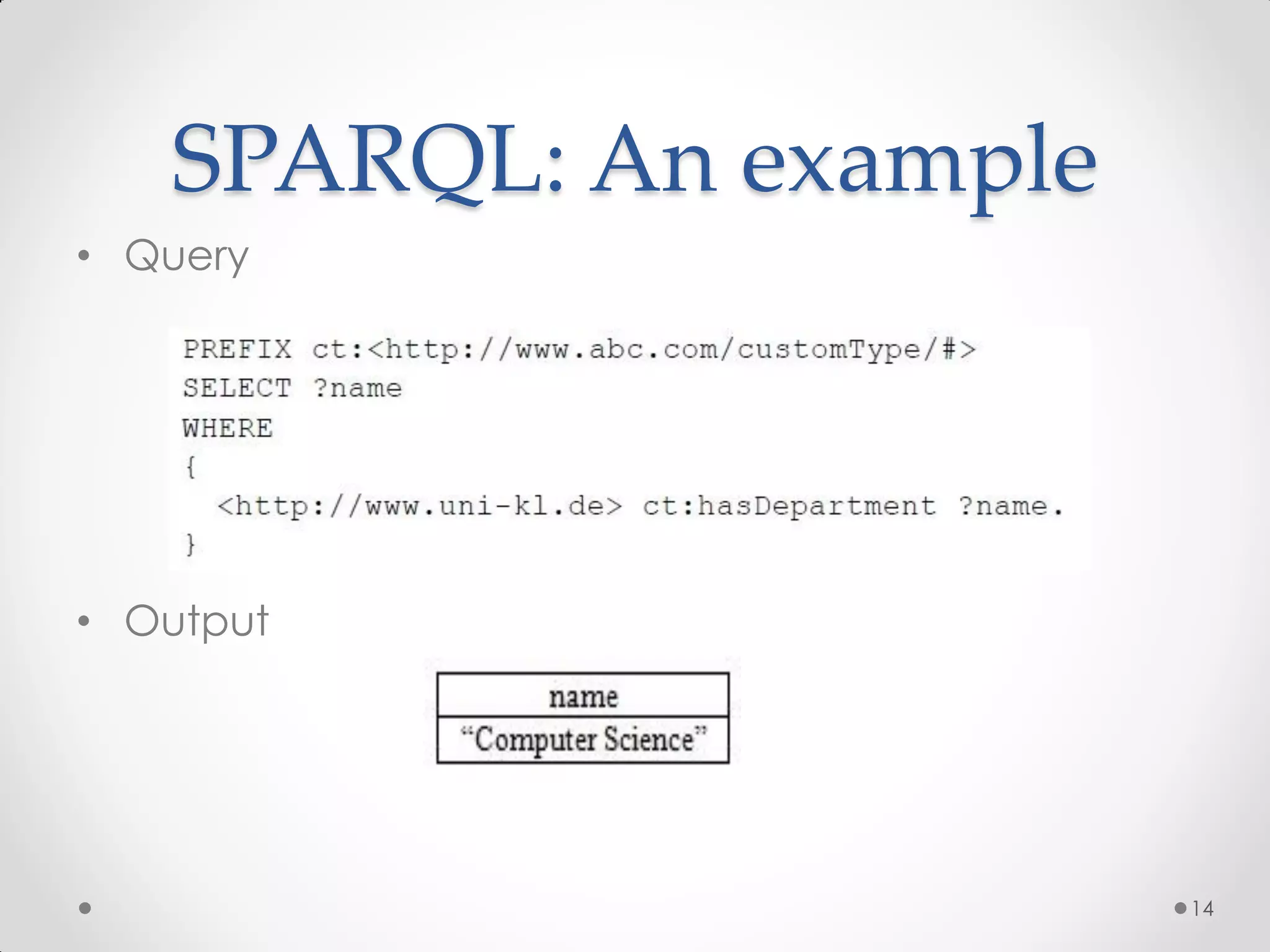
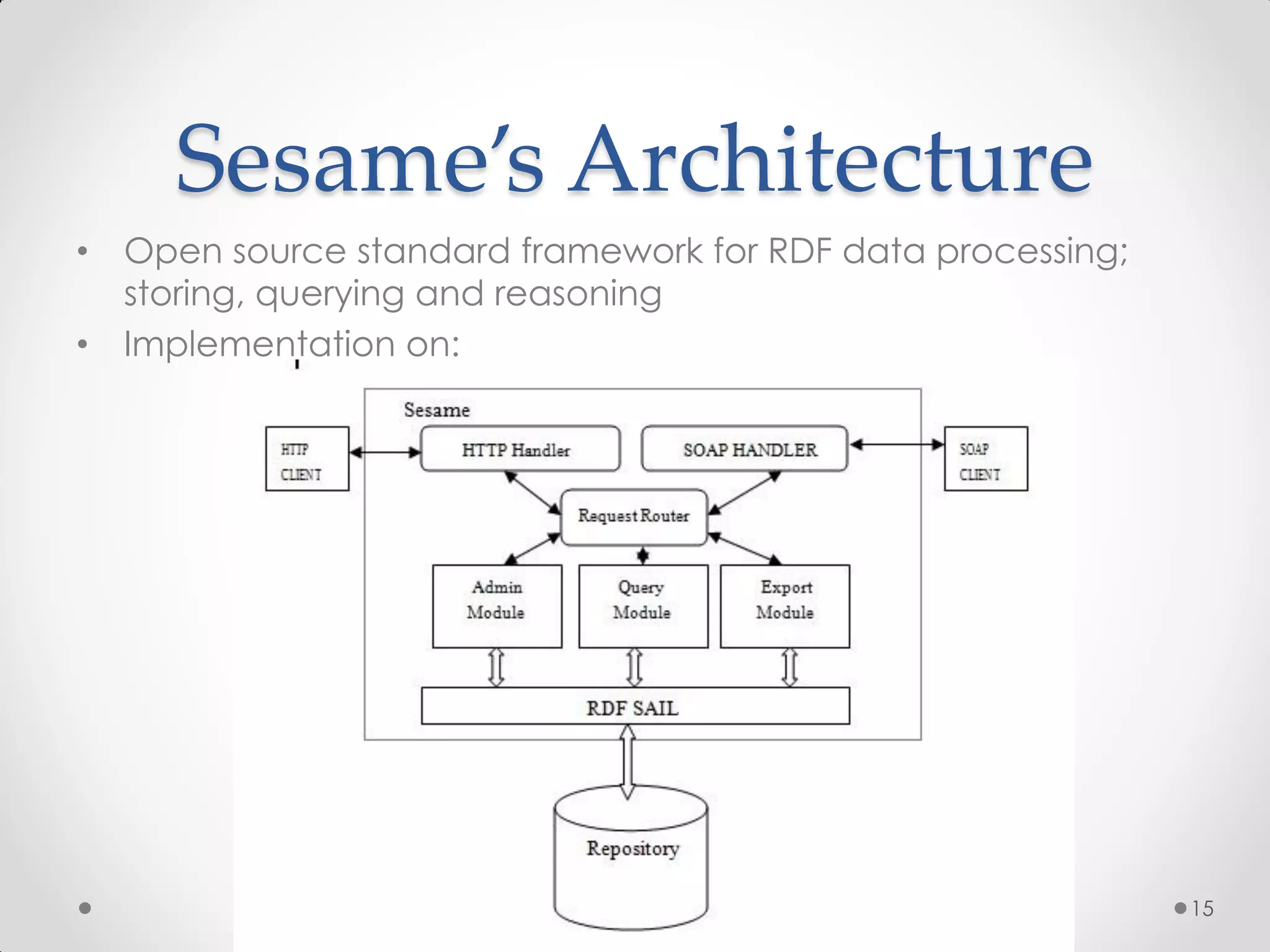
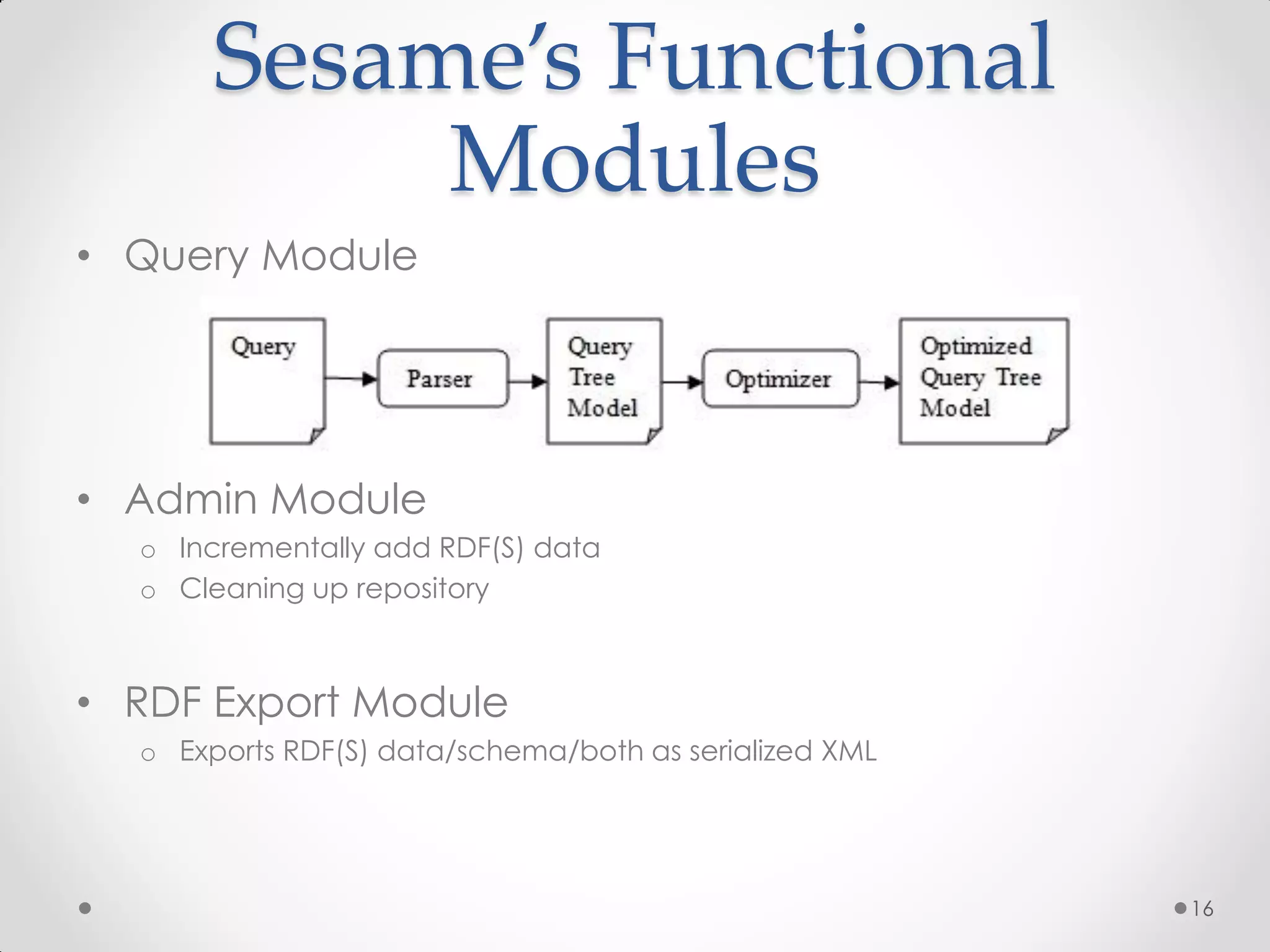
