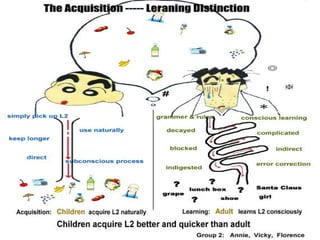
The Natural Approach is a language teaching philosophy developed in the 1970s that focuses on developing basic communication skills through comprehension and speech production. It has three stages: comprehension, early production, and speech emergence. In the comprehension stage, activities are designed to teach students to understand words in context without knowing every word. In early production, students begin using English words to answer simple questions. As speech production improves, more complex answers and sentences are used. The Natural Approach rejects formal grammar instruction and focuses on meaningful use of language through activities and experiences.