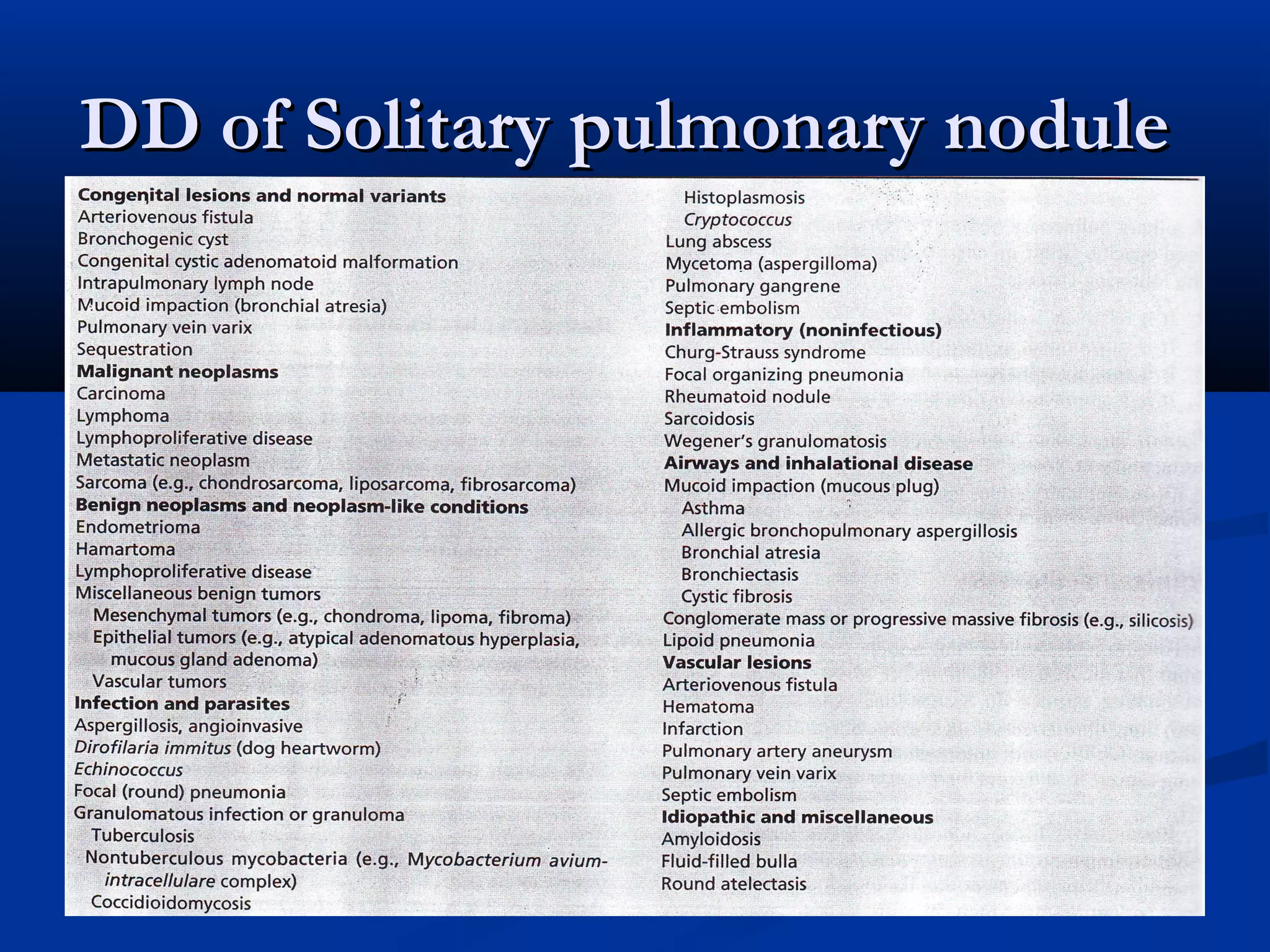
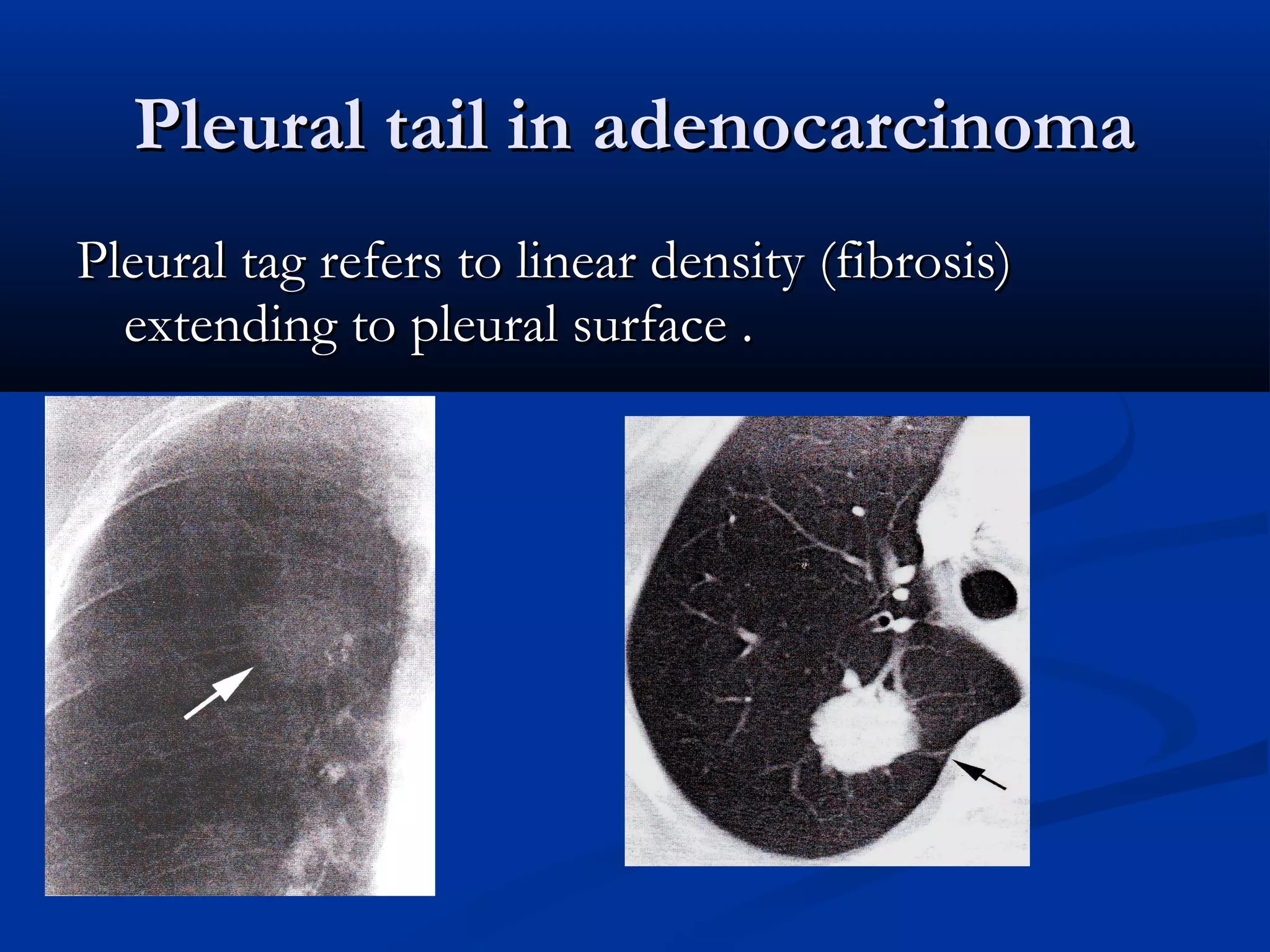
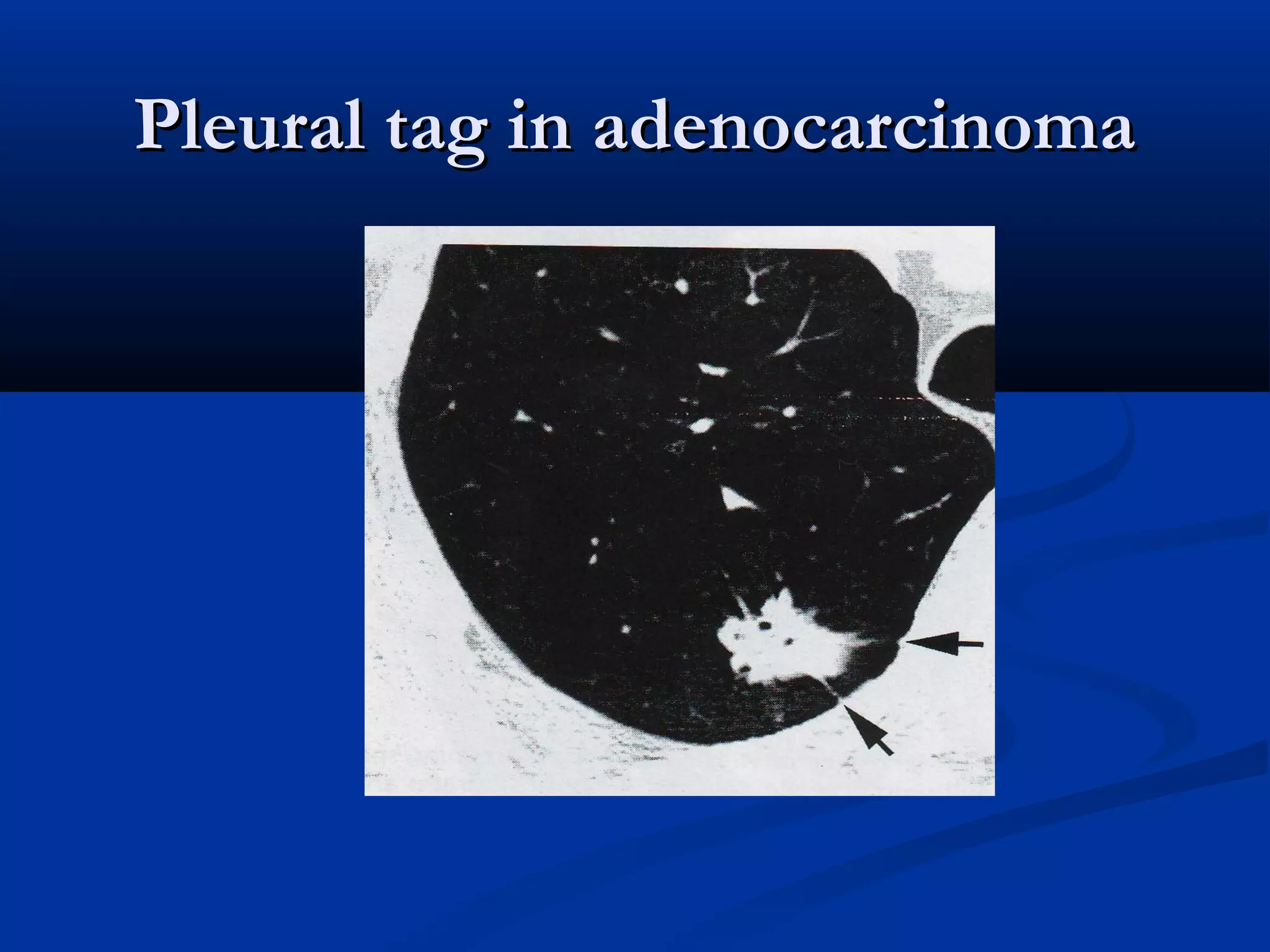
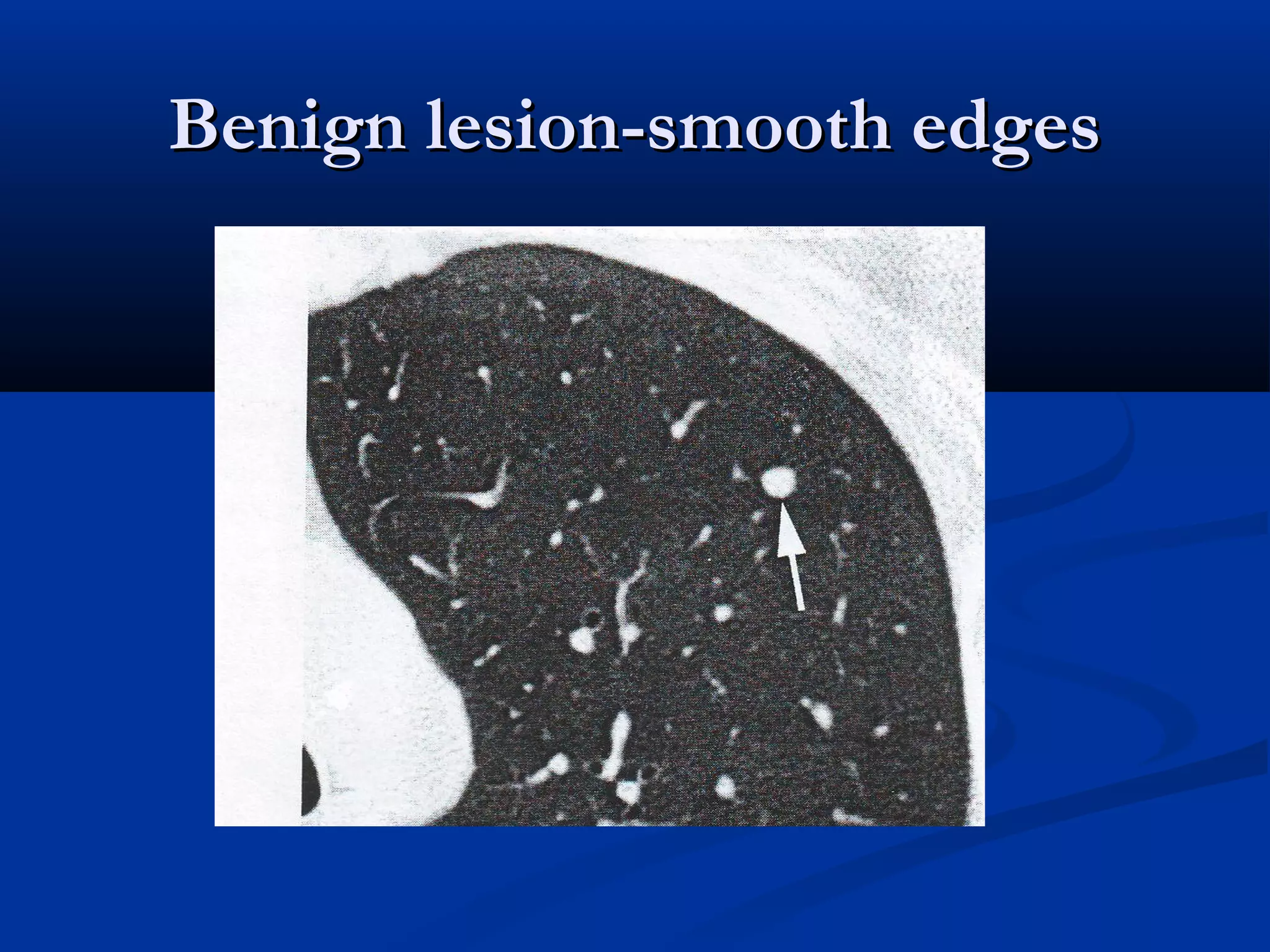
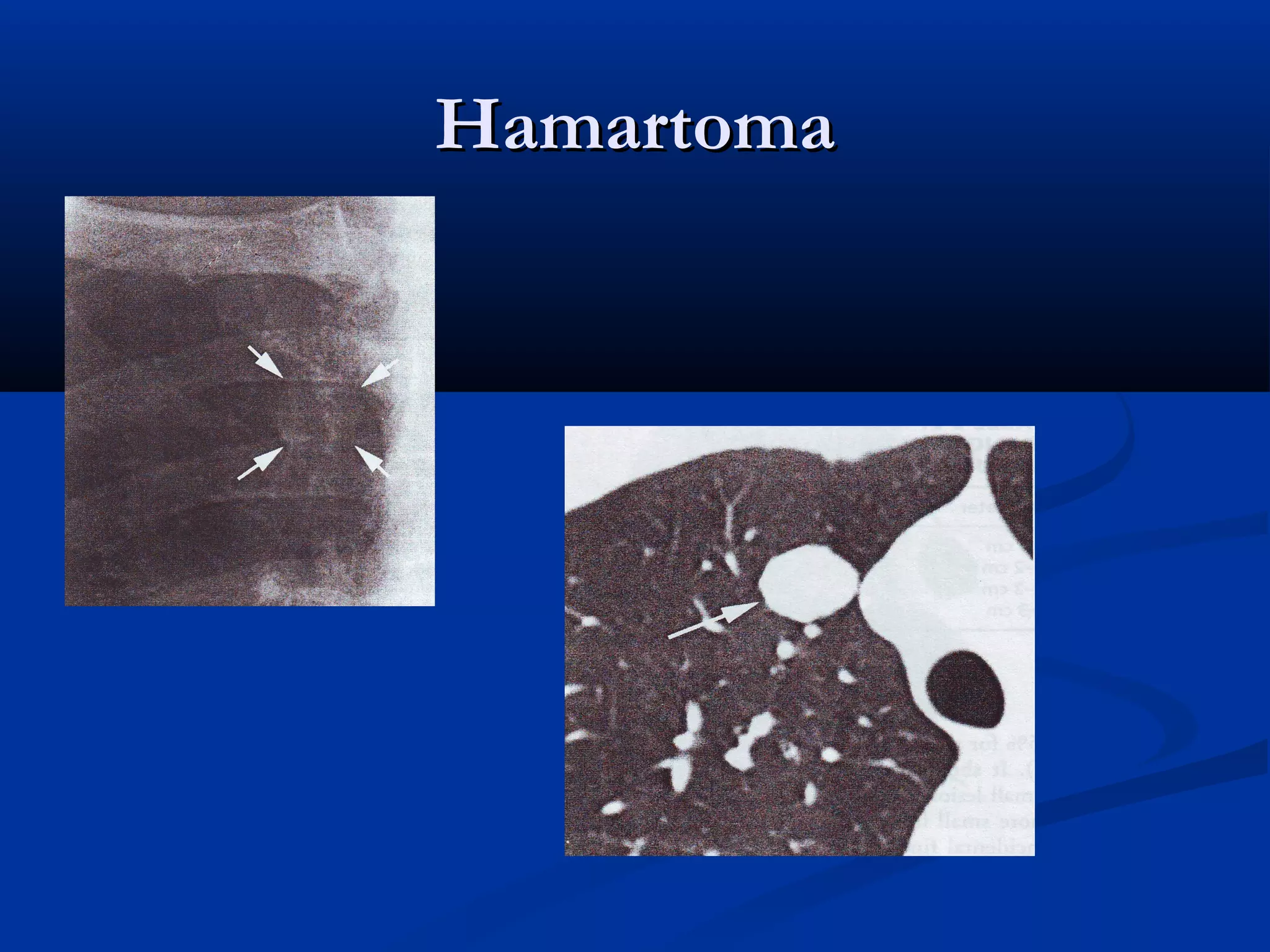
