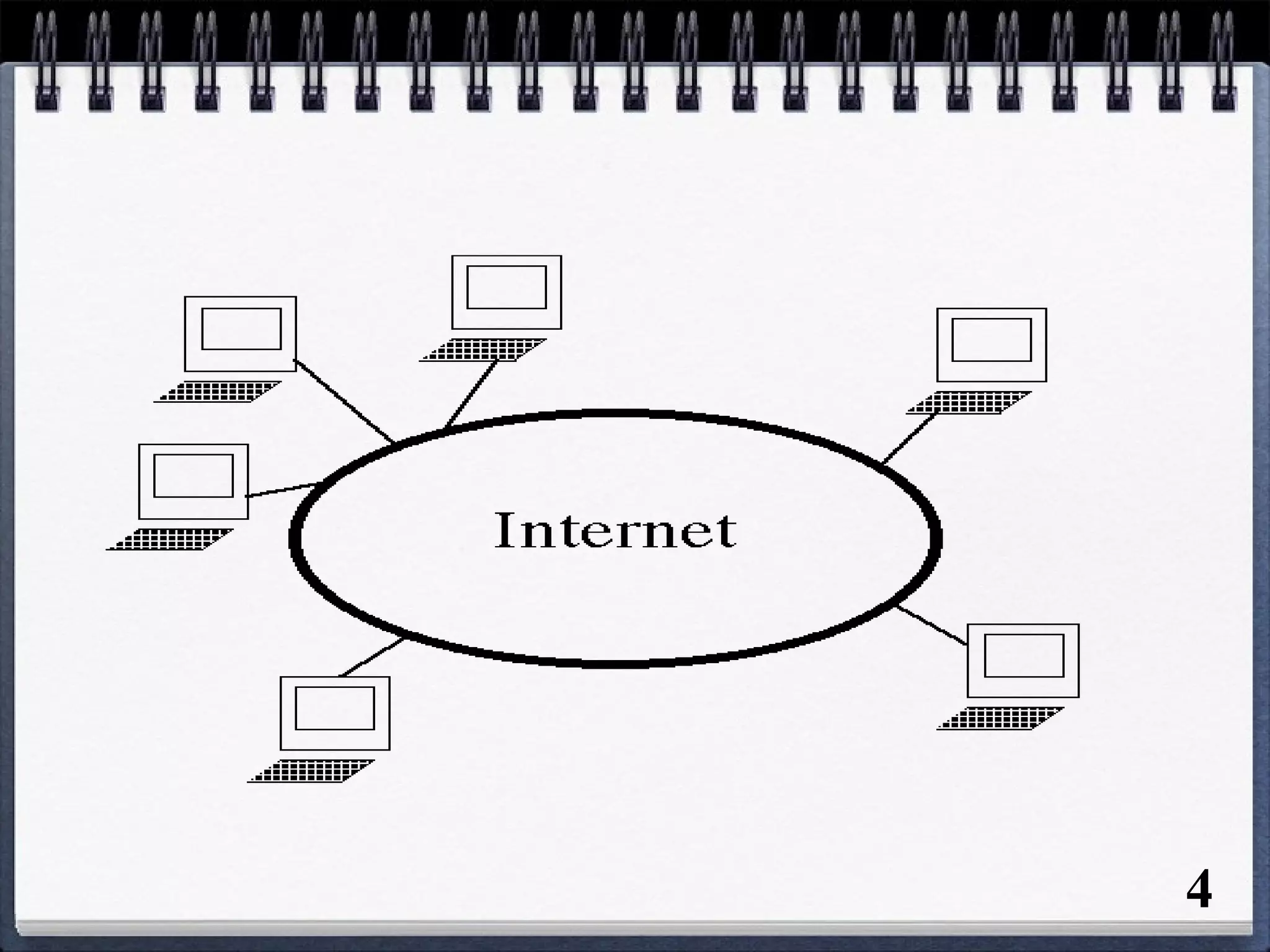
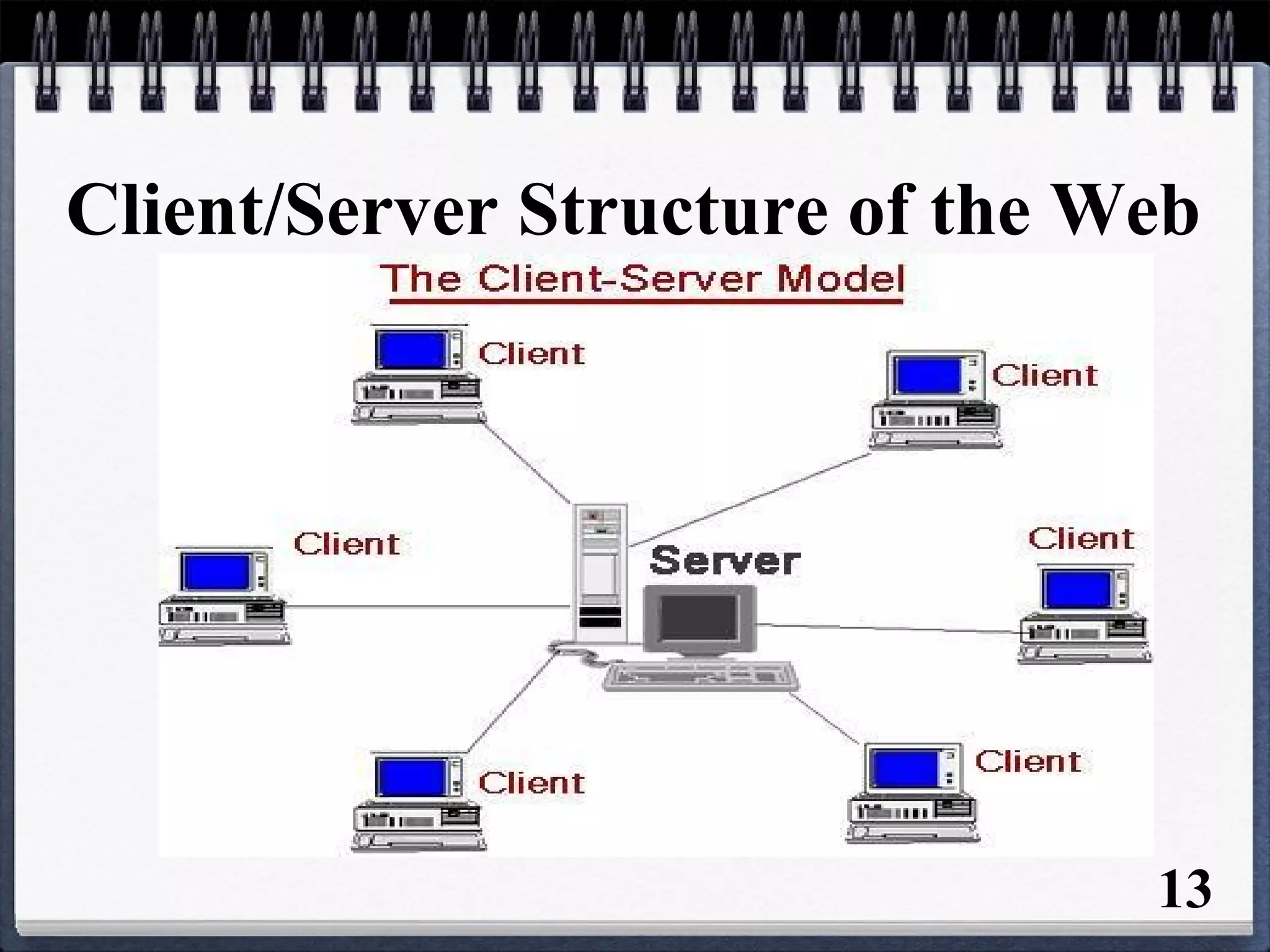
