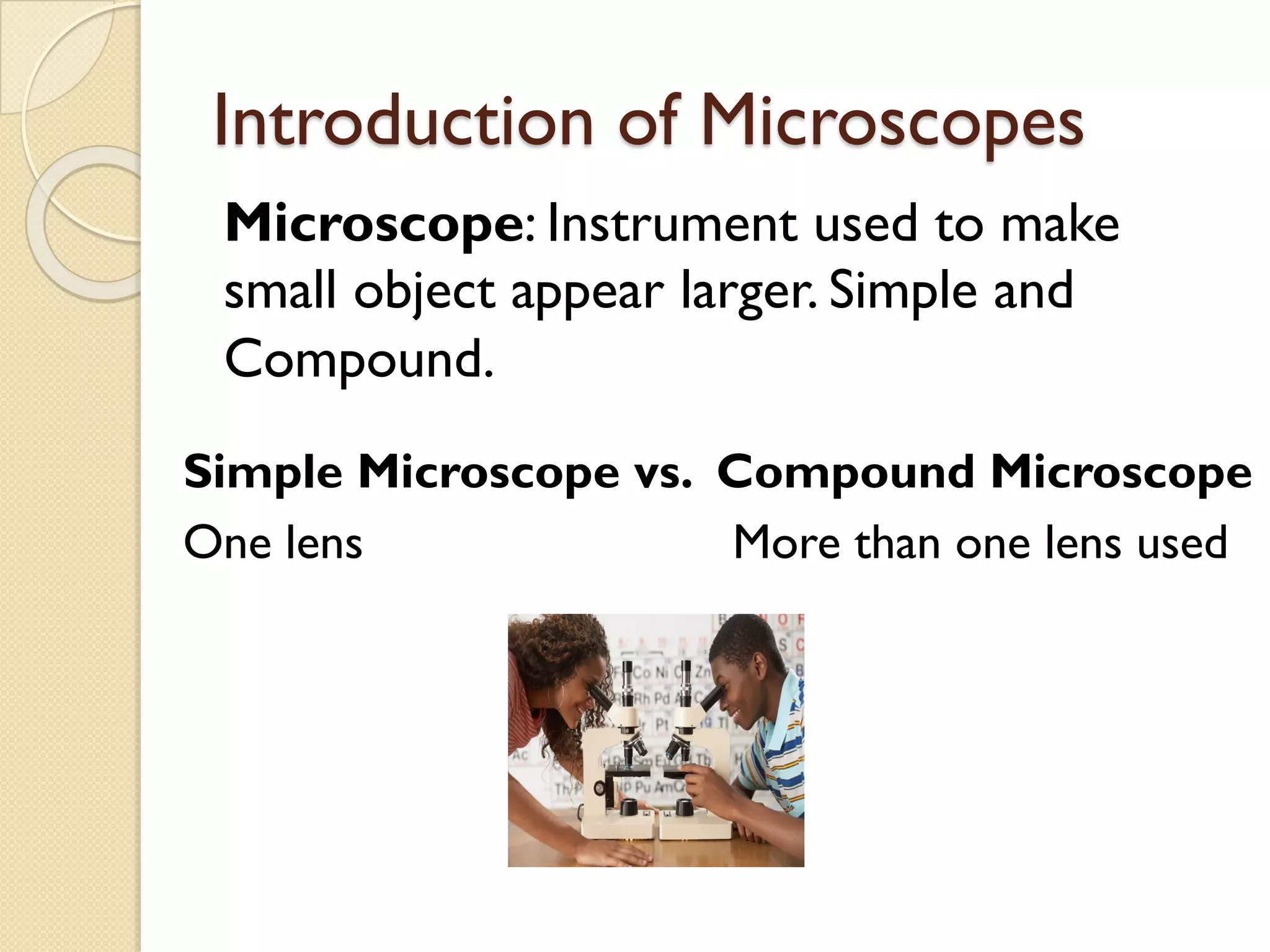
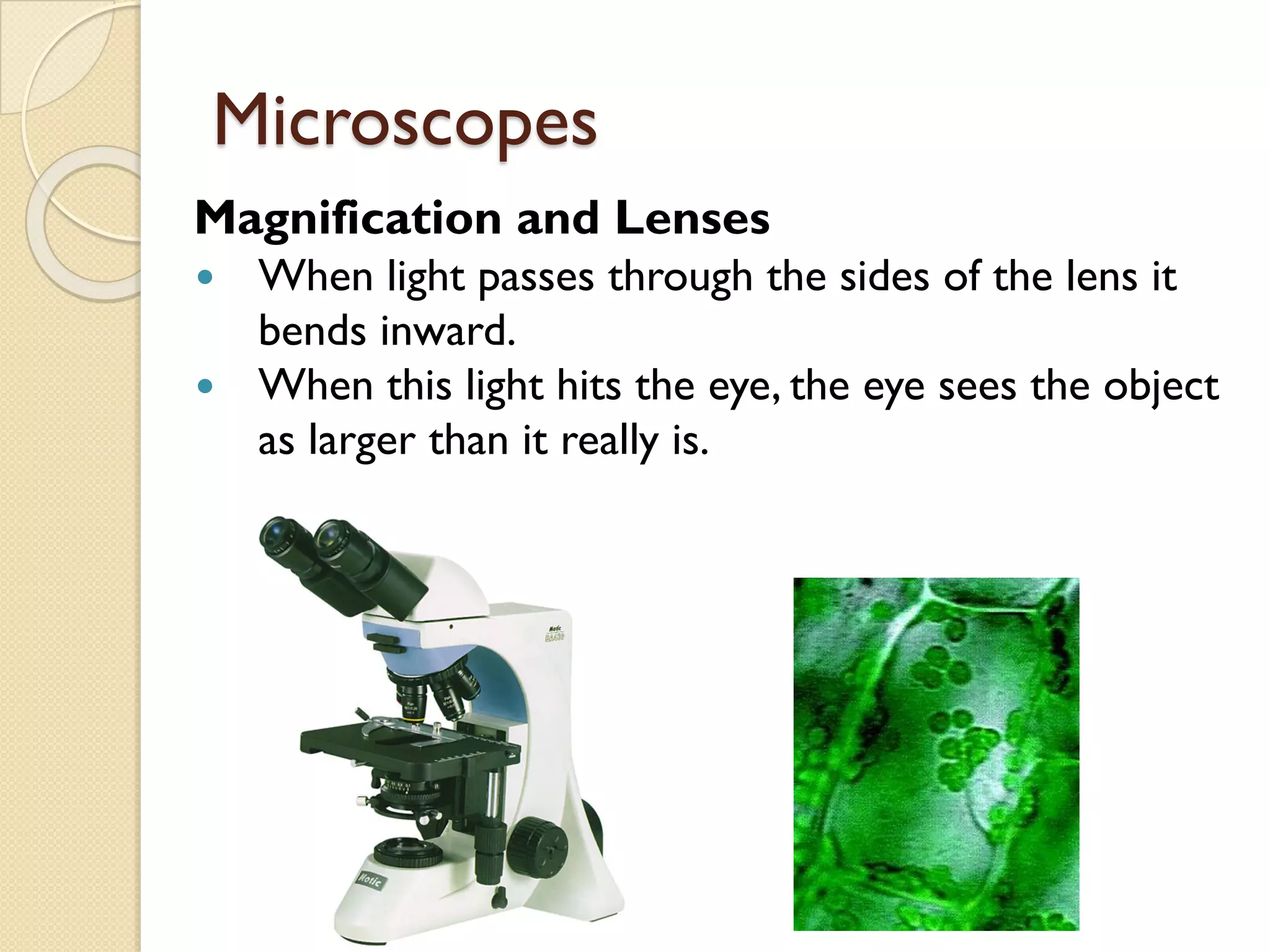
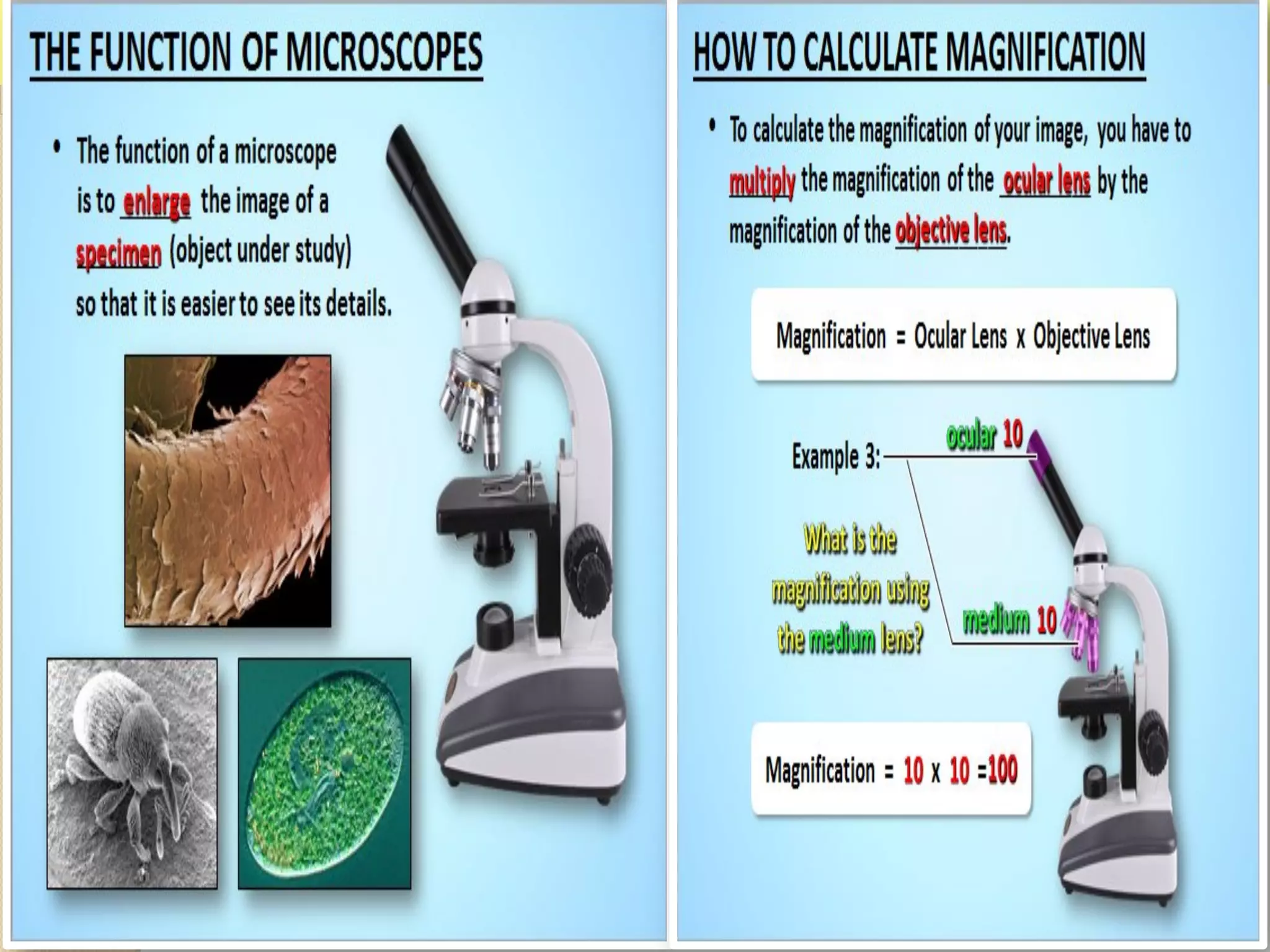
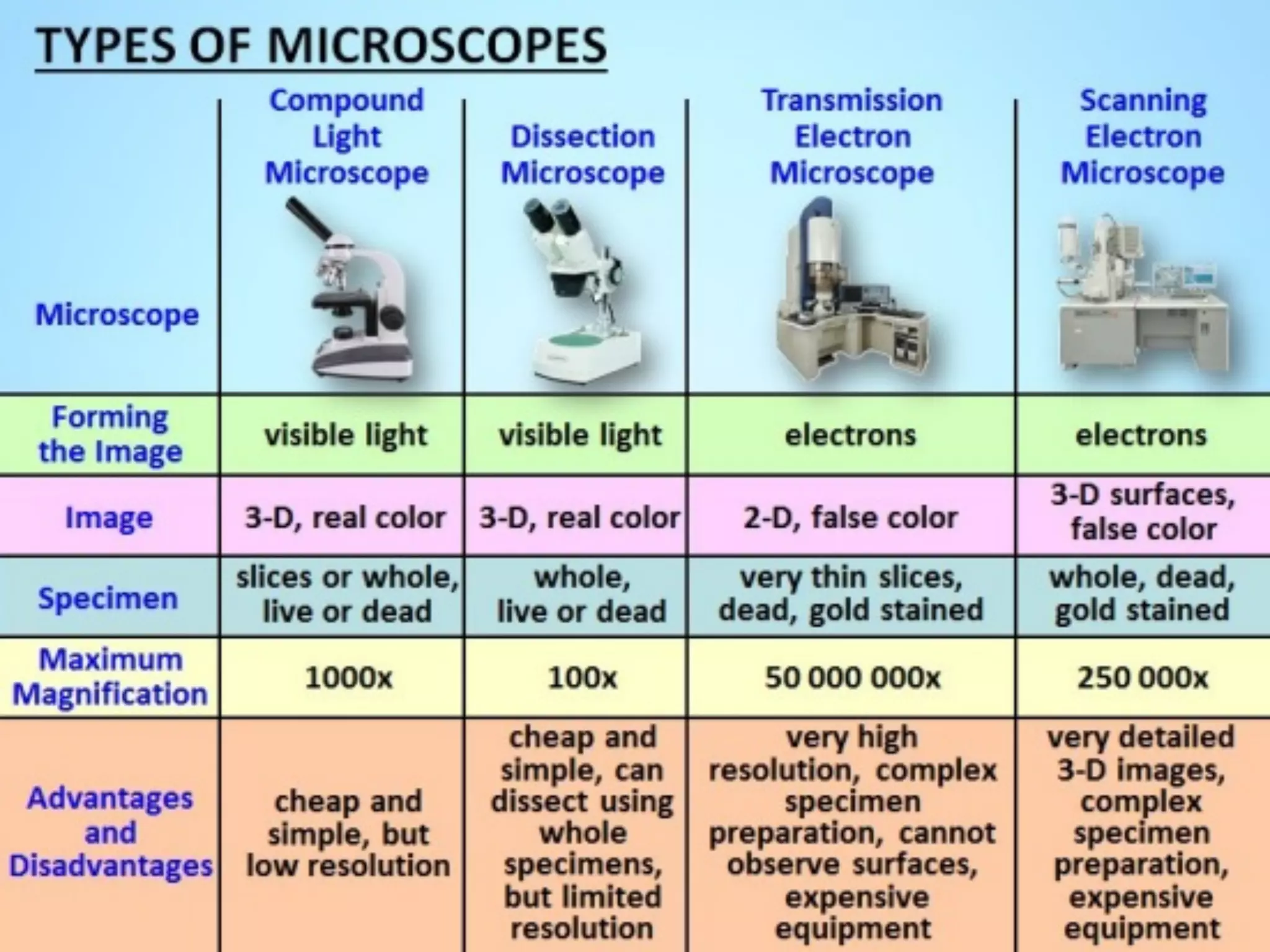