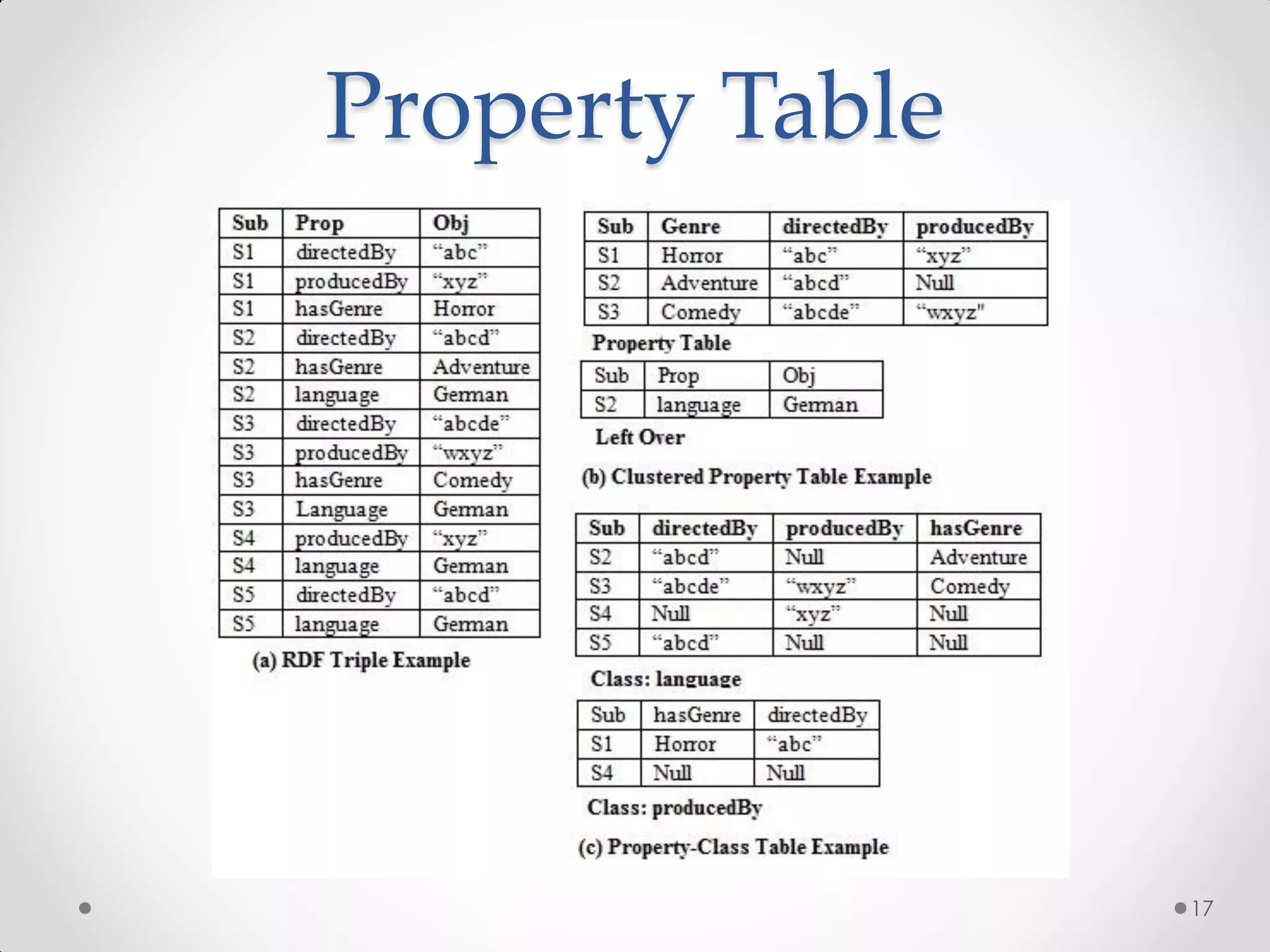
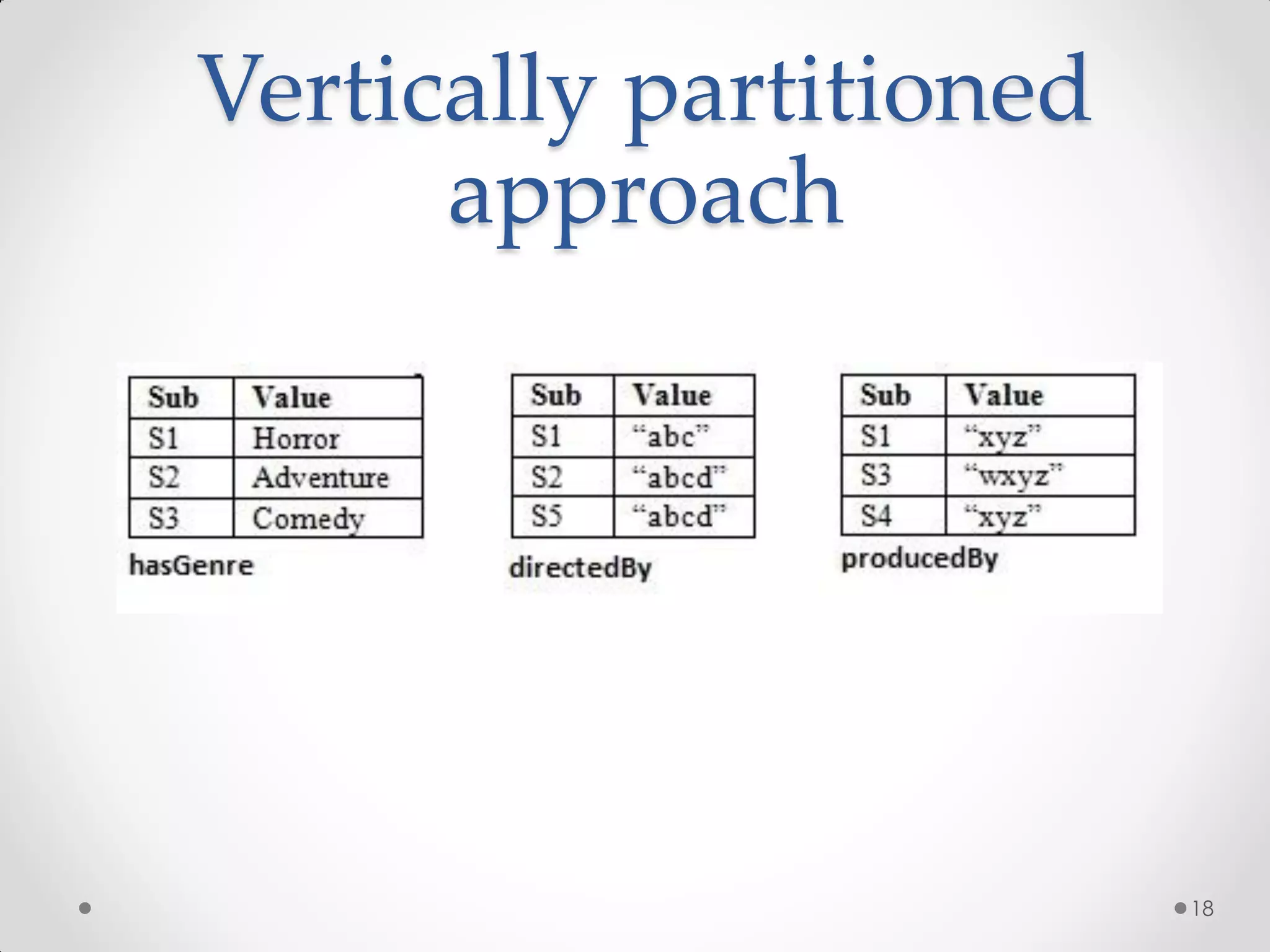
The document outlines the concepts of RDF triple stores, SPARQL, and the Semantic Web. It explains the structure and syntax of RDF, the purpose of the Semantic Web in enhancing machine understanding, and highlights storage solutions like Sesame and RDF-3x. Additionally, it emphasizes the transition from a syntactic to a semantic web model for better information representation and data management.