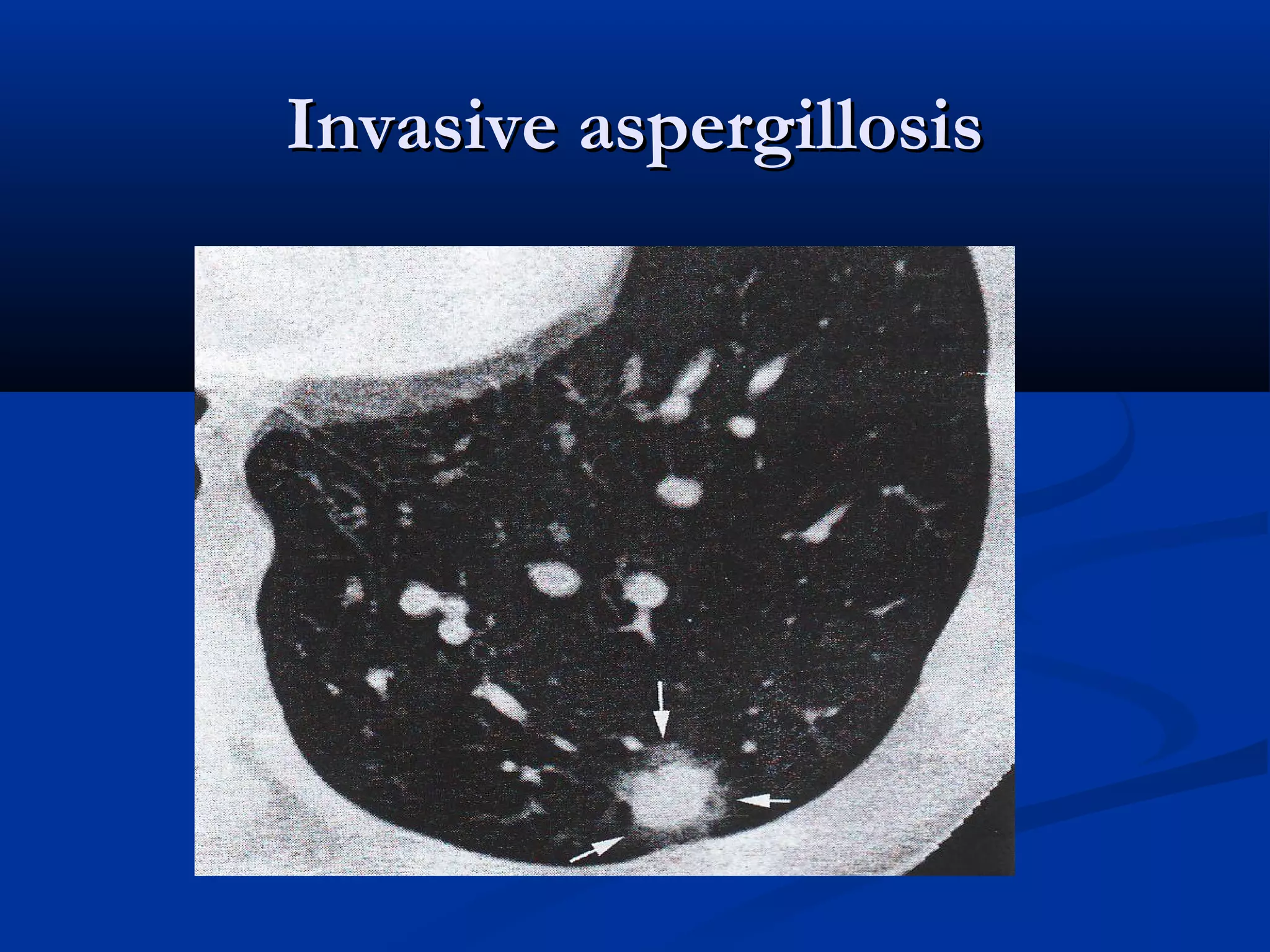
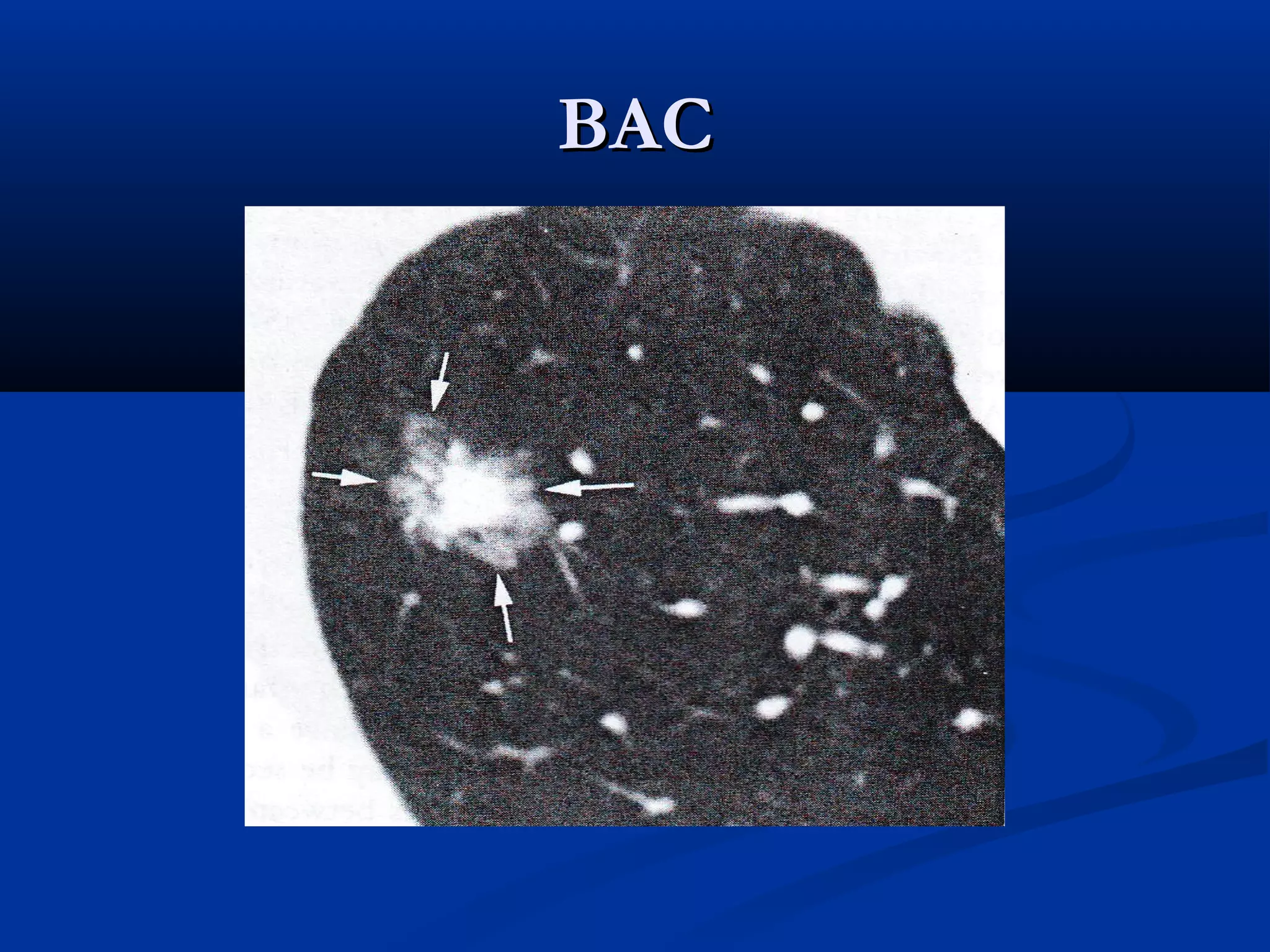
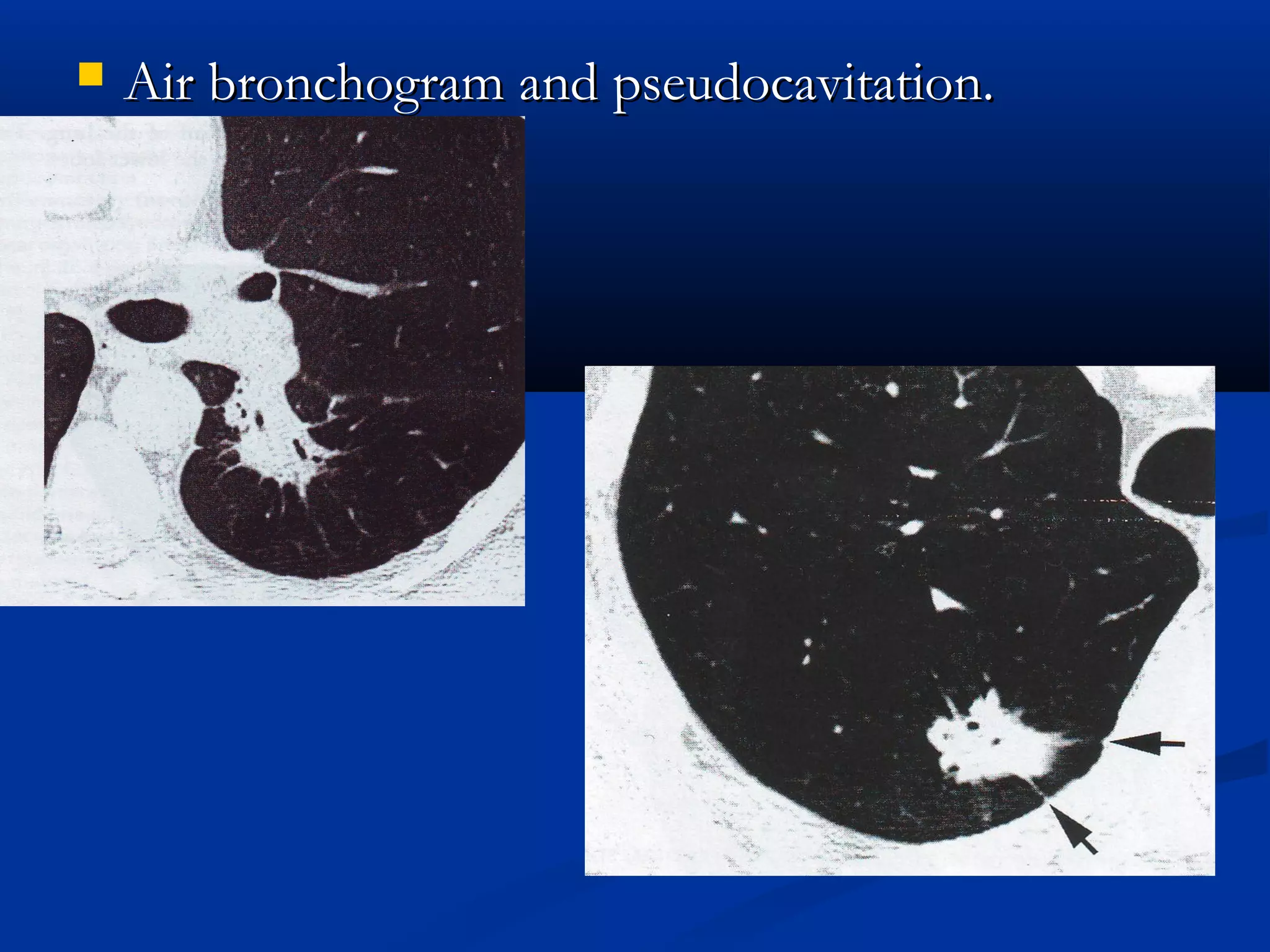
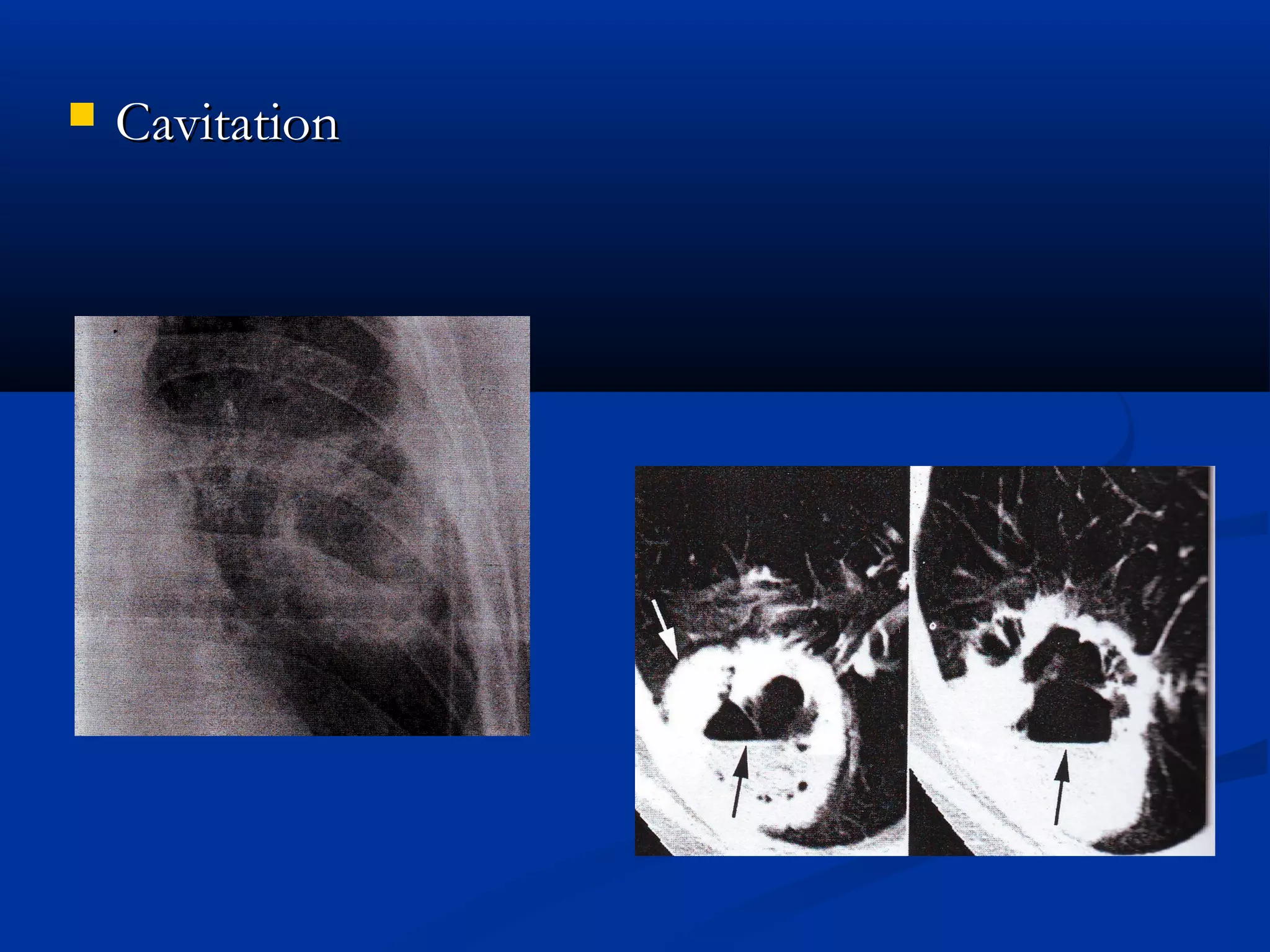
