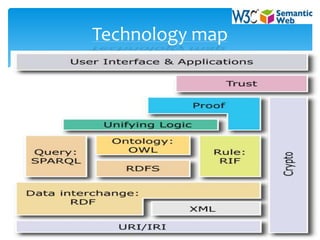
The document provides an overview of the semantic web including:
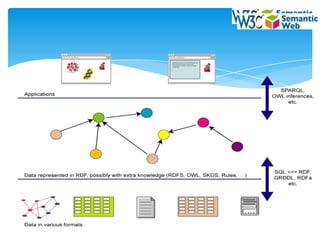
1. It describes the key technologies that power the semantic web such as RDF, RDFS, OWL, and SPARQL which allow data to be shared and reused across applications.
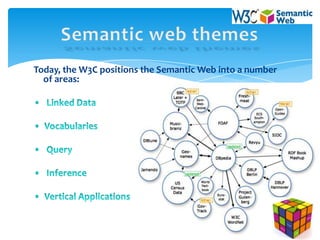
2. It discusses semantic web themes like linked data, vocabularies, and inference which enable data from multiple sources to be integrated and new insights to be discovered.
3. It outlines current and future applications of the semantic web such as in e-commerce, online advertising, and government where semantic technologies can enhance search, personalization and data sharing.











![RDF
RDF(Resource Description Framework) is the first and the fundamental technology of
semantic web.
It describes Resources through a series of Statements.
RDF has following important concepts
• Resource : The resources being described by RDF are anything that can be named via a
URI.
• Property : A property is also a resource that has a name, for instance Author or Title.
• Statement : A statement consists of the combination of a Resource, a Property, and
an associated value.
Each statement is a Property and Value that is about a Resource.
An RDF Triple (s,p,o) is such that:
“s”, “p” are URI-s, ie, resources on the Web; “o” is a URI or a literal
“s”, “p”, and “o” stand for “subject”, “property”, and “object
Resources can use any URI, e.g.:
http://www.example.org/file.xml#element(home)
http://www.example.org/file2.xml#xpath1(//q[@a=b])
URI-s can also denote non Web entities:
http://www.ivan-herman.net/me is me
not my home page, not my publication list, but me](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/semanticweb2-120902161709-phpapp01/85/Semantic-web-15-320.jpg)