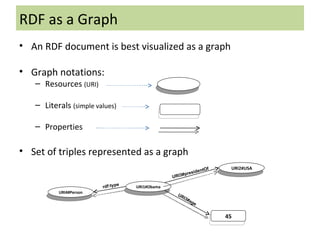
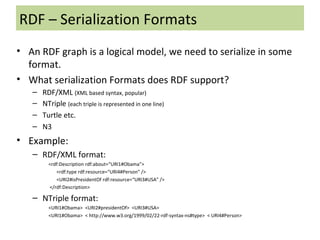
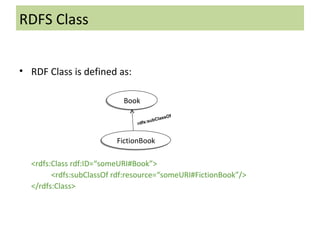
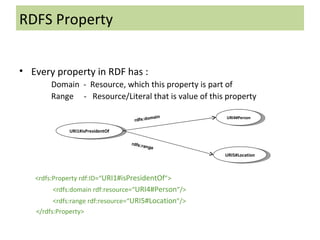
The document discusses the Semantic Web and Resource Description Framework (RDF). It defines the Semantic Web as making web data machine-understandable by describing web resources with metadata. RDF uses triples to describe resources, properties, and relationships. RDF data can be visualized as a graph and serialized in formats like RDF/XML. RDF Schema (RDFS) provides a basic vocabulary for defining classes, properties, and hierarchies to enable reasoning about RDF data.