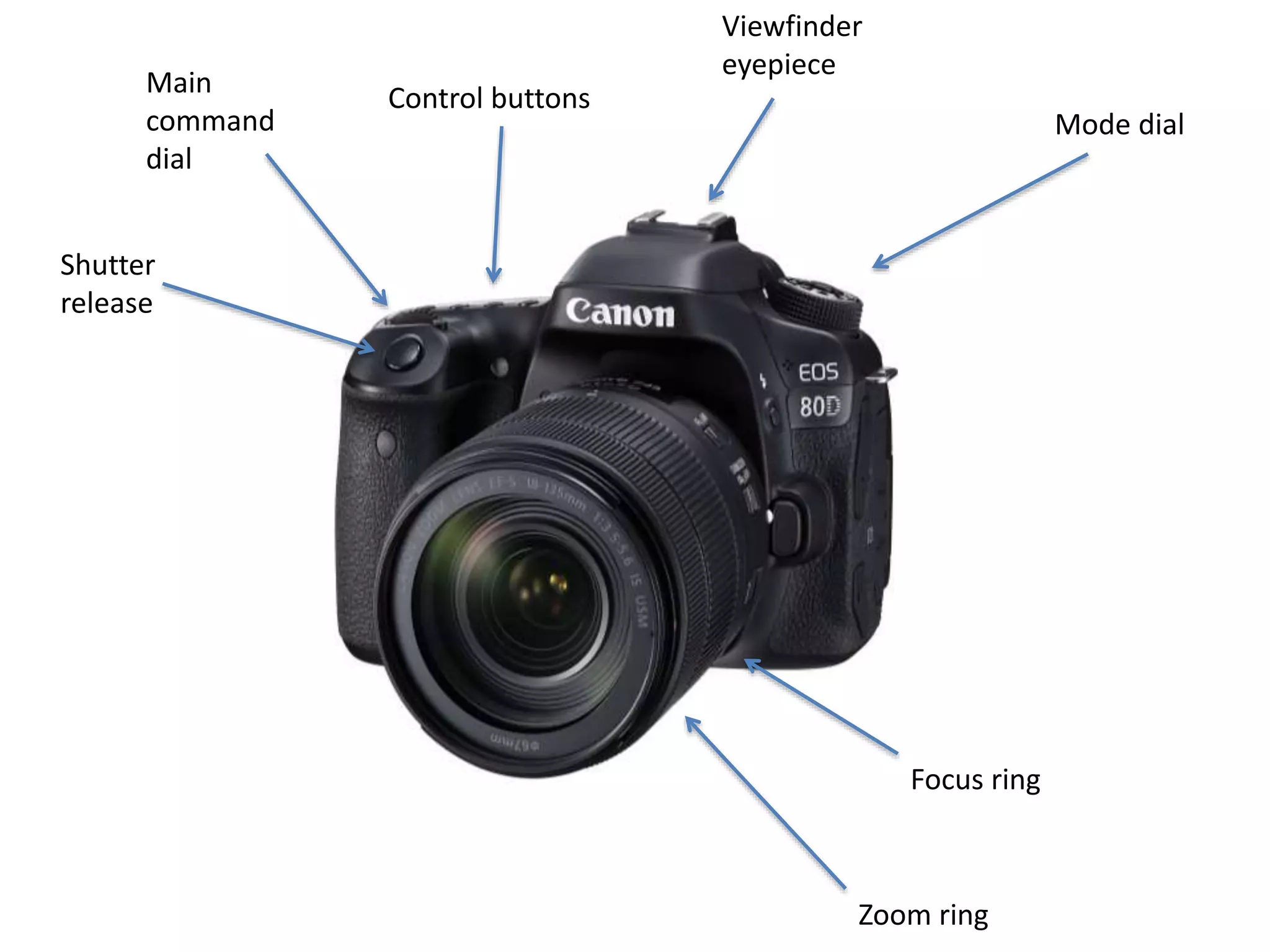
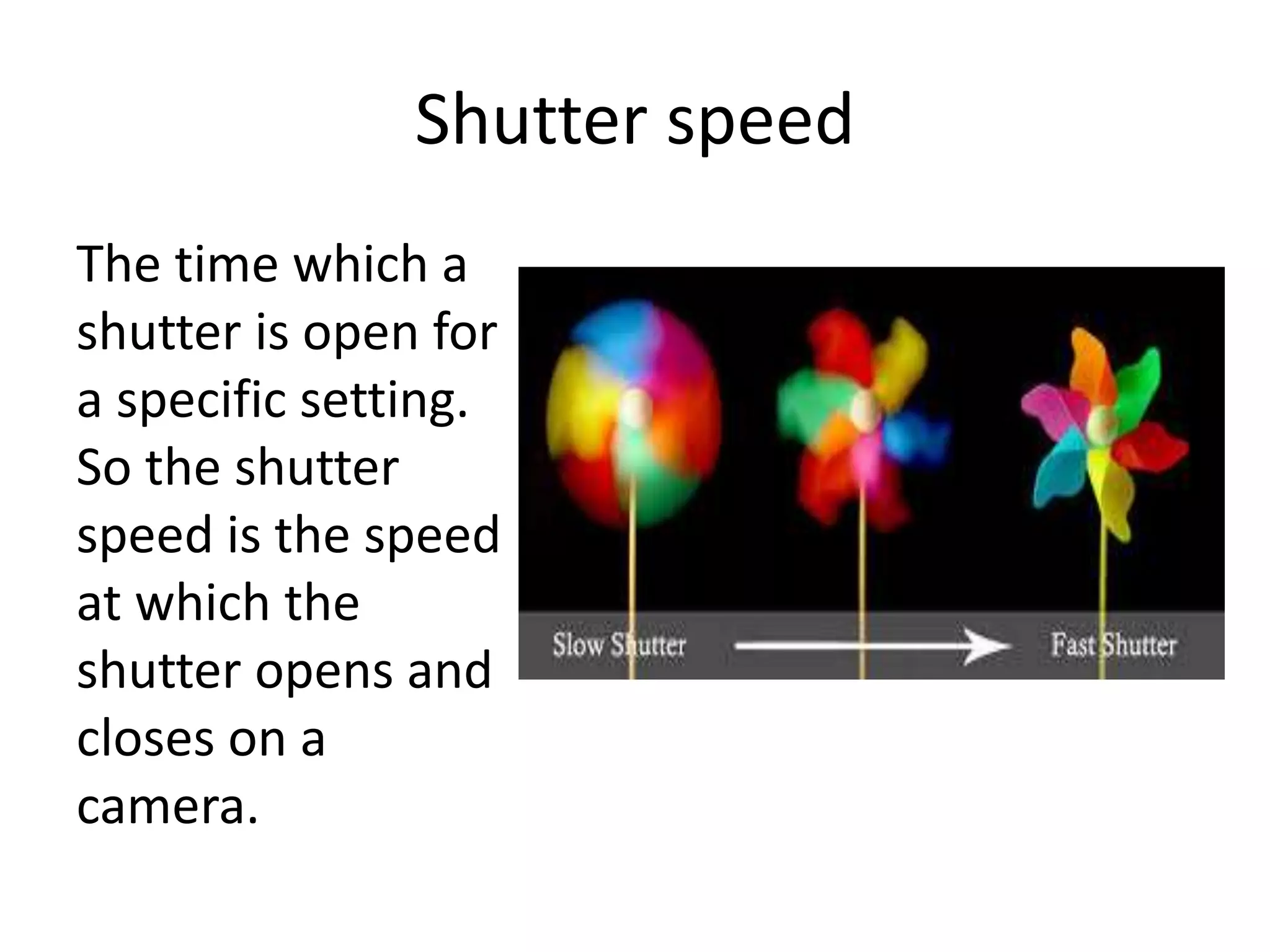
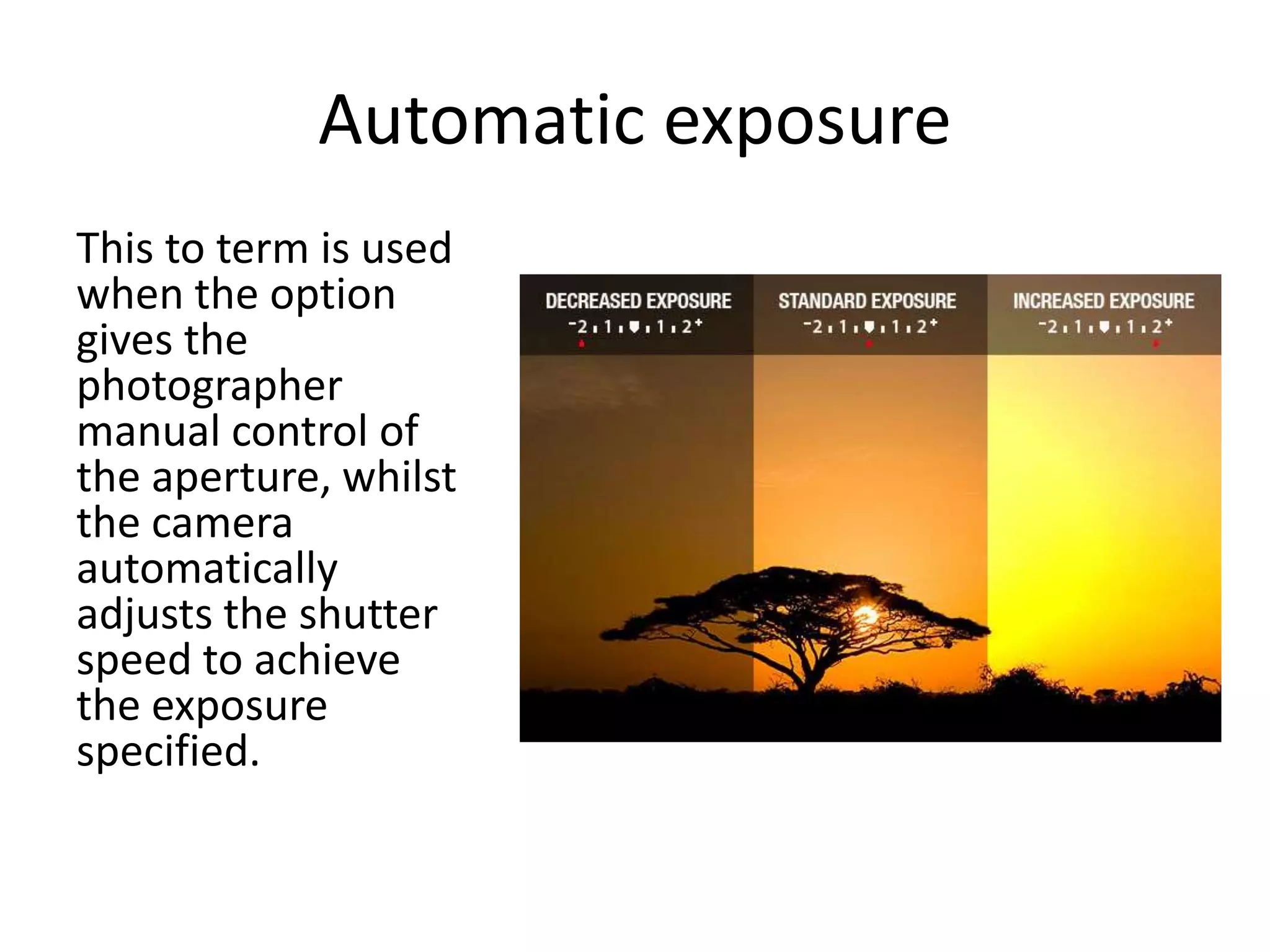
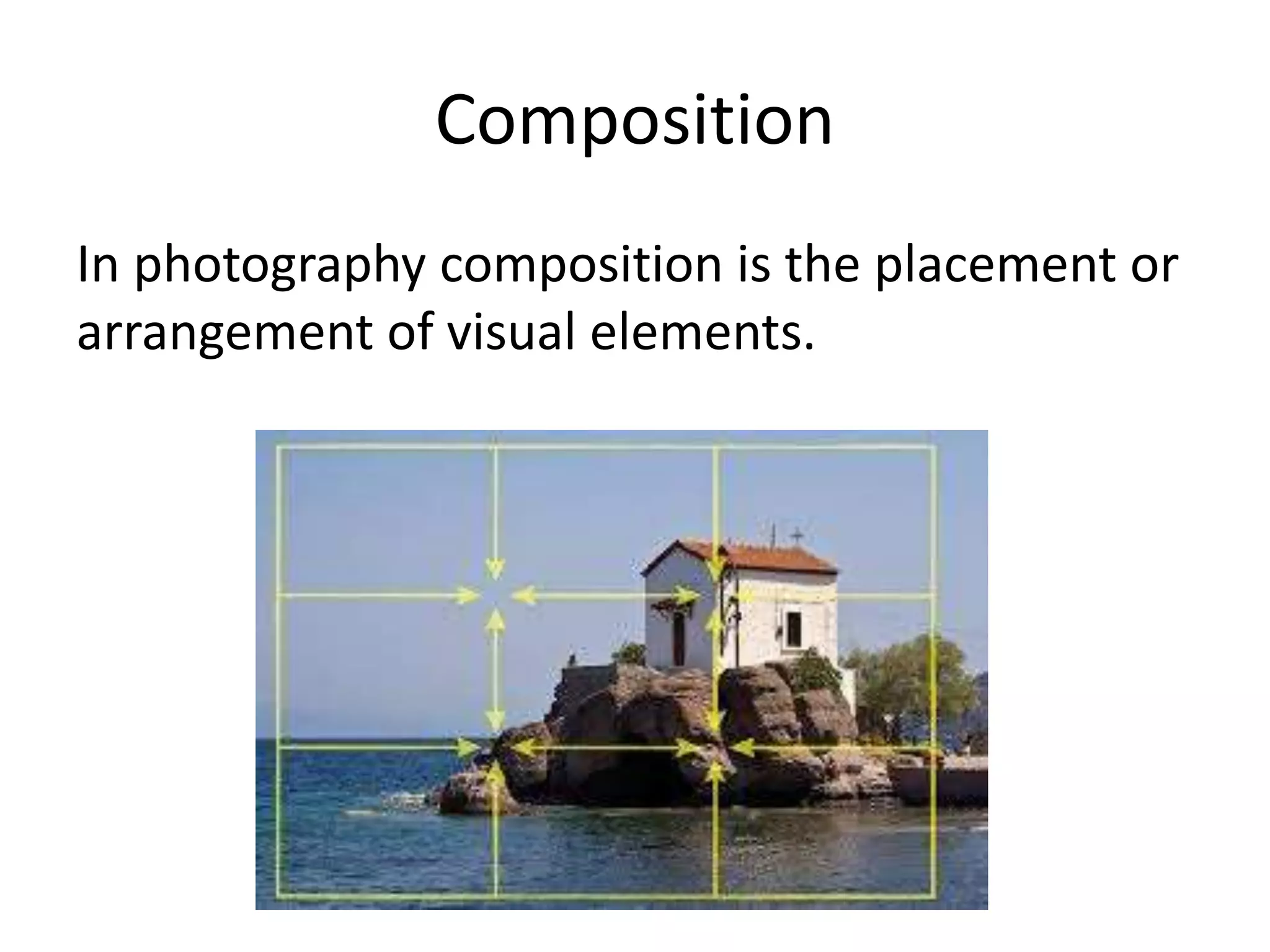
The document discusses key concepts in digital photography including camera parts like the mode dial and shutter release. It covers technical settings like shutter speed which determines how long the shutter is open, and ISO which measures the camera's light sensitivity. Aperture and depth of field are also explained, which determine the distance between the nearest and furthest objects that appear in focus. Manual and automatic exposure options are described along with other important topics like color balance, white balance, composition techniques, and macro photography.