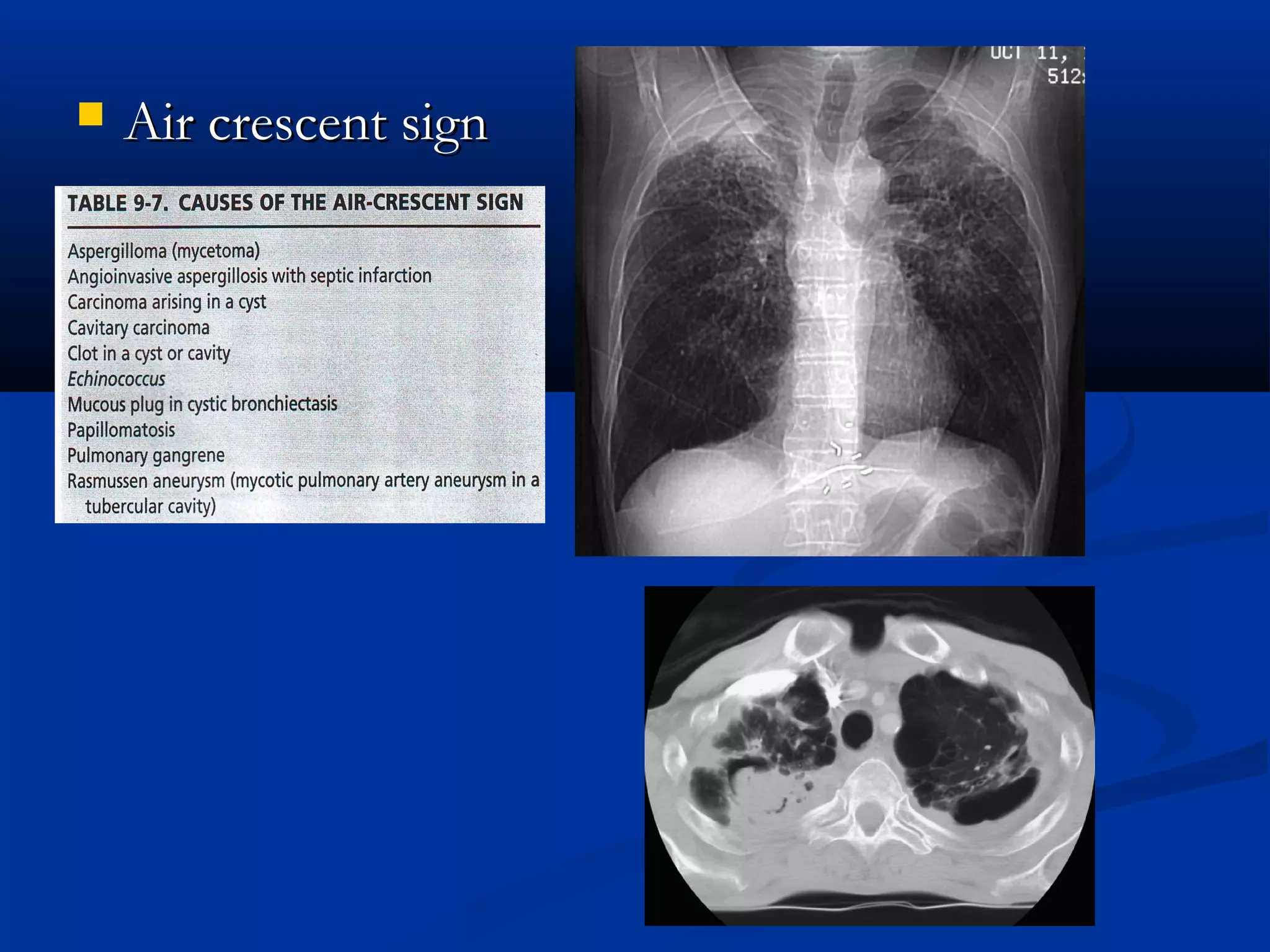
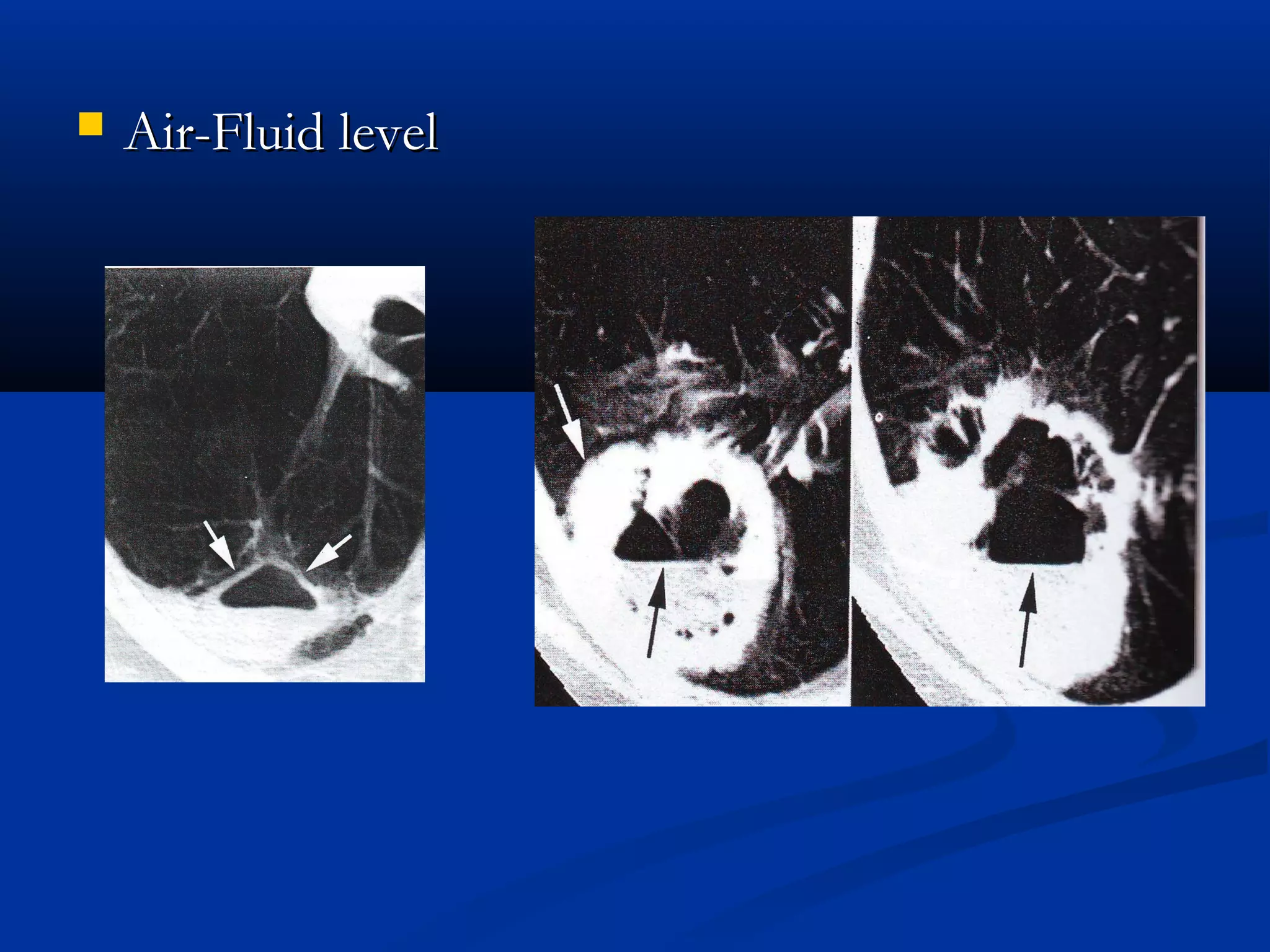
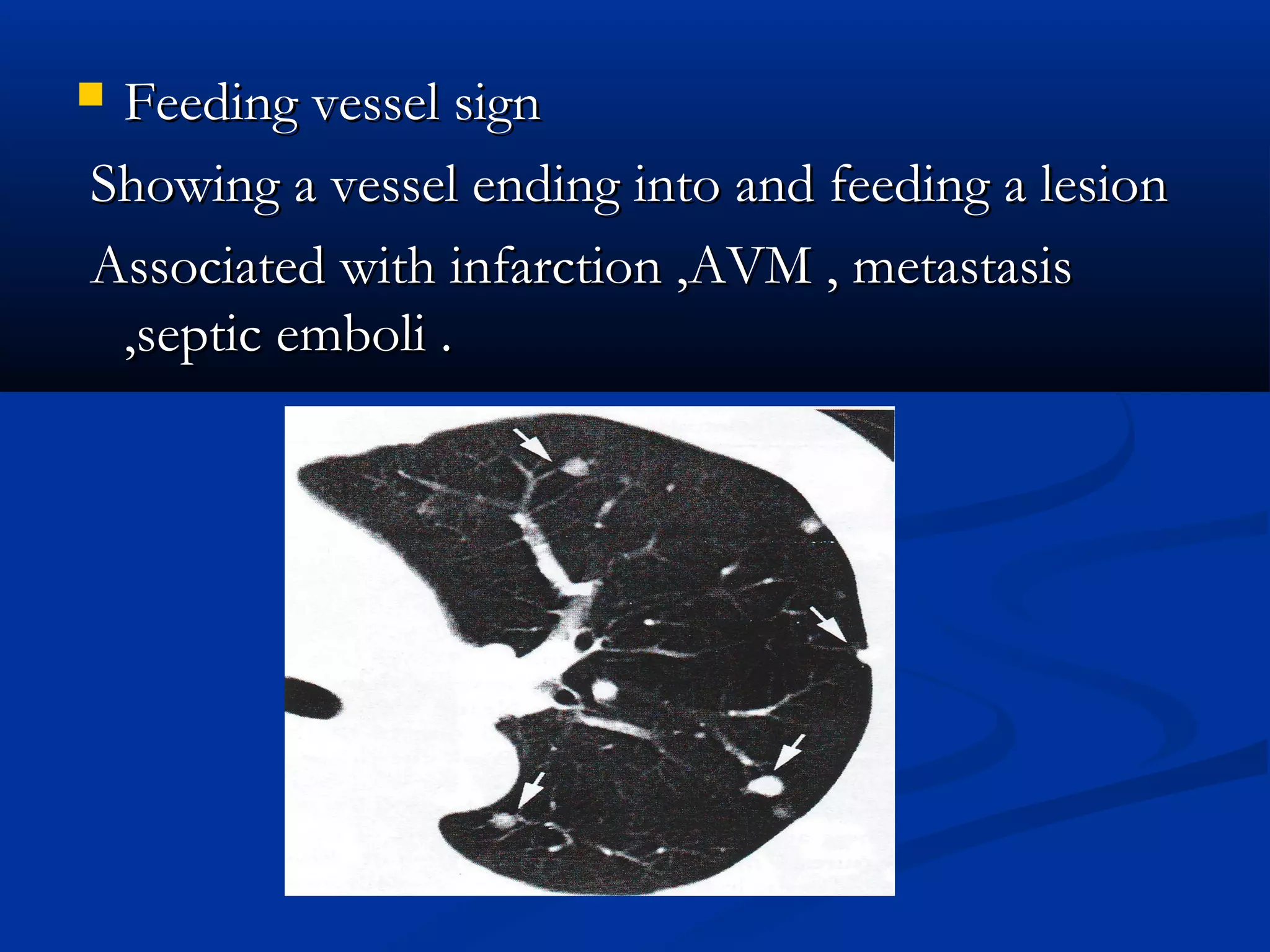
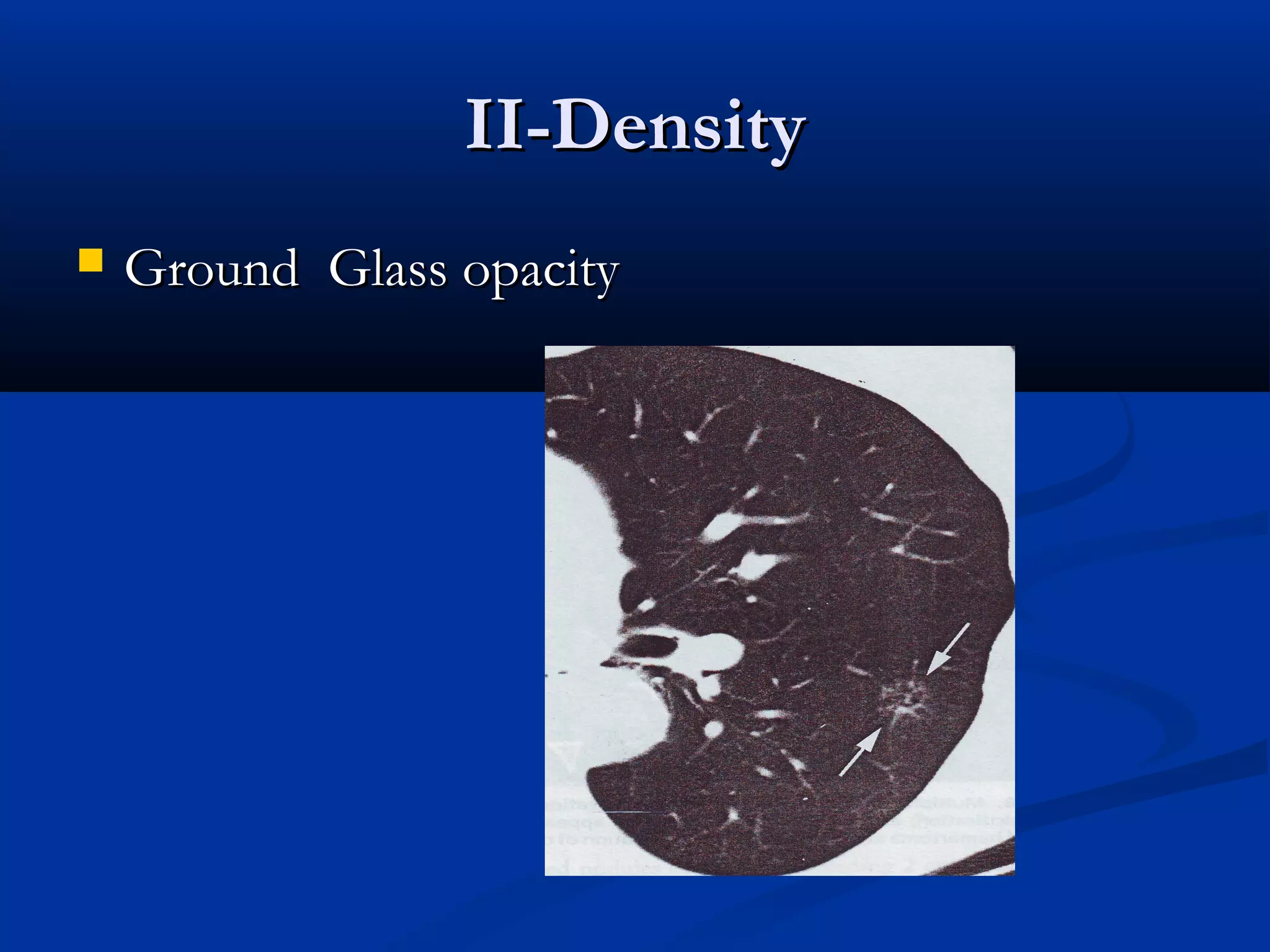
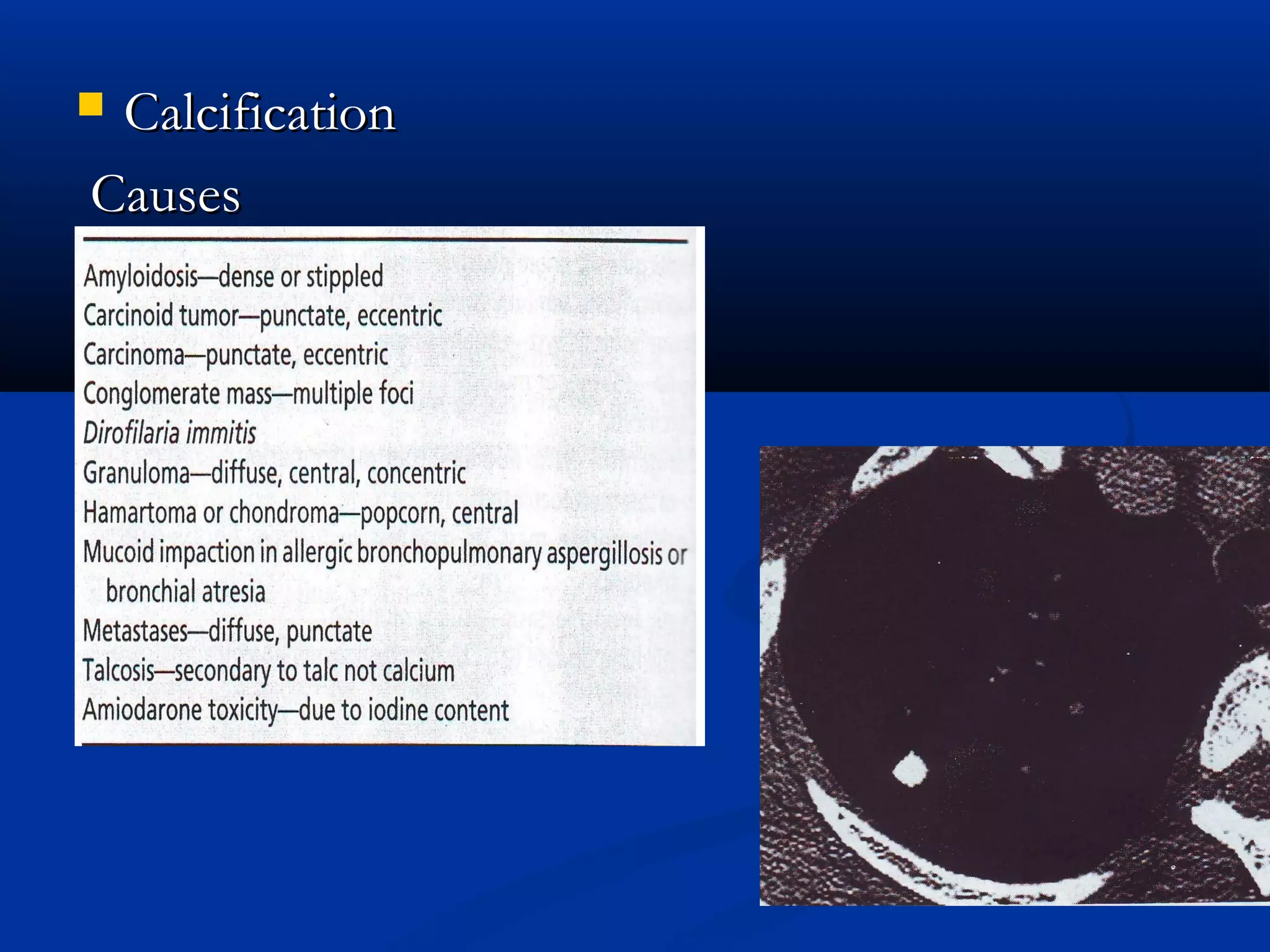
