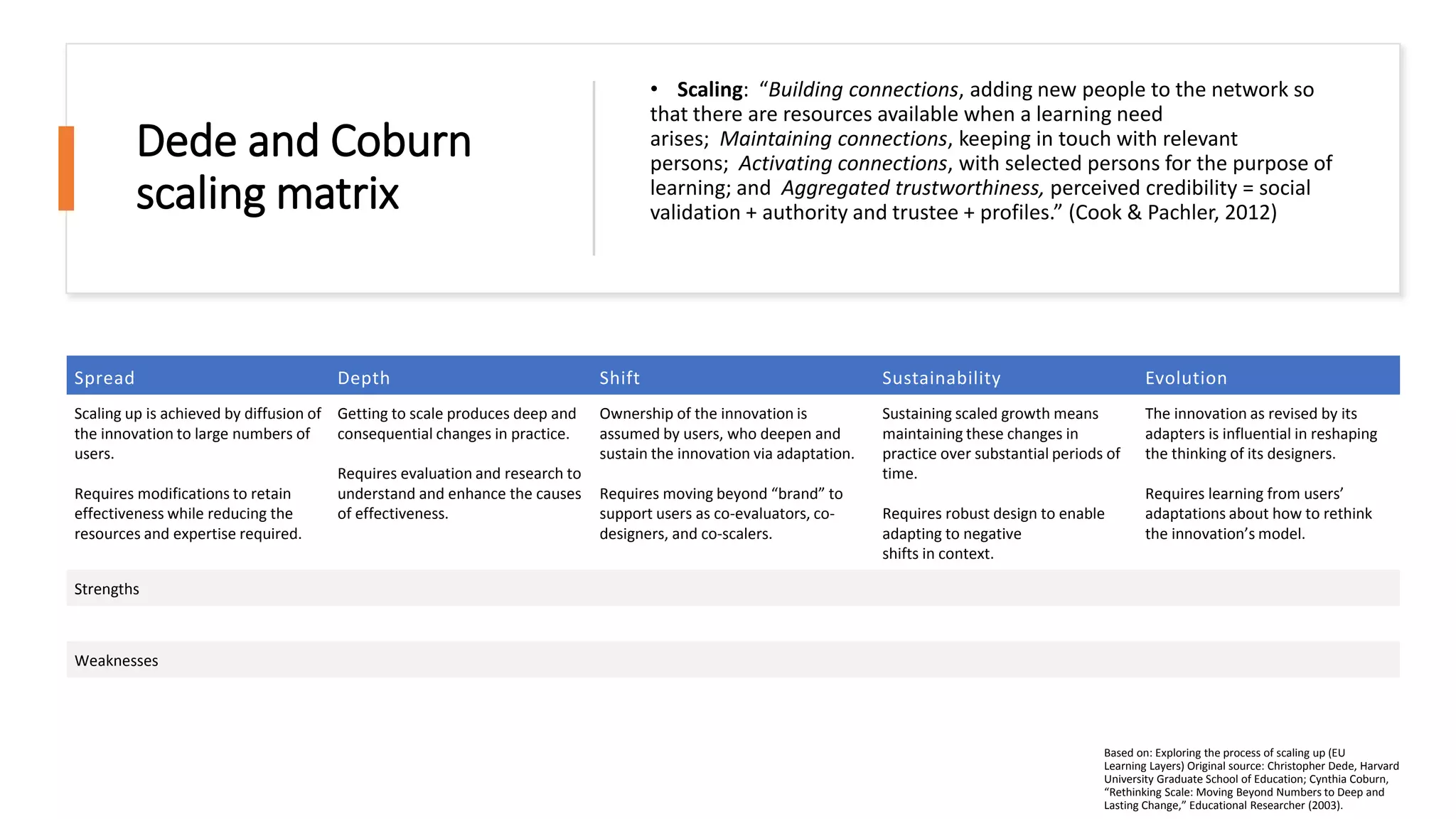
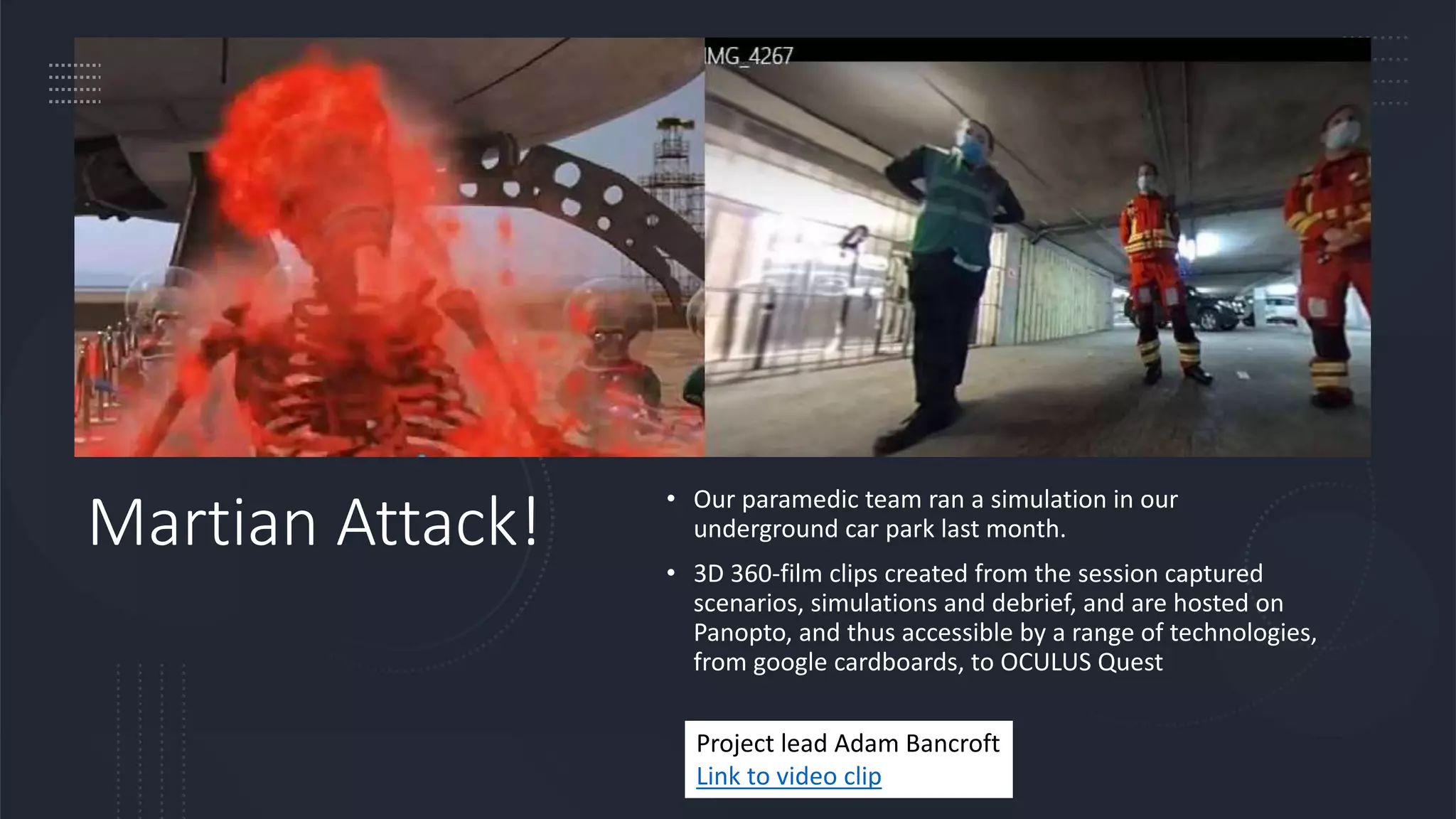
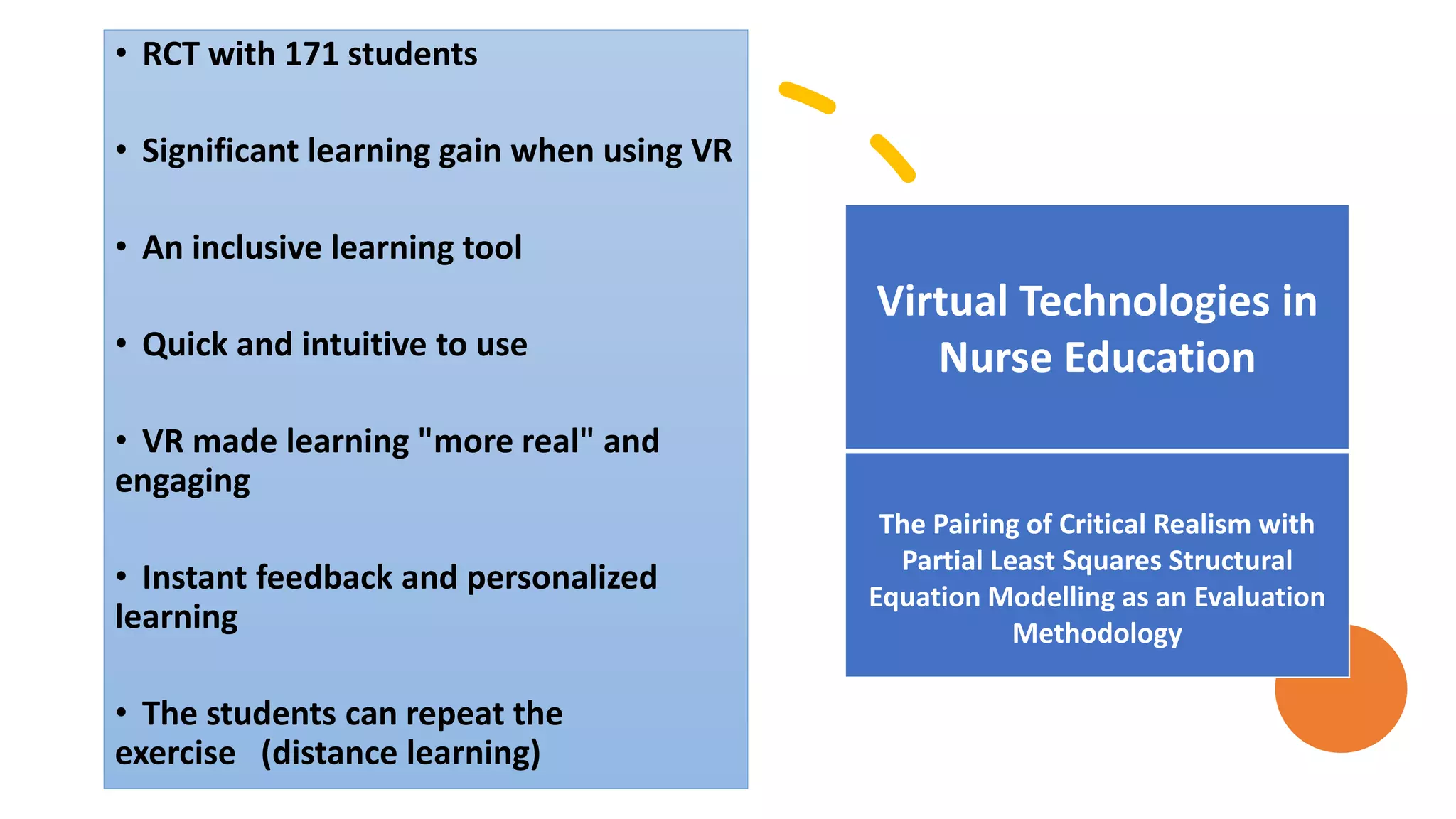
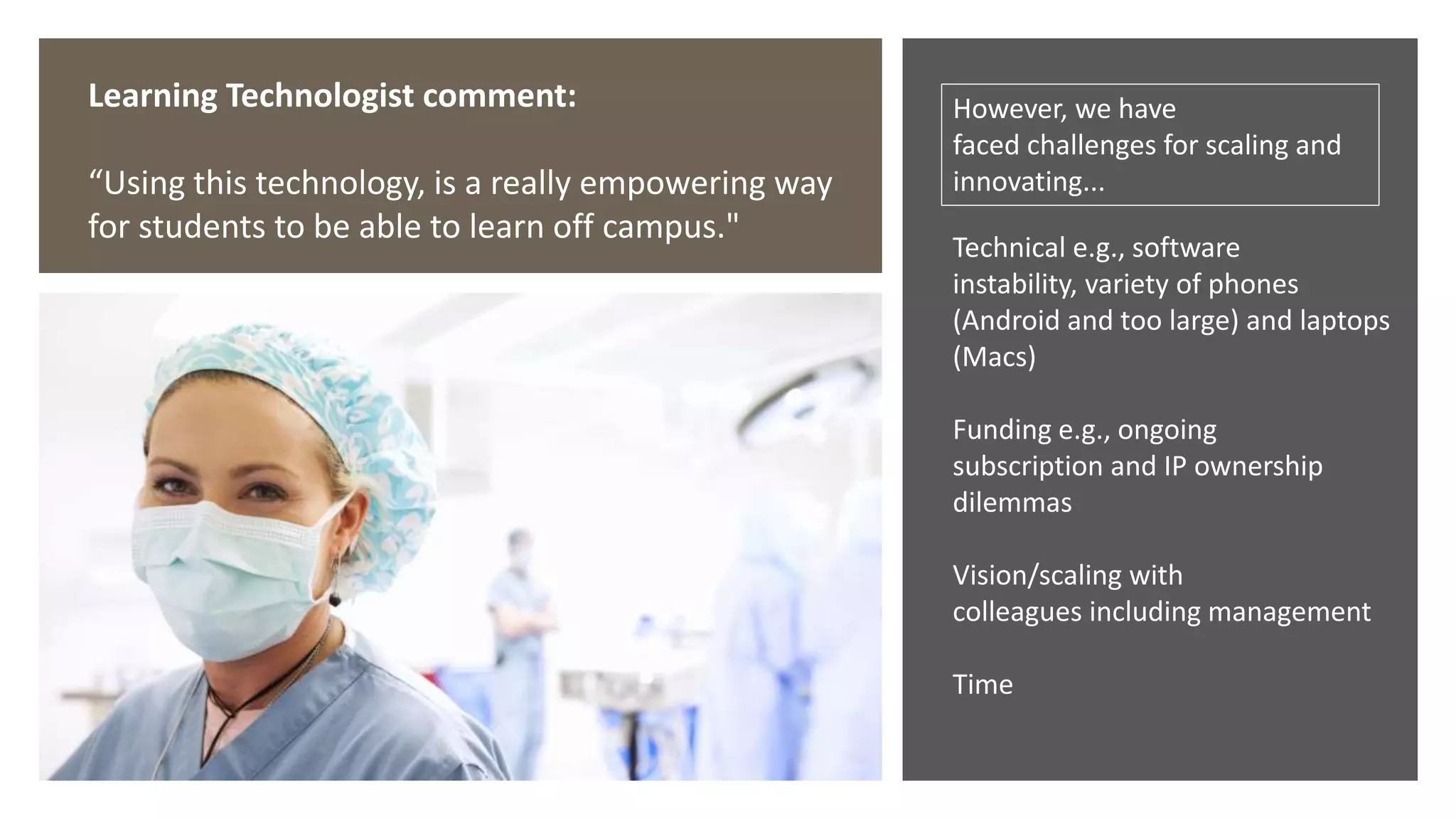
The document discusses the challenges and innovations in nursing education, focusing on the integration of digital technologies and immersive learning experiences. It highlights the low percentage of students experiencing realistic simulations and the need for ownership and adaptation of innovations to enhance learning outcomes. Furthermore, it addresses various projects utilizing virtual reality in teaching, emphasizing their benefits and challenges for scale and sustainability.