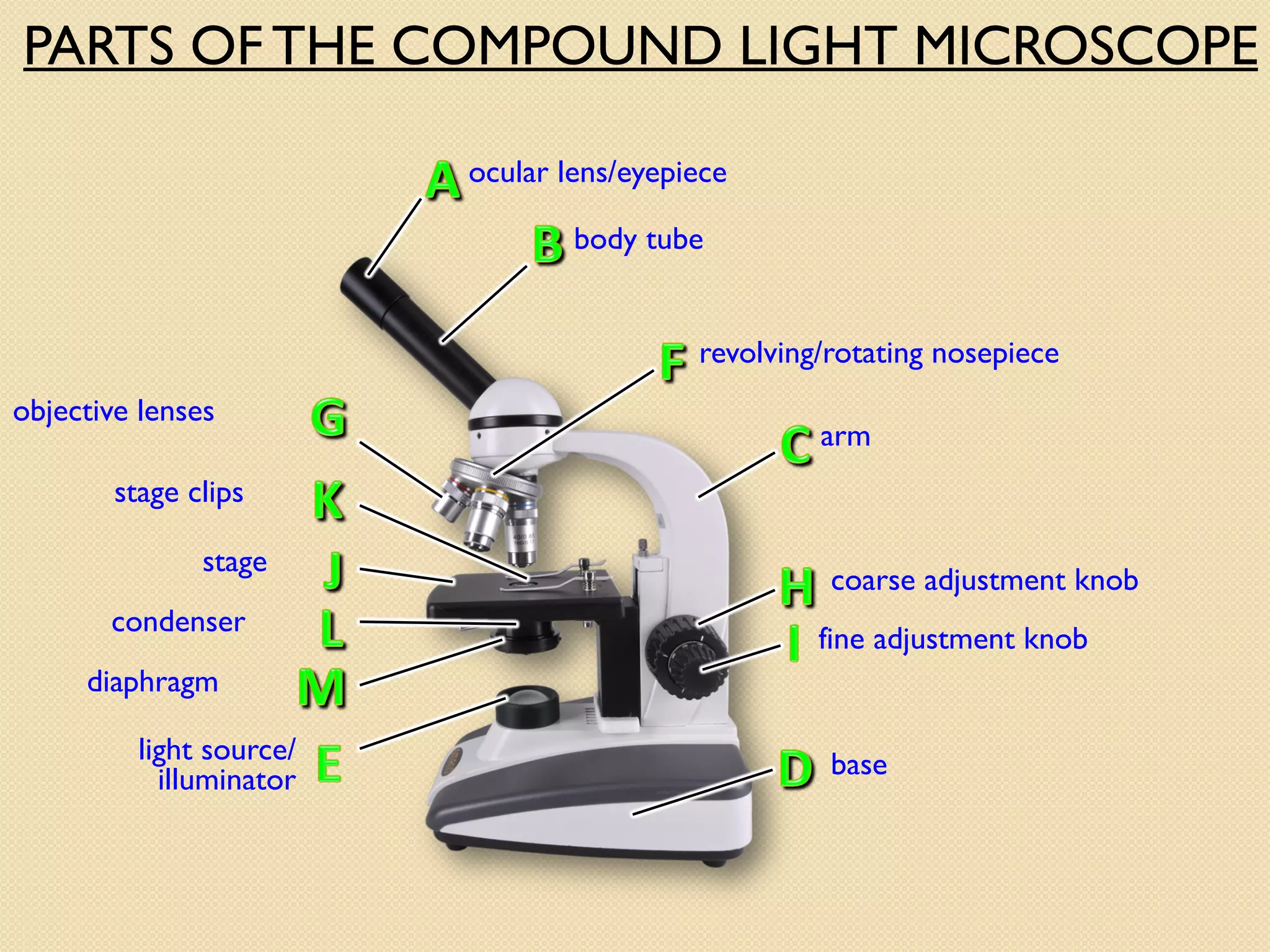
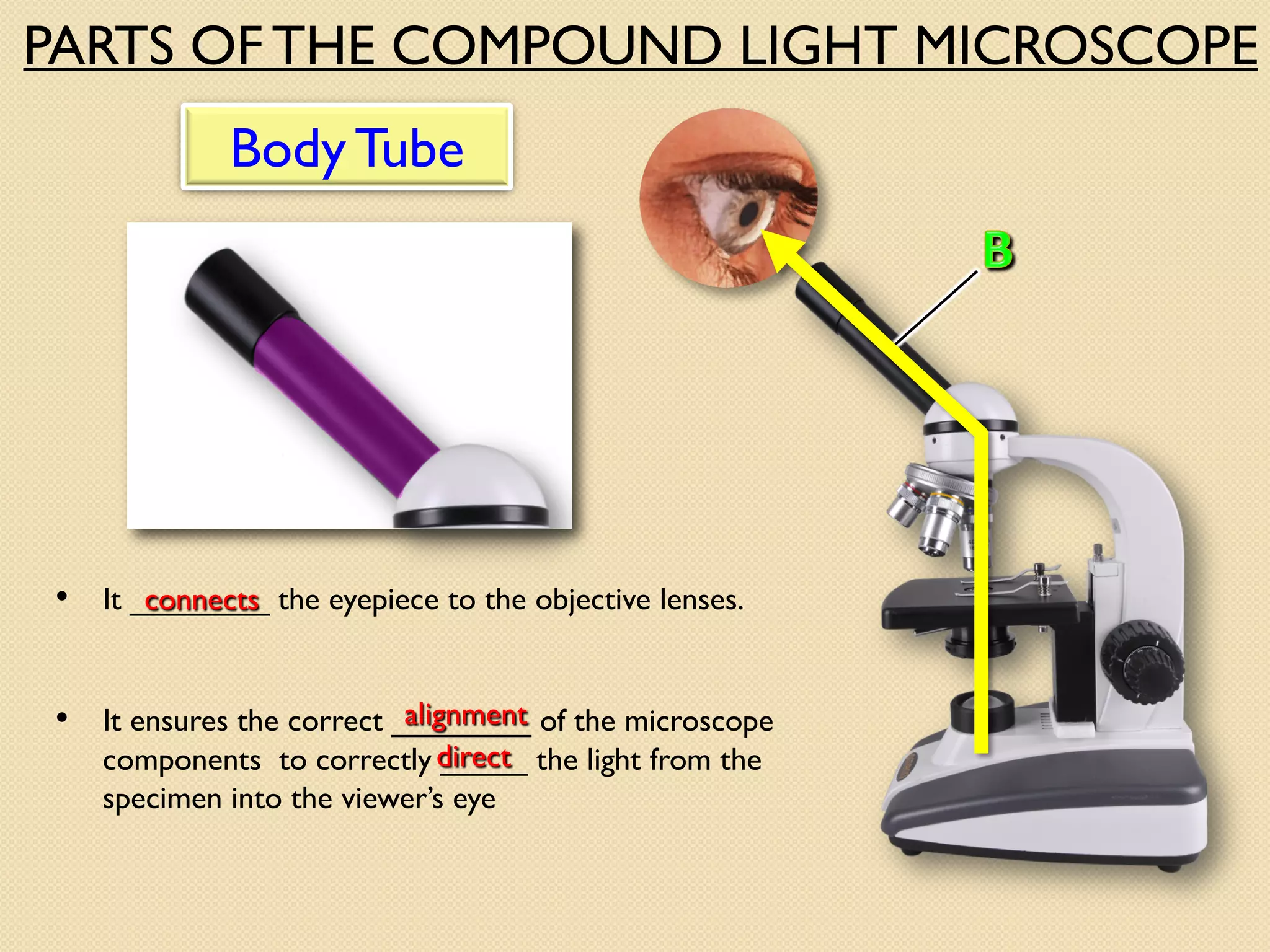
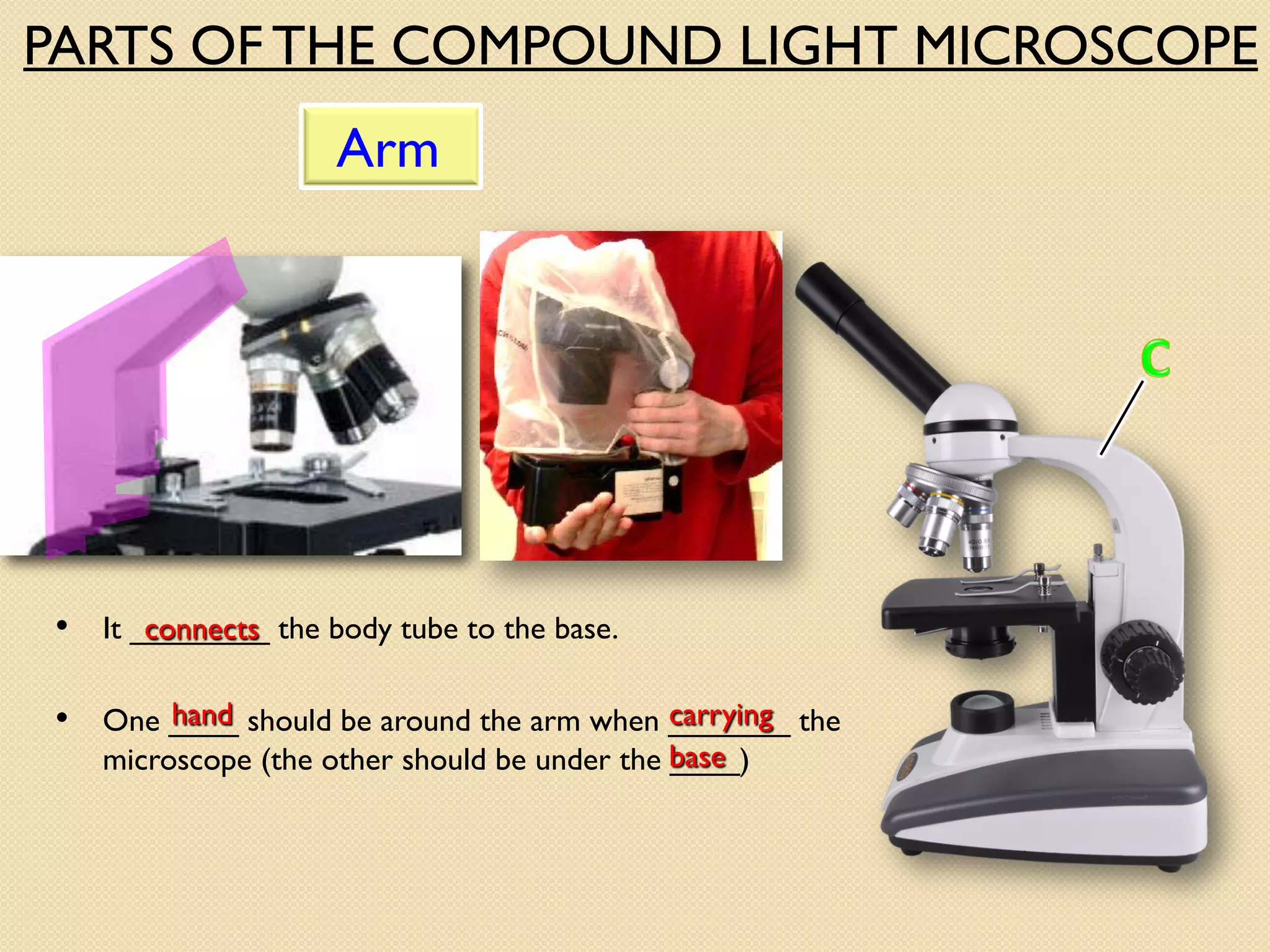