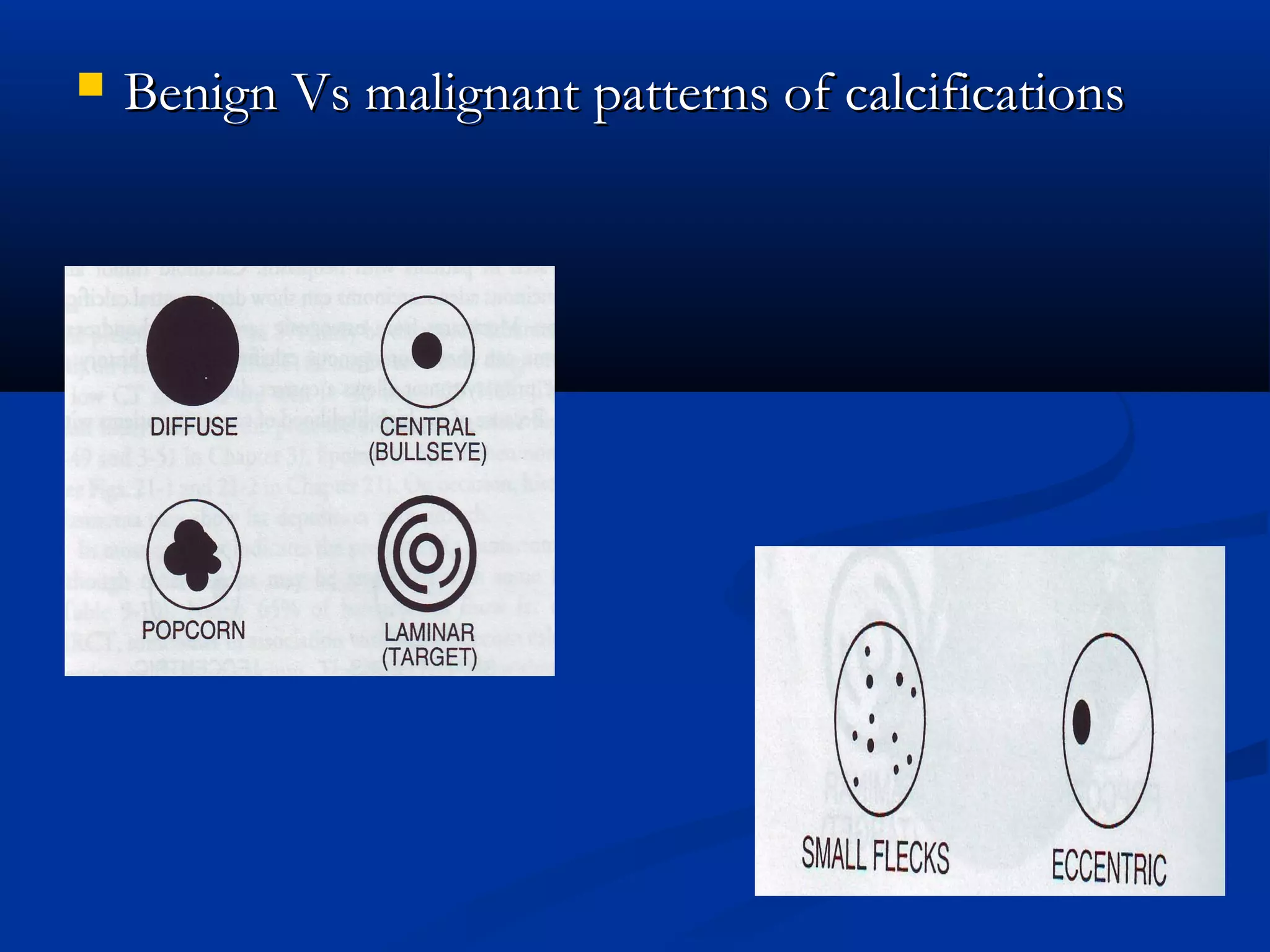
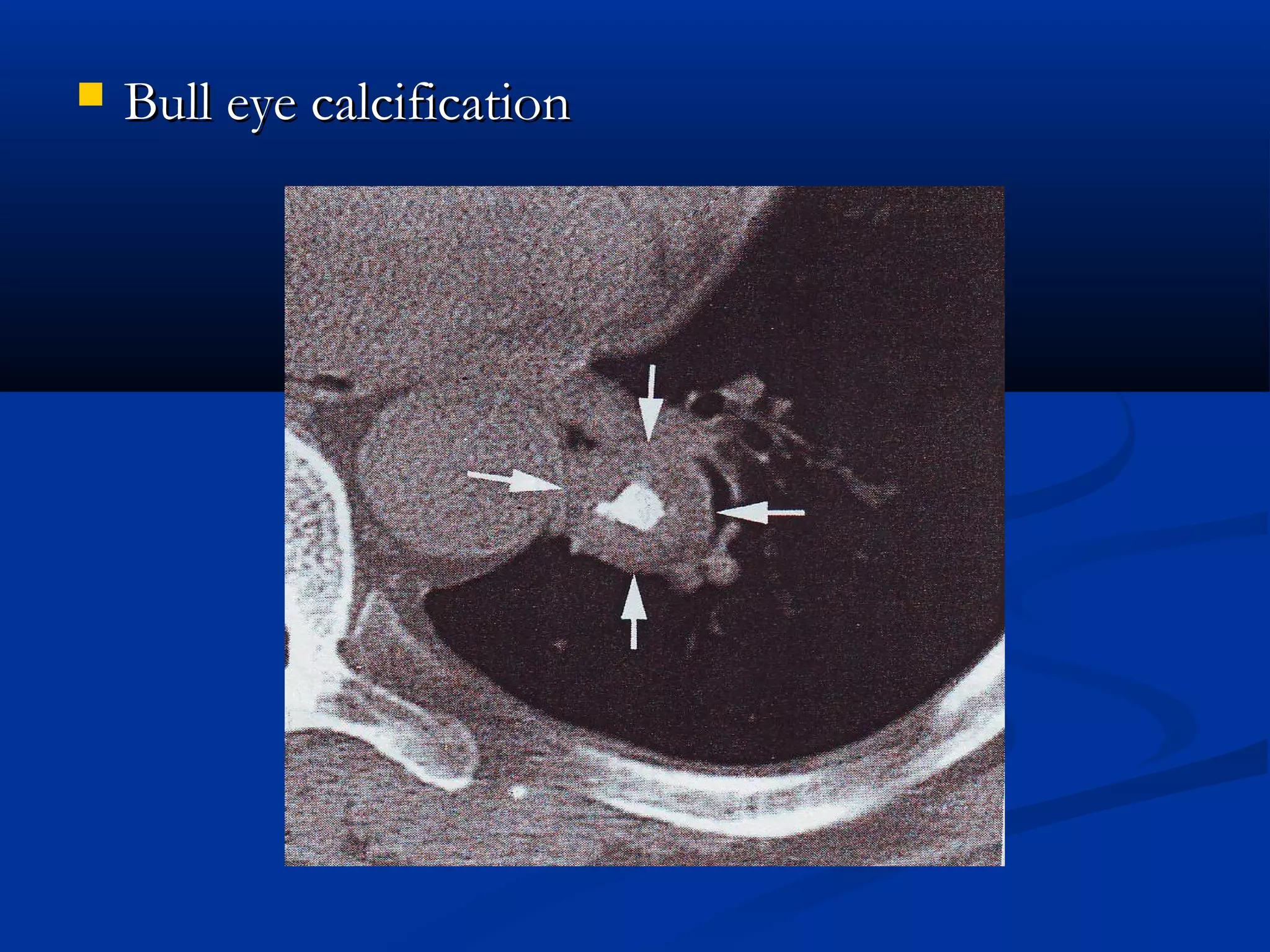
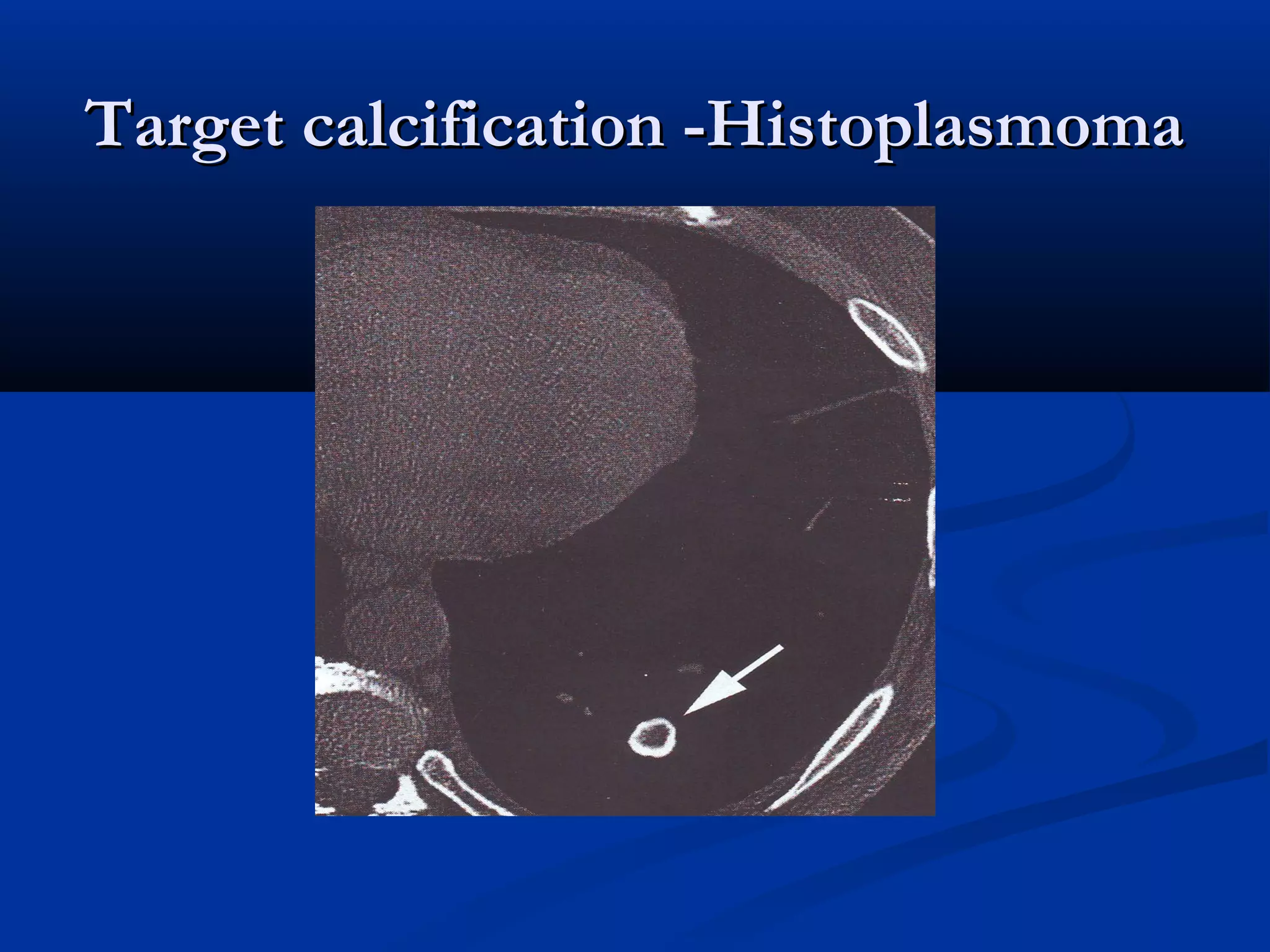
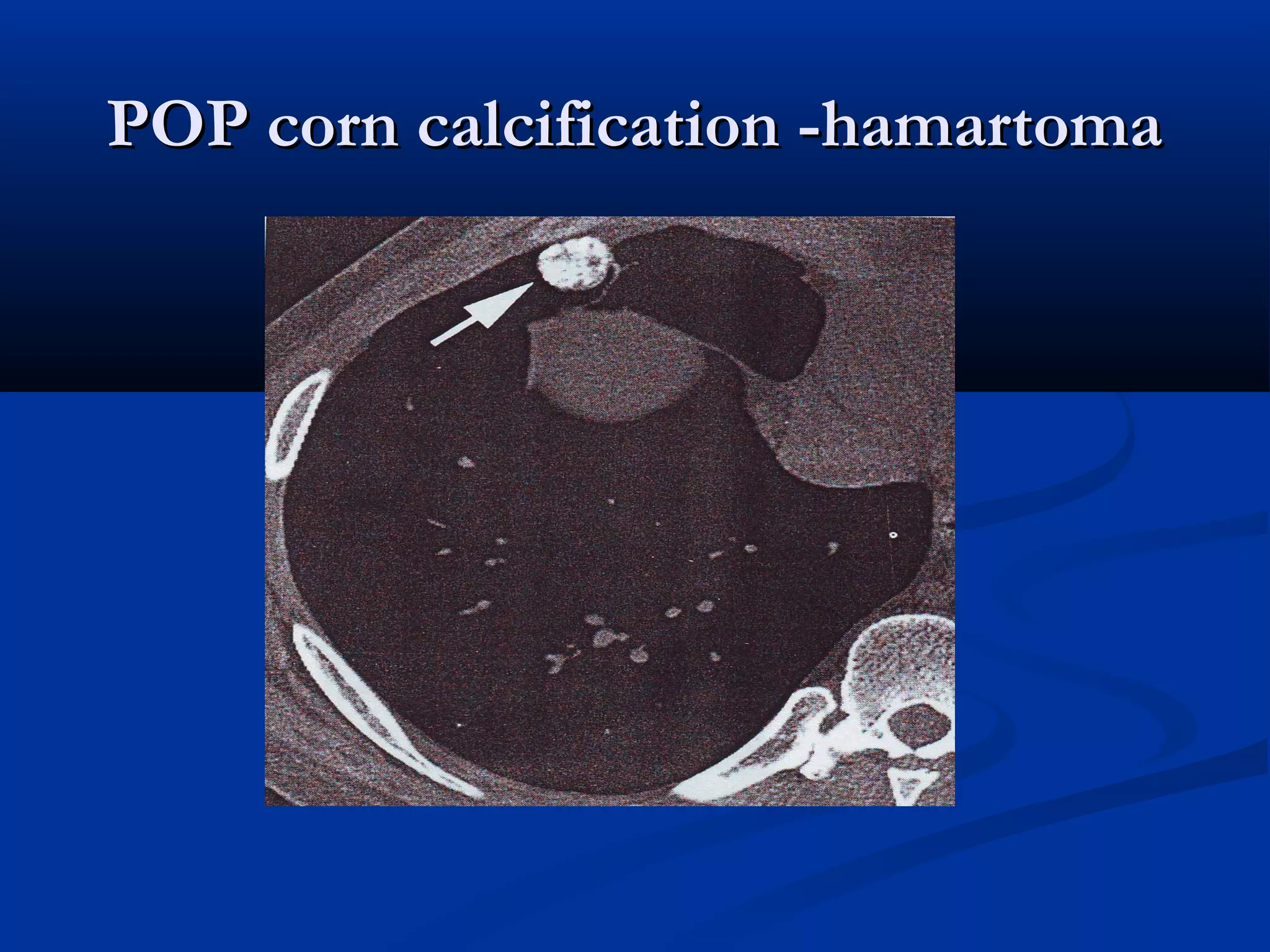
