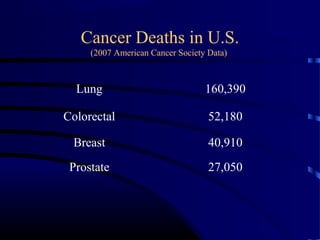
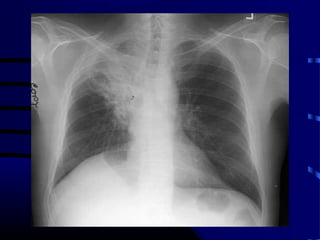
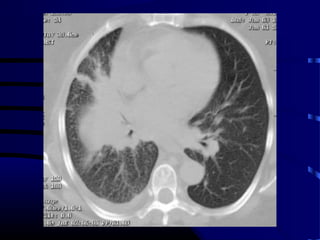
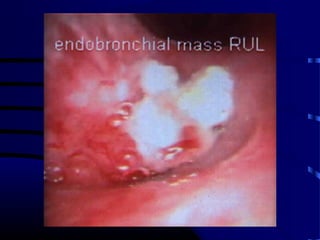
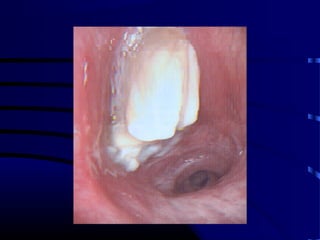
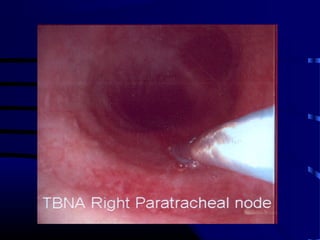
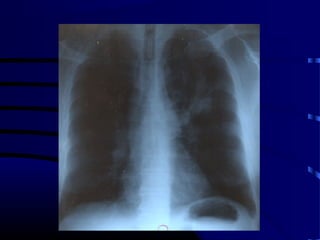
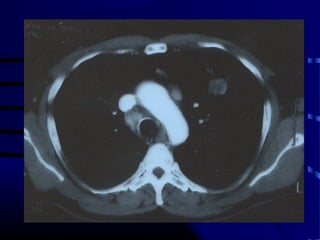
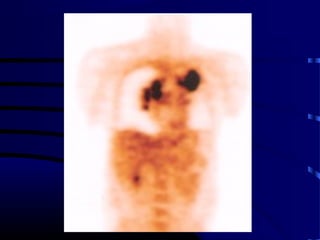
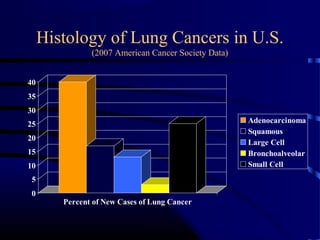
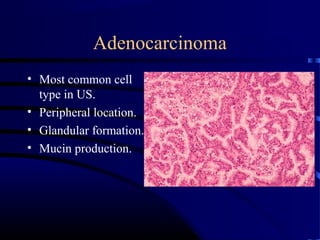
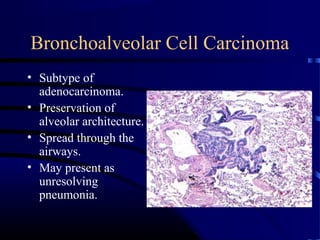
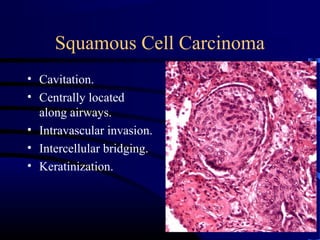
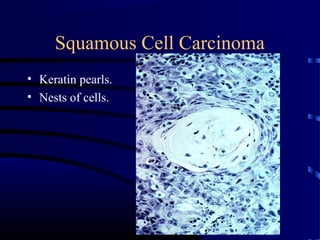
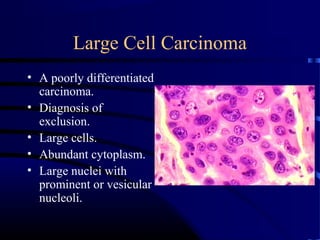
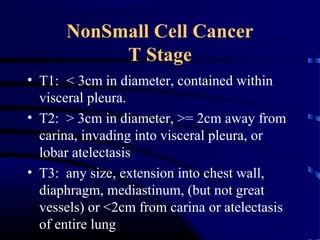
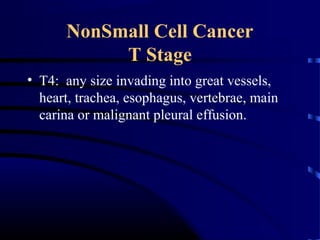
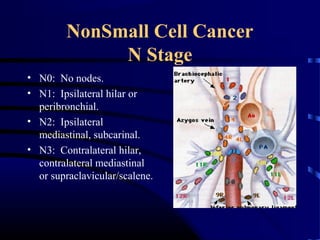
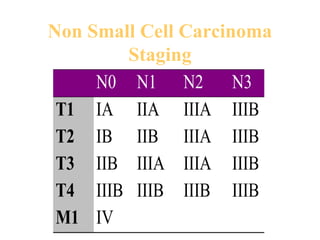
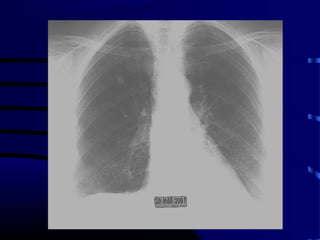
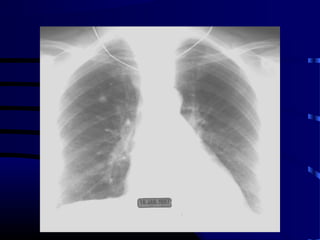
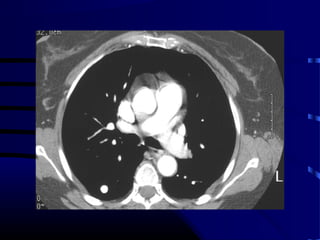
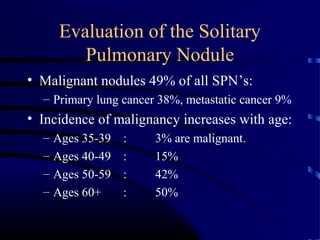
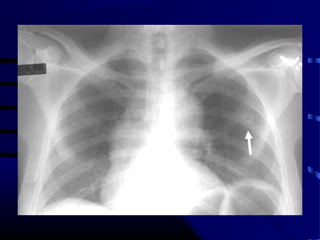
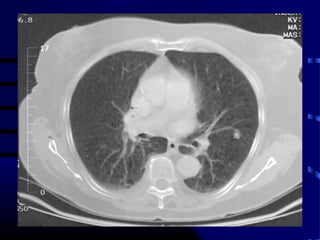
- A 60 year old smoker presented for a routine physical and was found to have an abnormality on chest x-ray
- The next appropriate test would be a CT scan of the chest with IV contrast to further characterize any lung lesions found on CXR
- A CT-guided biopsy would not be the next test, as further imaging is needed first to identify and stage any potential lung cancer before invasive testing
The best answer is A) CT chest with IV contrast to further evaluate and characterize any lung abnormalities found on CXR before considering an invasive biopsy.