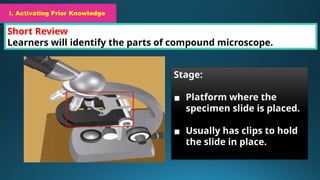
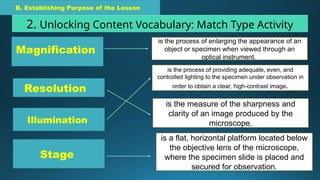
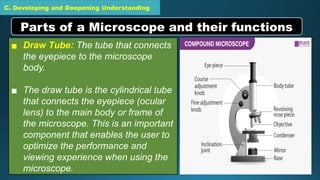
The document outlines a science lesson plan focused on exploring the compound microscope, including objectives for students to identify its parts and demonstrate proper handling. Key components of the microscope, such as eyepiece, objective lenses, and diaphragm are described, along with techniques for preparing wet mount slides and adjusting focus. The lesson also emphasizes reflection on learning and evaluation through labeling tasks.