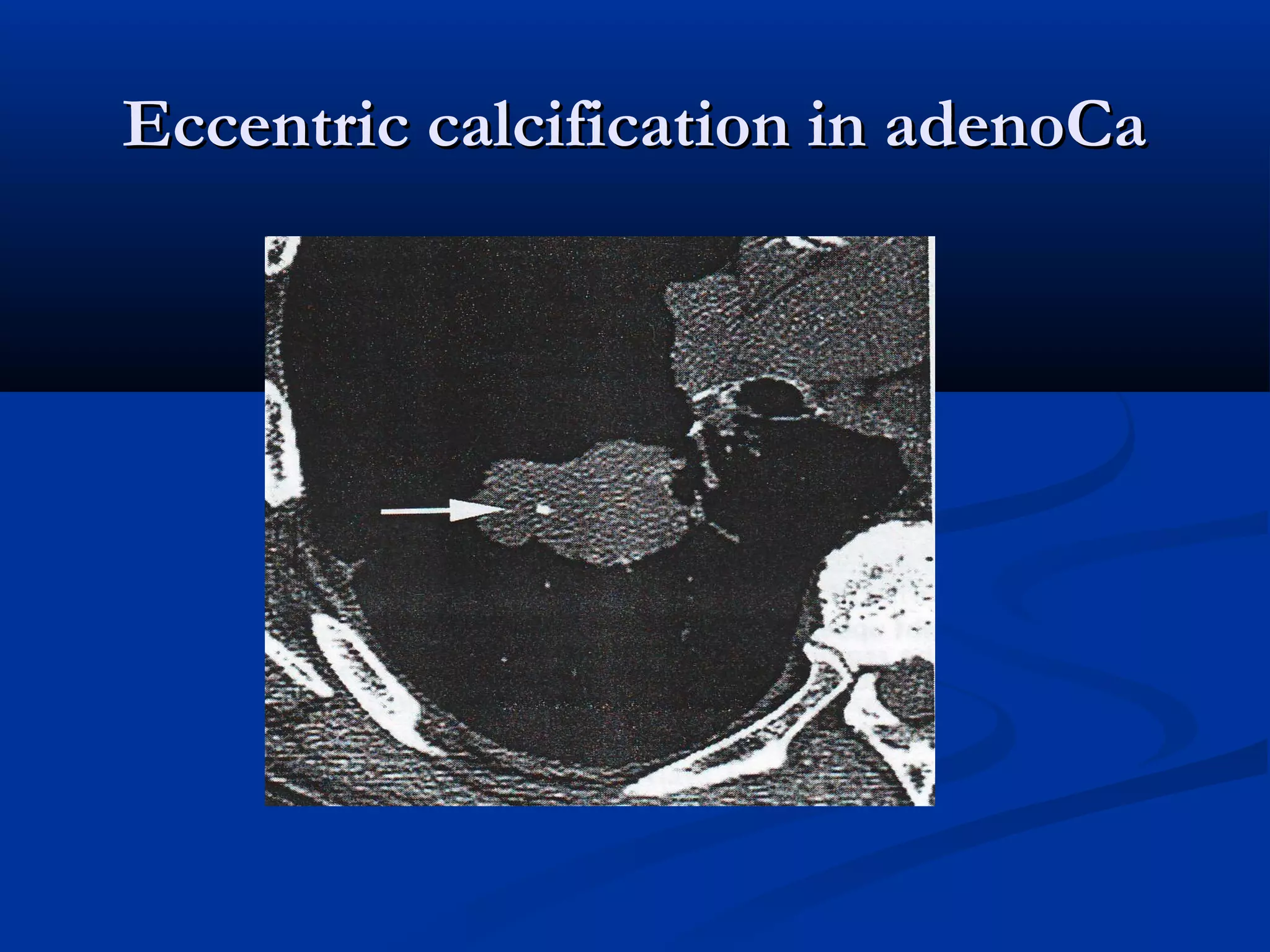
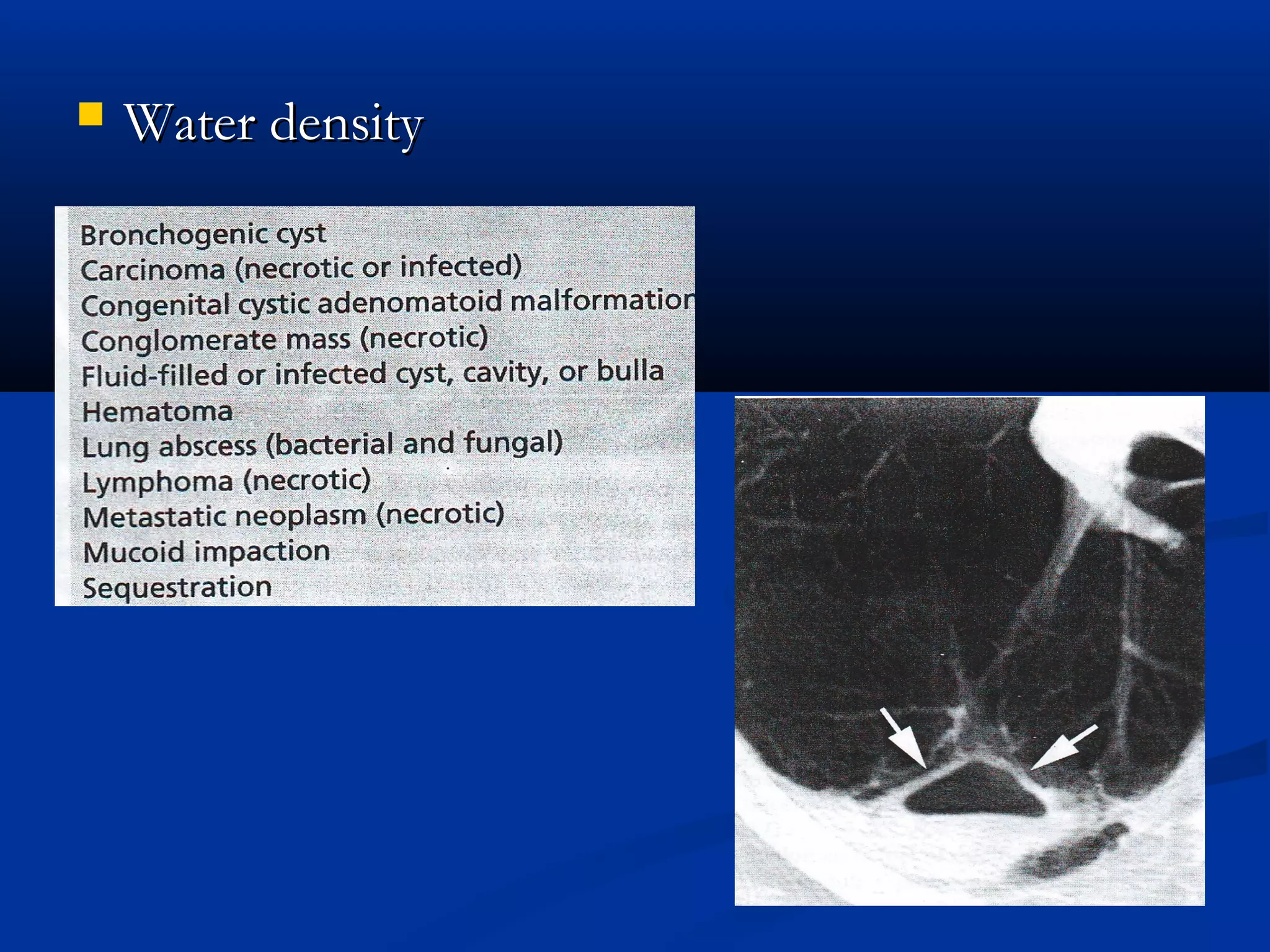
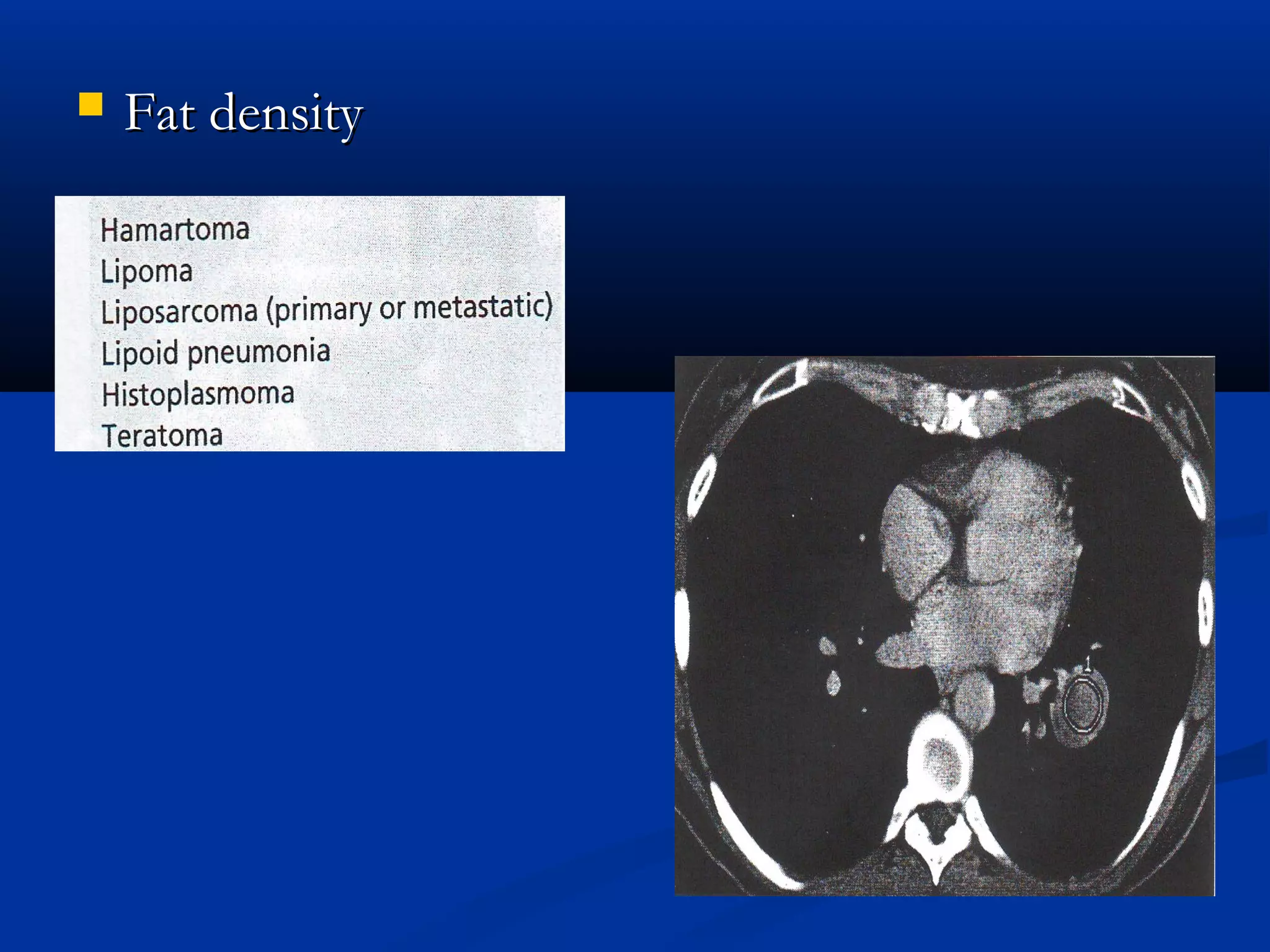
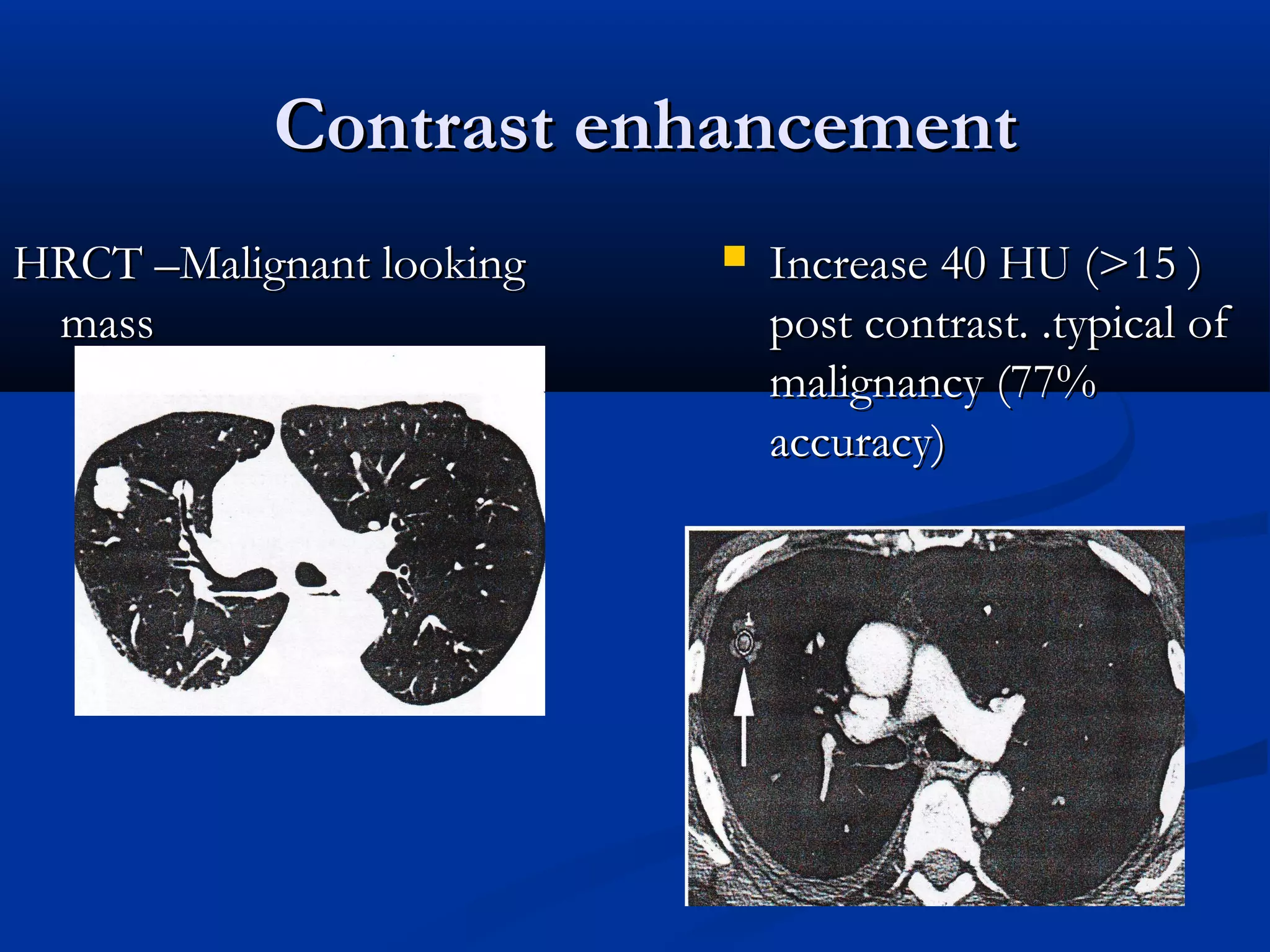
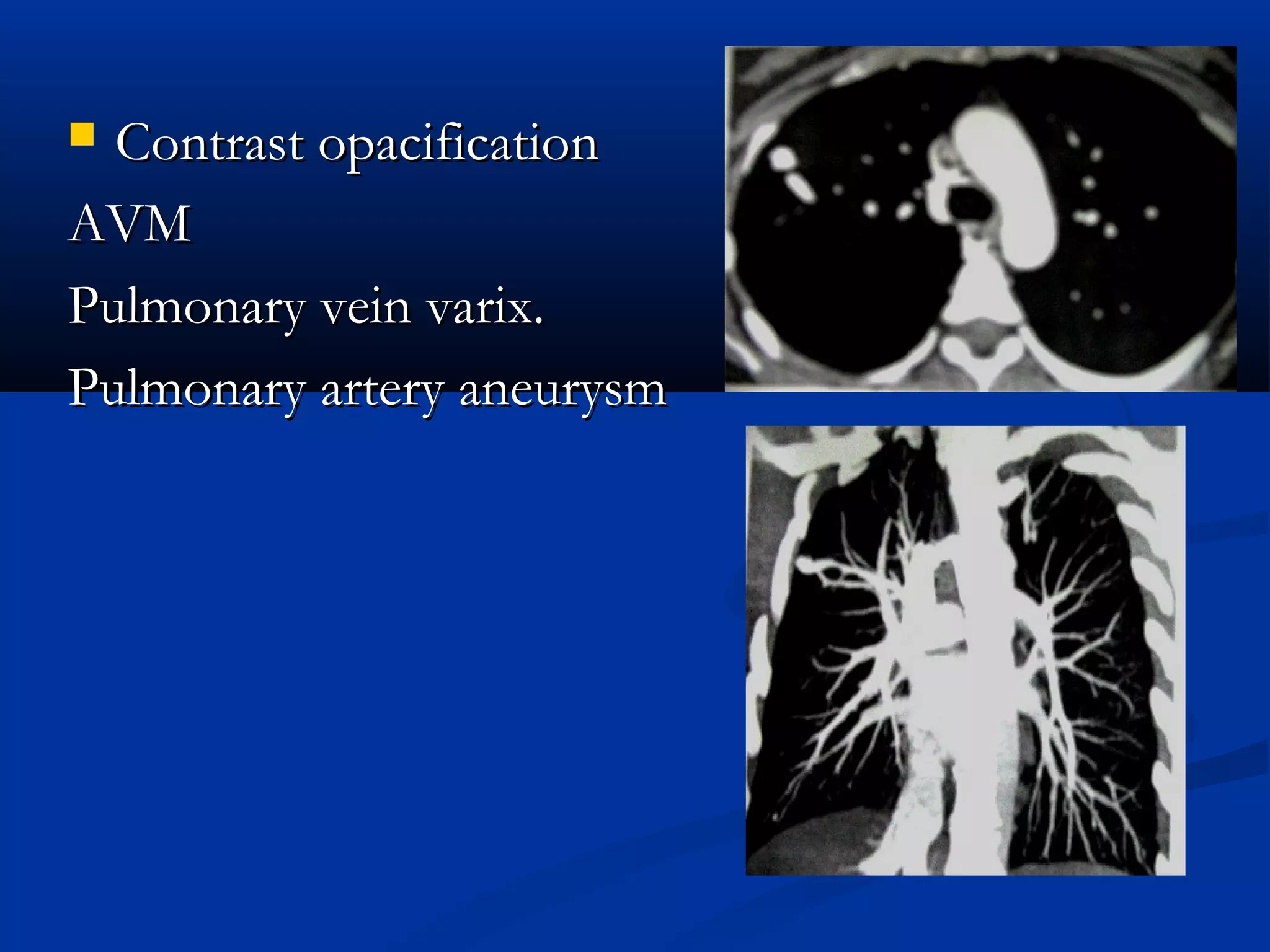