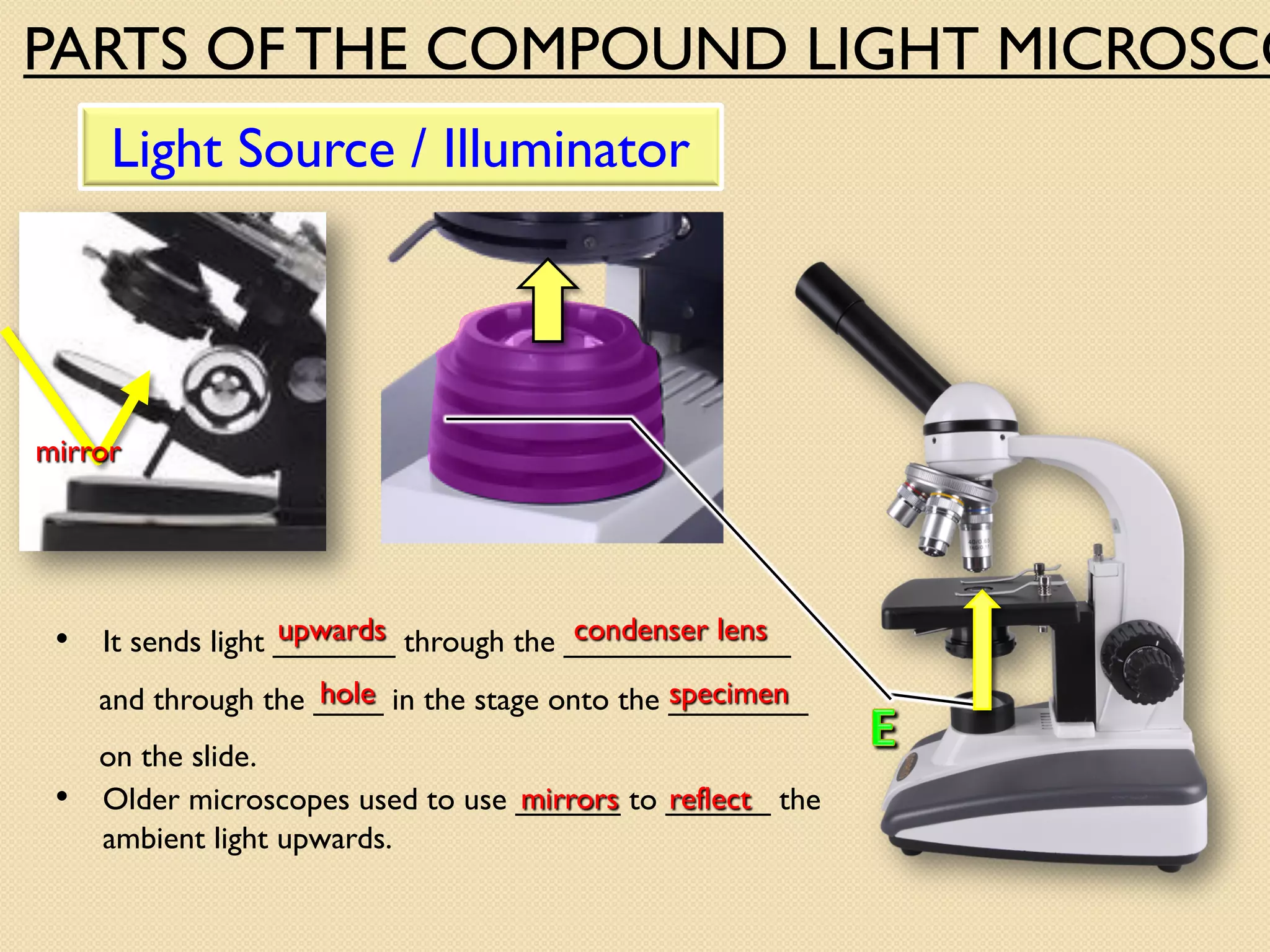
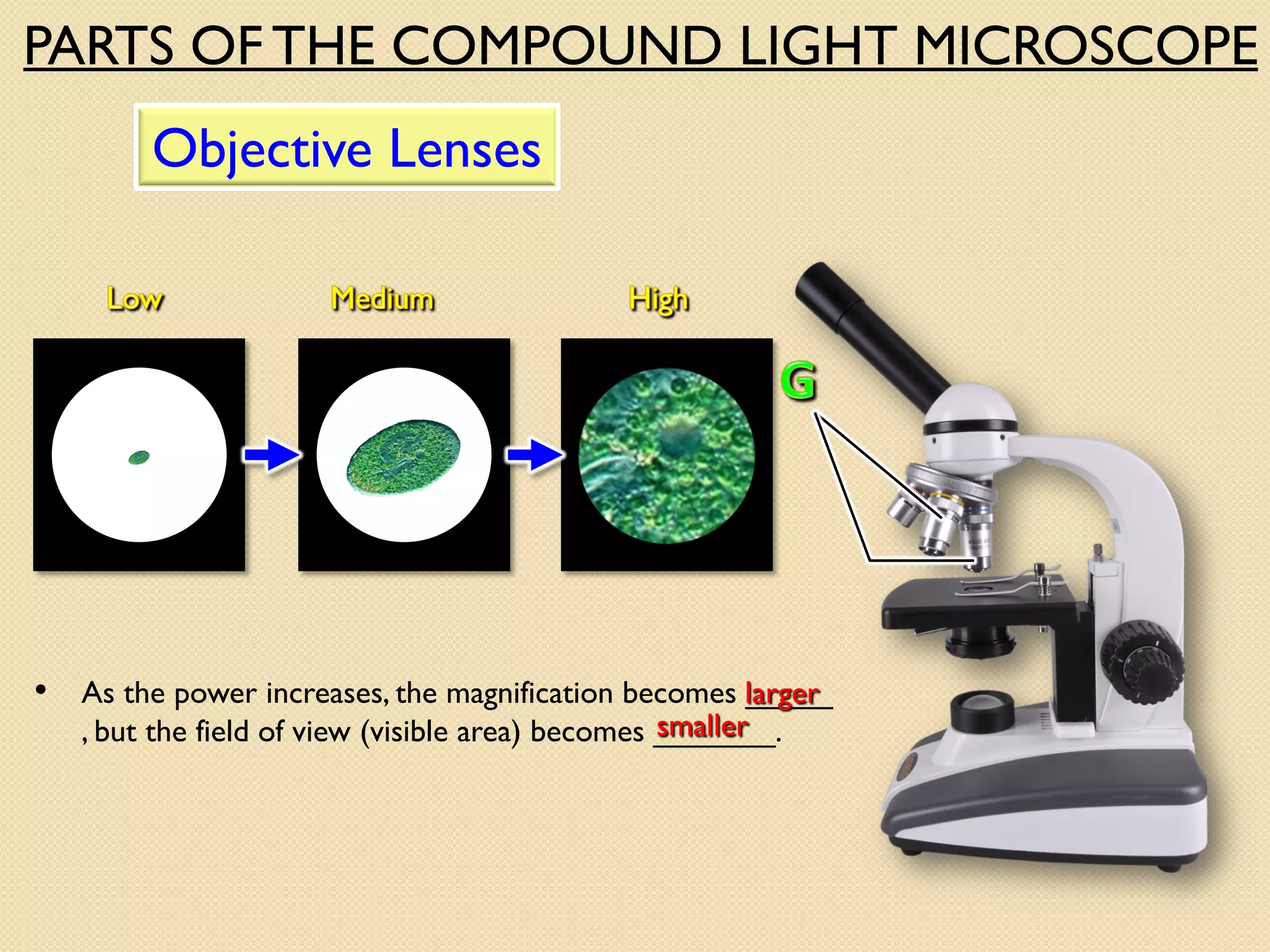
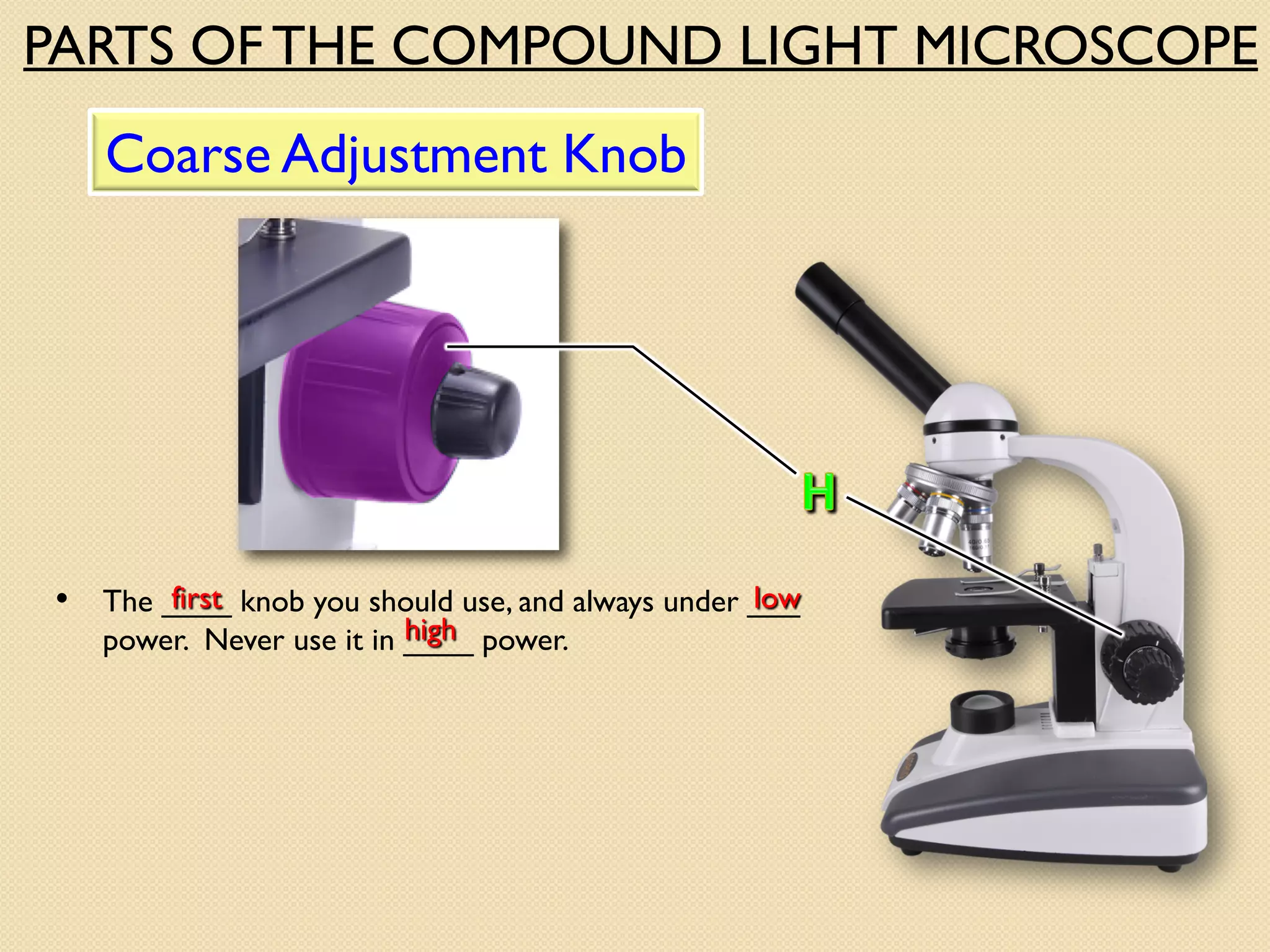
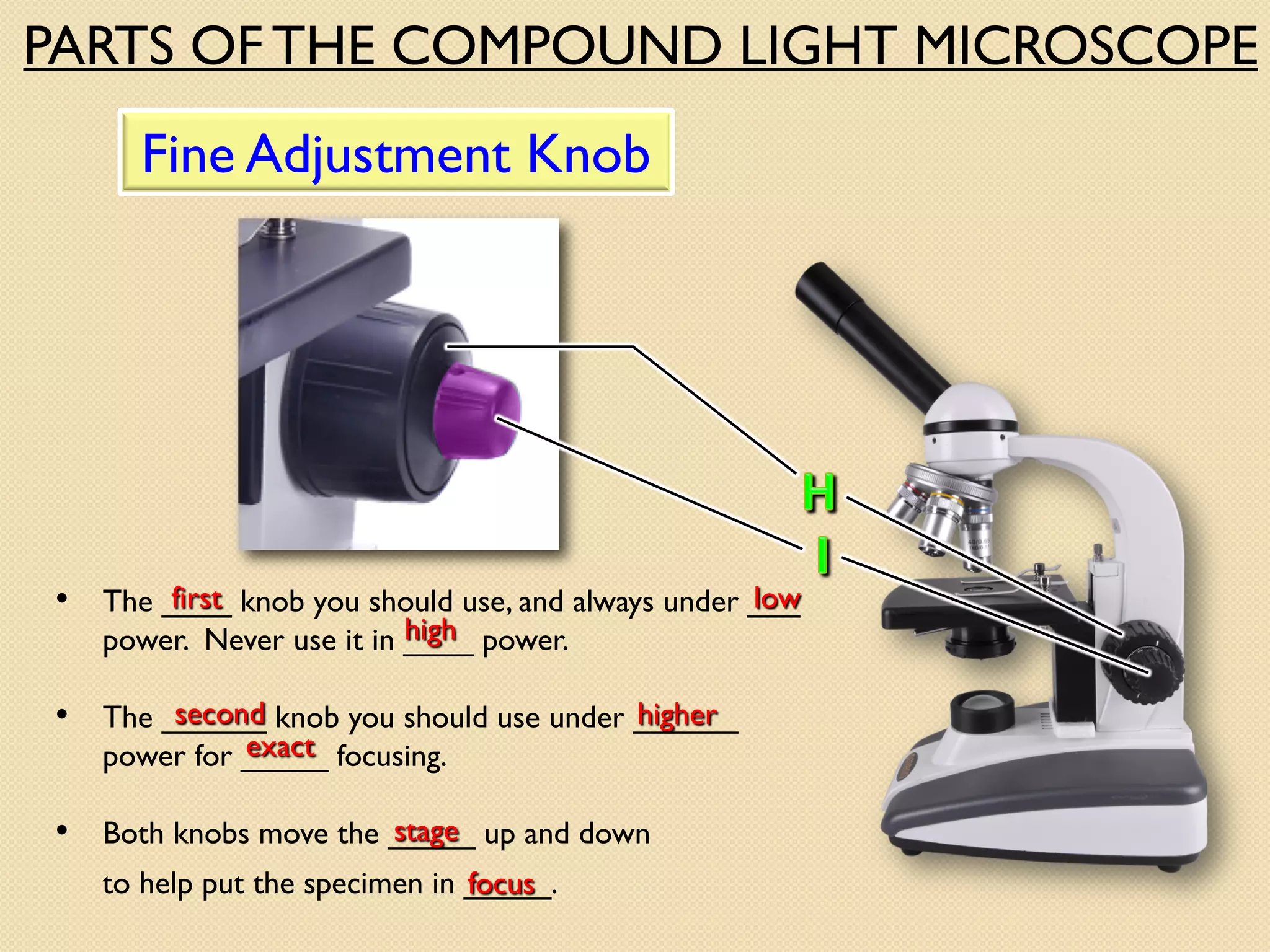
