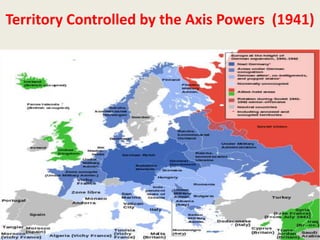
The document discusses key events and policies leading up to US involvement in World War II. It provides statistics on US casualties and costs from World War I, contributing to isolationist sentiment. It also outlines the Neutrality Acts of the late 1930s which aimed to keep the US out of future conflicts by limiting trade and loans to belligerents. However, the 1941 Lend-Lease Act ended US neutrality and committed major economic support to fight against Germany, marking America's shift towards aiding the Allies.






![Lend-Lease Act 1941
• Ended U.S. neutrality!
• The U.S. committed huge
economic resources to
fighting [against]
Germany.
–Becomes “arsenal of
democracy”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wwiiapril18-160418220740/85/WWII-Neutrality-Lend-Lease-8-320.jpg)