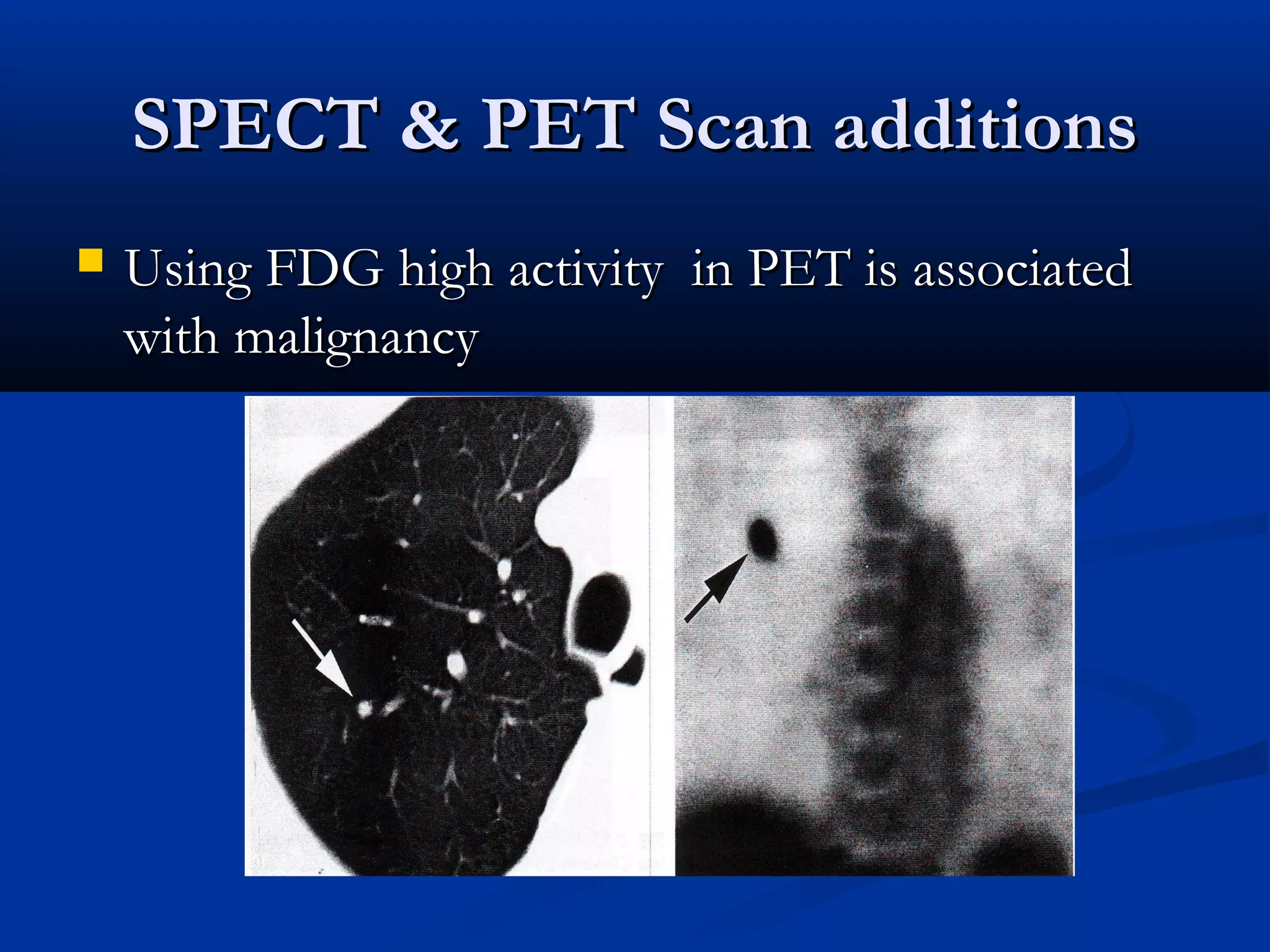
The document outlines the definition and clinical evaluation criteria for solitary pulmonary nodules (SPN), detailing their imaging characteristics, risk factors, and likelihood of malignancy based on size and other features. It emphasizes the importance of morphological characteristics, density, and growth rate in assessing SPNs, along with methods for further evaluation like PET scans and biopsies. The document serves as a guide for radiologists in distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions.