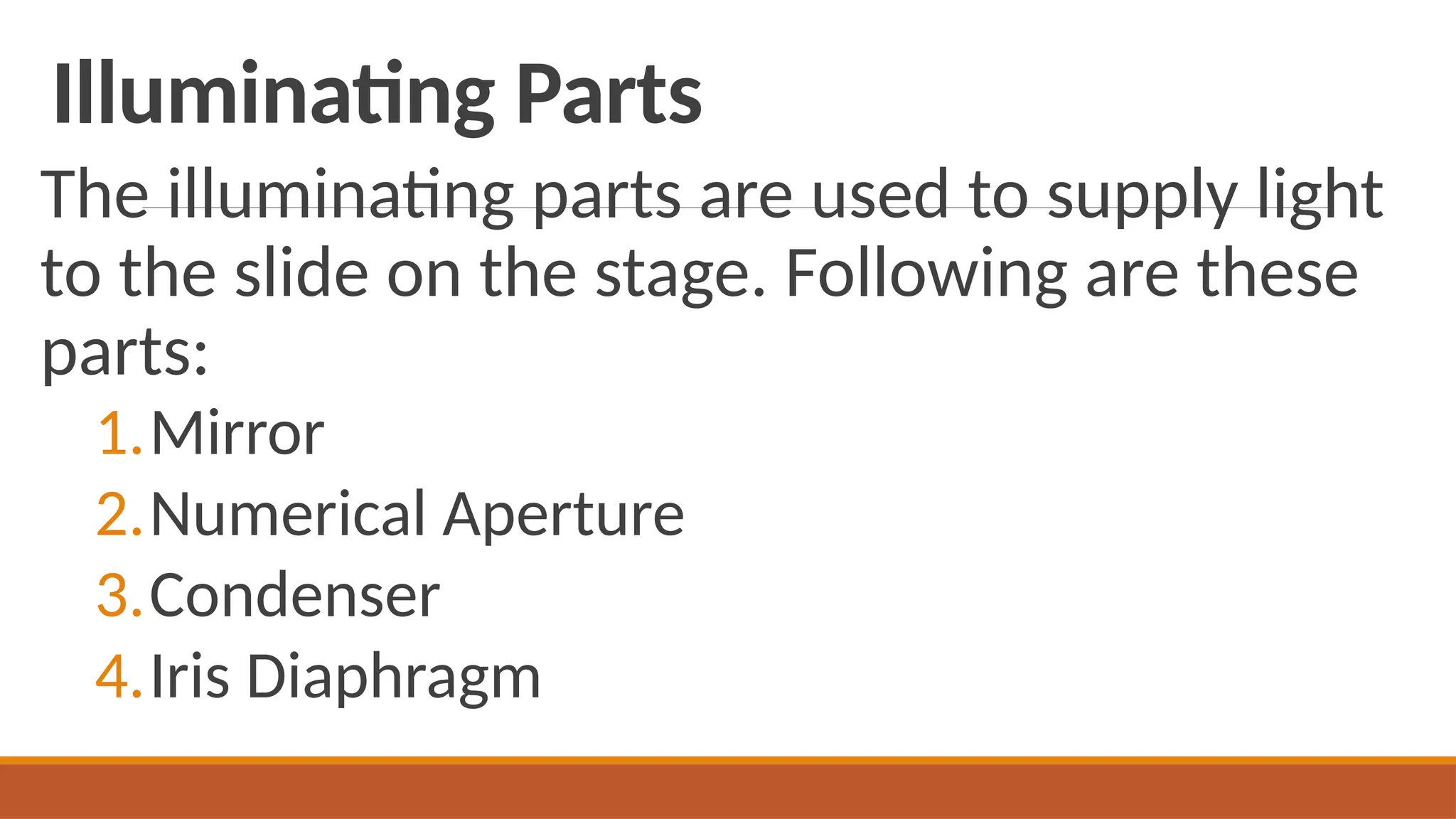
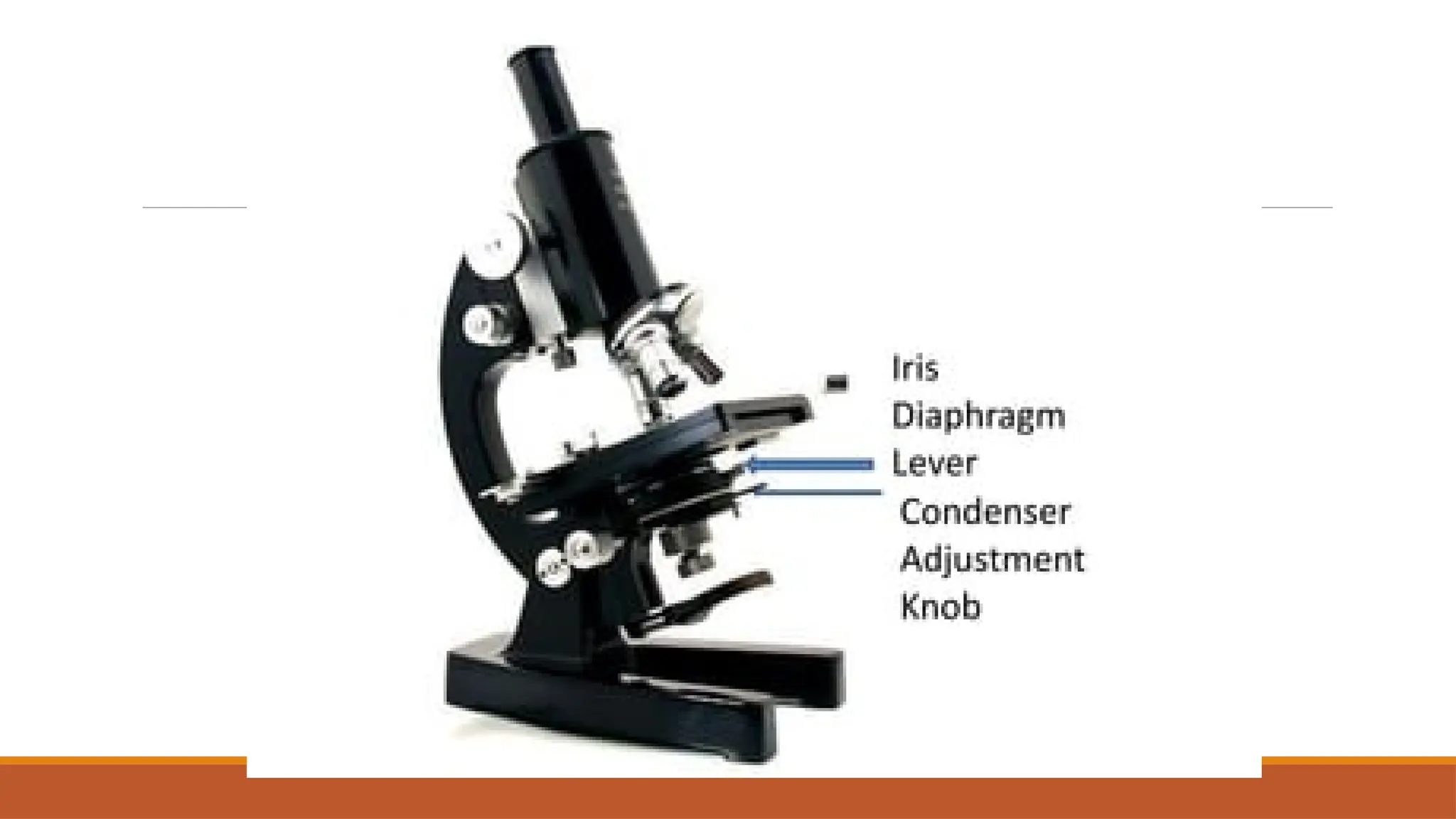
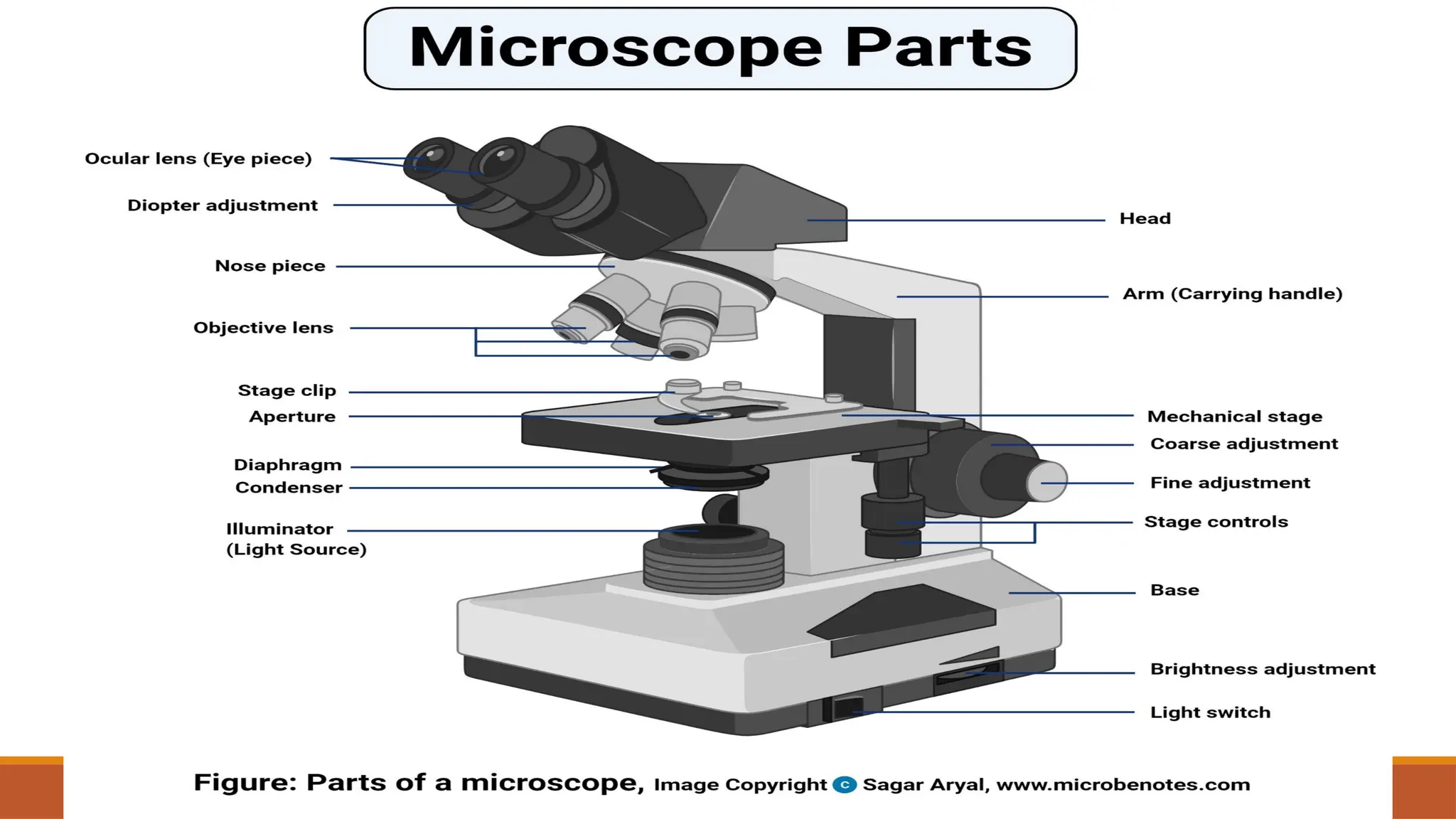
Light microscopy is a general term used for any type of microscopy where light is being transmitted from a source which is on the opposite side of the sample, to the objective lens. Generally, the light is passed through a condenser to focus it on the sample to have maximum brightness. After the light has passed through the sample, it goes through the objective lens to magnify the image of the sample & then to the oculars, where the enlarged image is viewed.
Image
Microscope
Light microscopic techniques have significantly developed over the past 20 years & now provide an indispensable tool to study molecular events at subcellular level in order to gain temporal & spatial information at high resolution. To achieve optimal results, it is essential to carefully plan & carry out microscopy-based experiments, which requires the understanding of at least the basics of cell biology, sample preparation & fluorescence light microscopy.