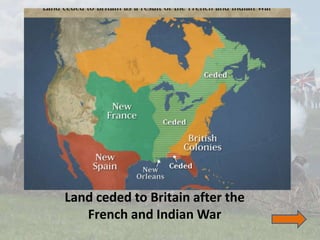
The document outlines the escalating tensions between the American colonies and Britain leading to the American Revolution, highlighting key events such as the French and Indian War, various tax acts, and the Boston Tea Party. It describes how Britain’s policies sparked resentment and unity among the colonies, culminating in the formation of the First and Second Continental Congresses and the eventual outbreak of war. The narrative illustrates the impact of British actions on colonial sentiment, emphasizing their fight against perceived oppression and the quest for independence.