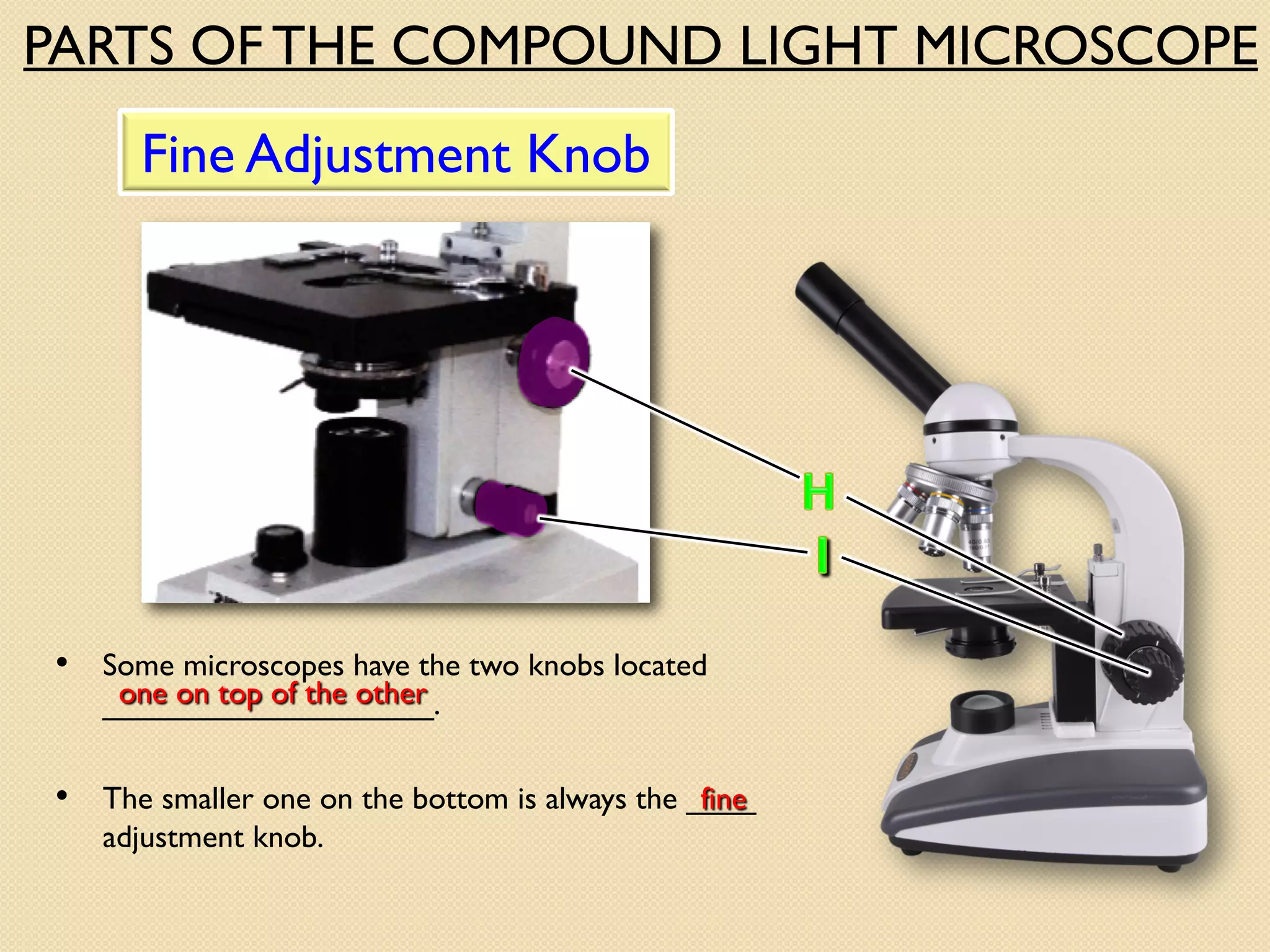
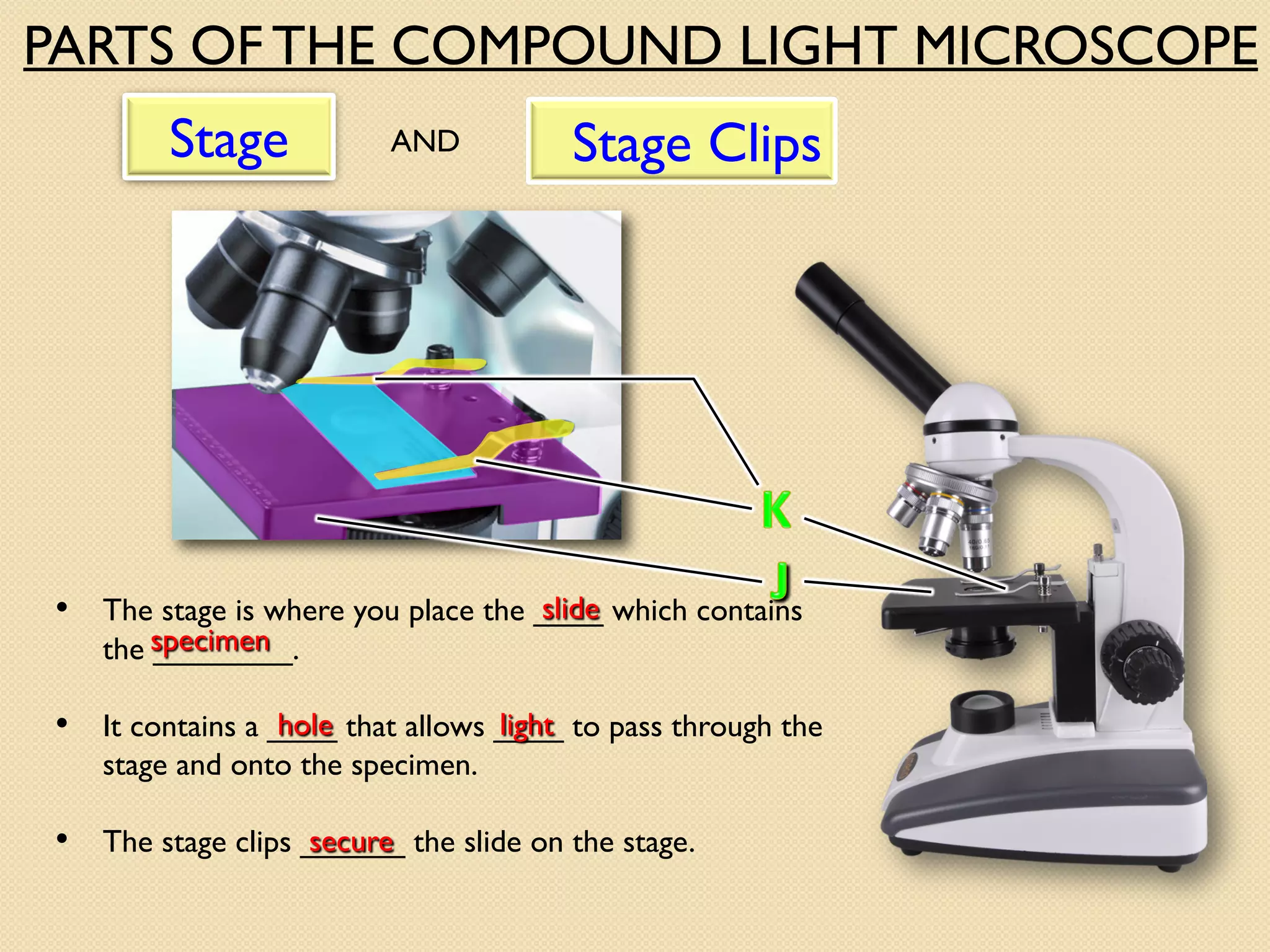
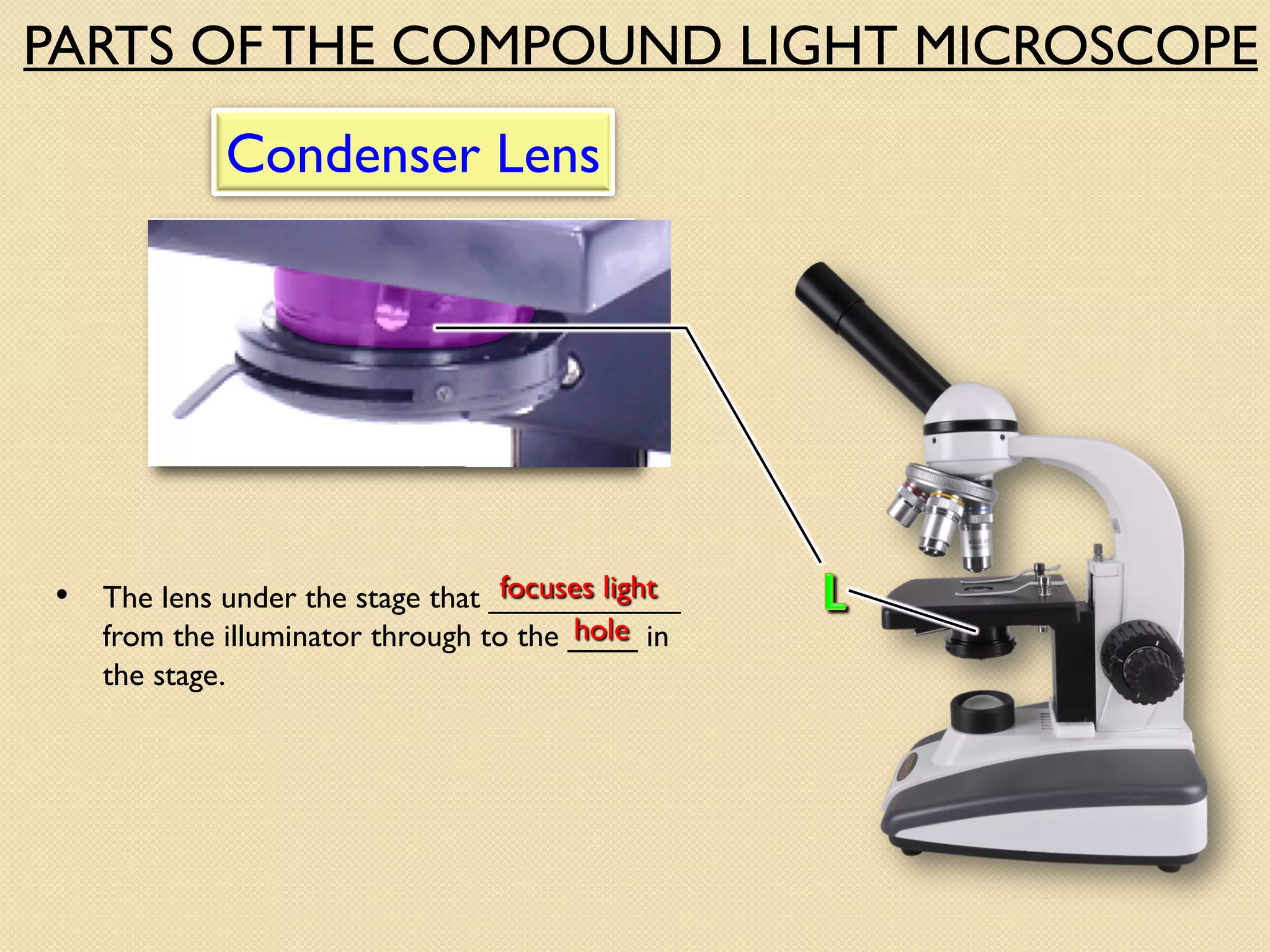
