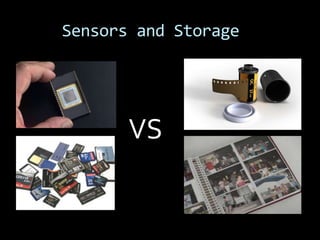
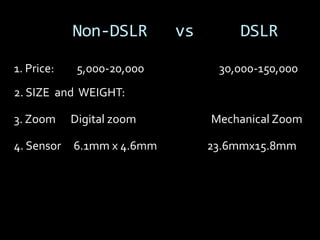
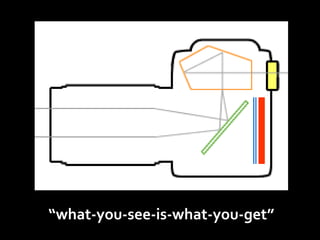
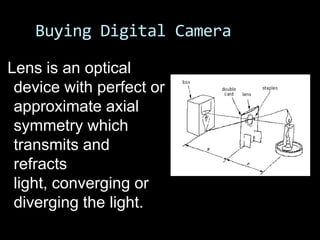
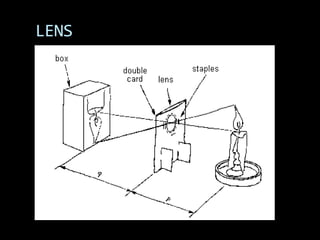
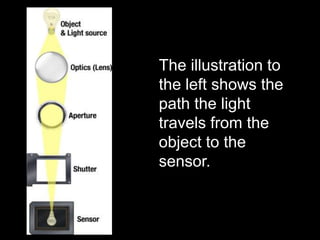
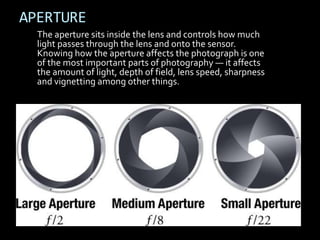
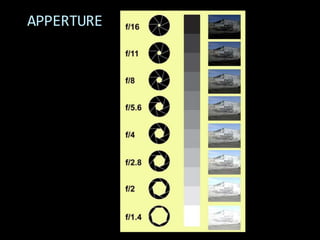
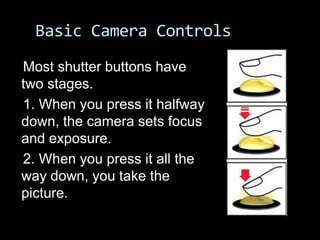
This document provides an introduction to digital photography, including an overview of digital cameras and their advantages over film cameras. It discusses basic camera components like sensors and storage as well as different types of digital cameras. It also covers lenses, megapixels, image stabilization, and basic camera controls like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. The goal is to educate newcomers to digital photography about selecting and using a digital camera.