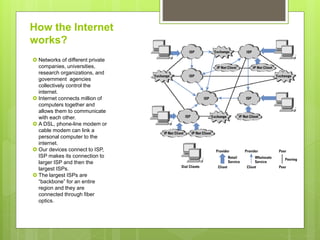
The document discusses the key concepts and components of how the internet works. It explains that the internet connects millions of private networks run by companies, universities, and government agencies. It also describes some of the main ways people access the internet, such as through a modem, local area network, or high-speed connection. Additionally, it outlines several common internet tools and protocols used for communication online, including web servers, clients, browsers, and IP addressing.