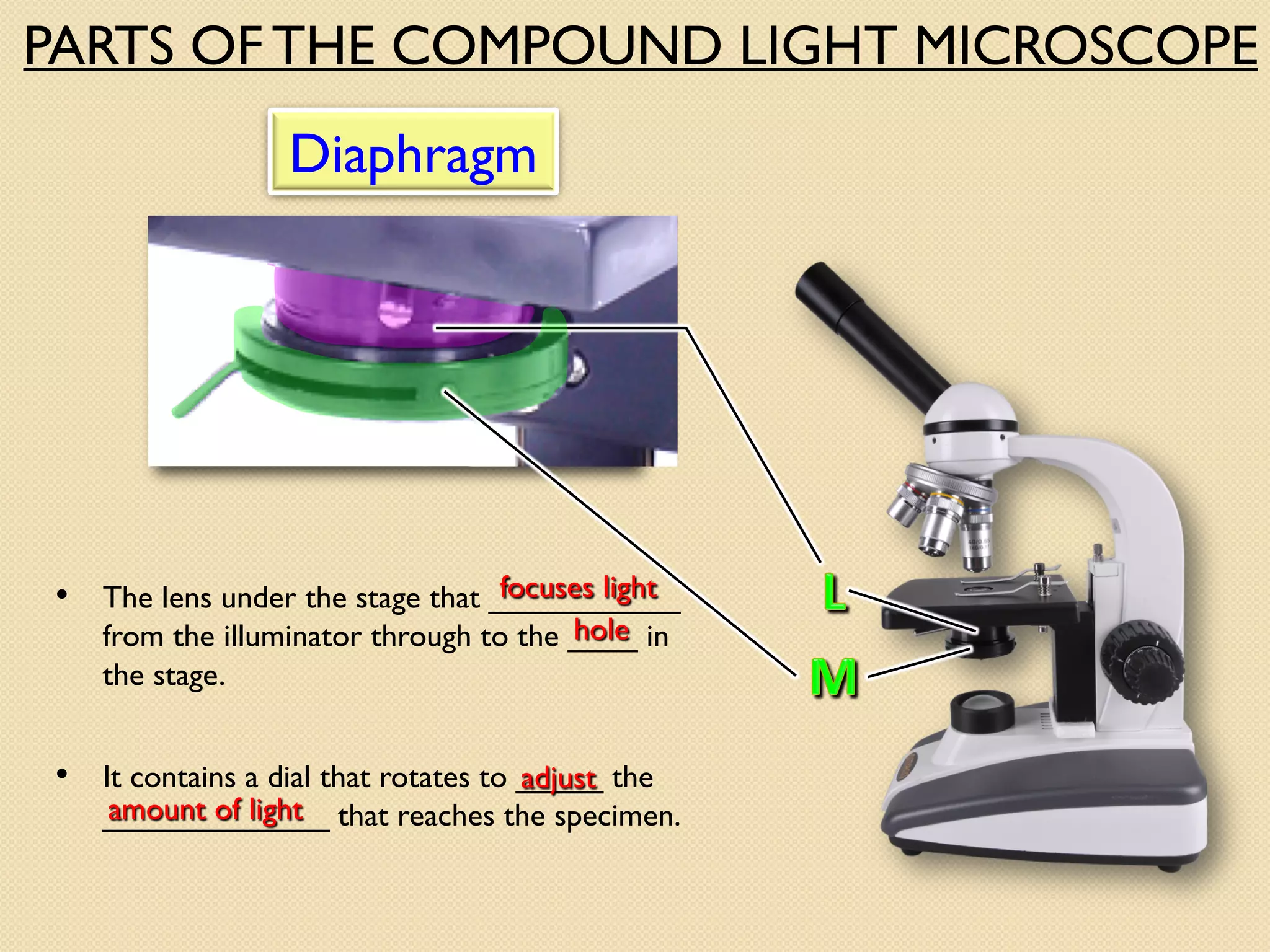
Microscopes are instruments that magnify small objects so they can be seen more clearly. There are two main types: simple microscopes, which use a single lens, and compound microscopes, which use multiple lenses to provide higher magnification. Compound microscopes have various parts, including objective lenses of different magnifications, eyepieces, a stage to hold samples, and focus knobs to adjust the image sharpness. They work by using lenses to bend light from the sample through the microscope's optical system and into the user's eye.