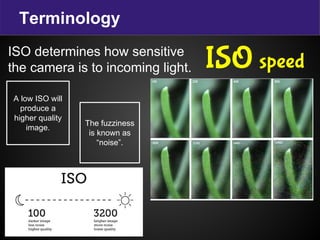
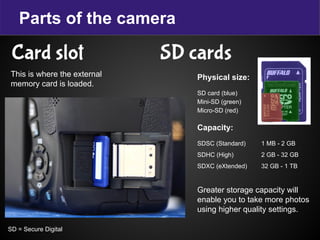
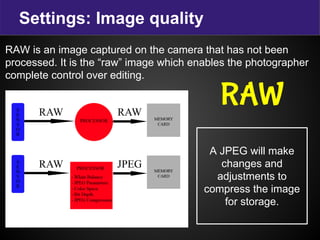
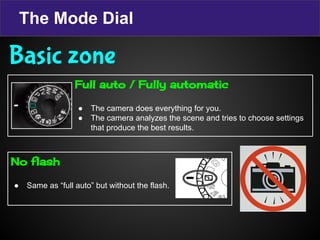
The document provides terminology and guidance for taking photos with a digital camera. It defines key terms like focus, exposure, aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. It describes camera parts such as the body, lens, flash, battery, memory card, LCD screen, and mode dial. It explains how to adjust settings for image quality, shooting modes, and erasing photos. Basic steps for taking a photo include planning the purpose, ensuring the camera is ready with charged battery and clean lens, and allowing enough light whether natural or artificial.