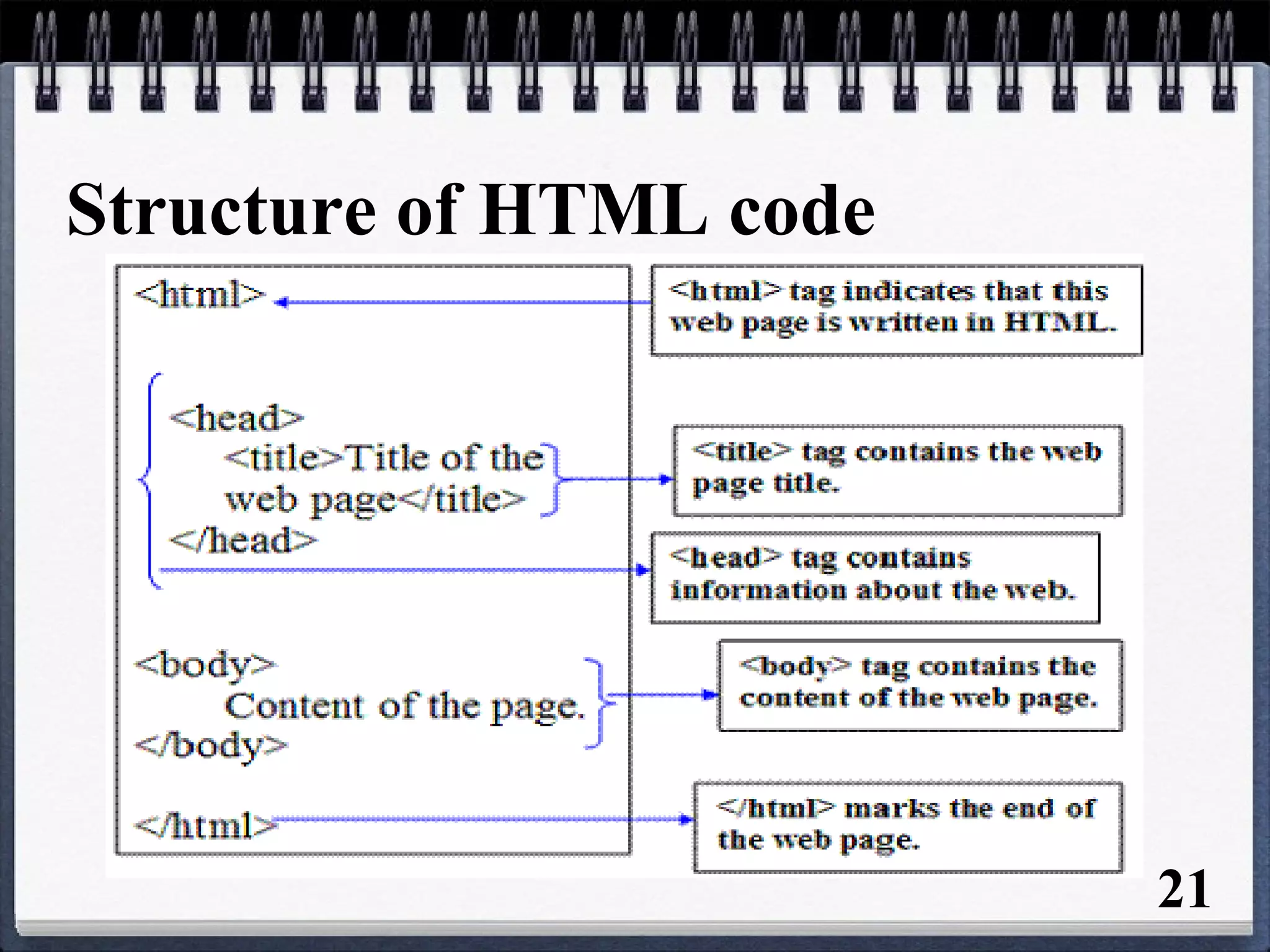
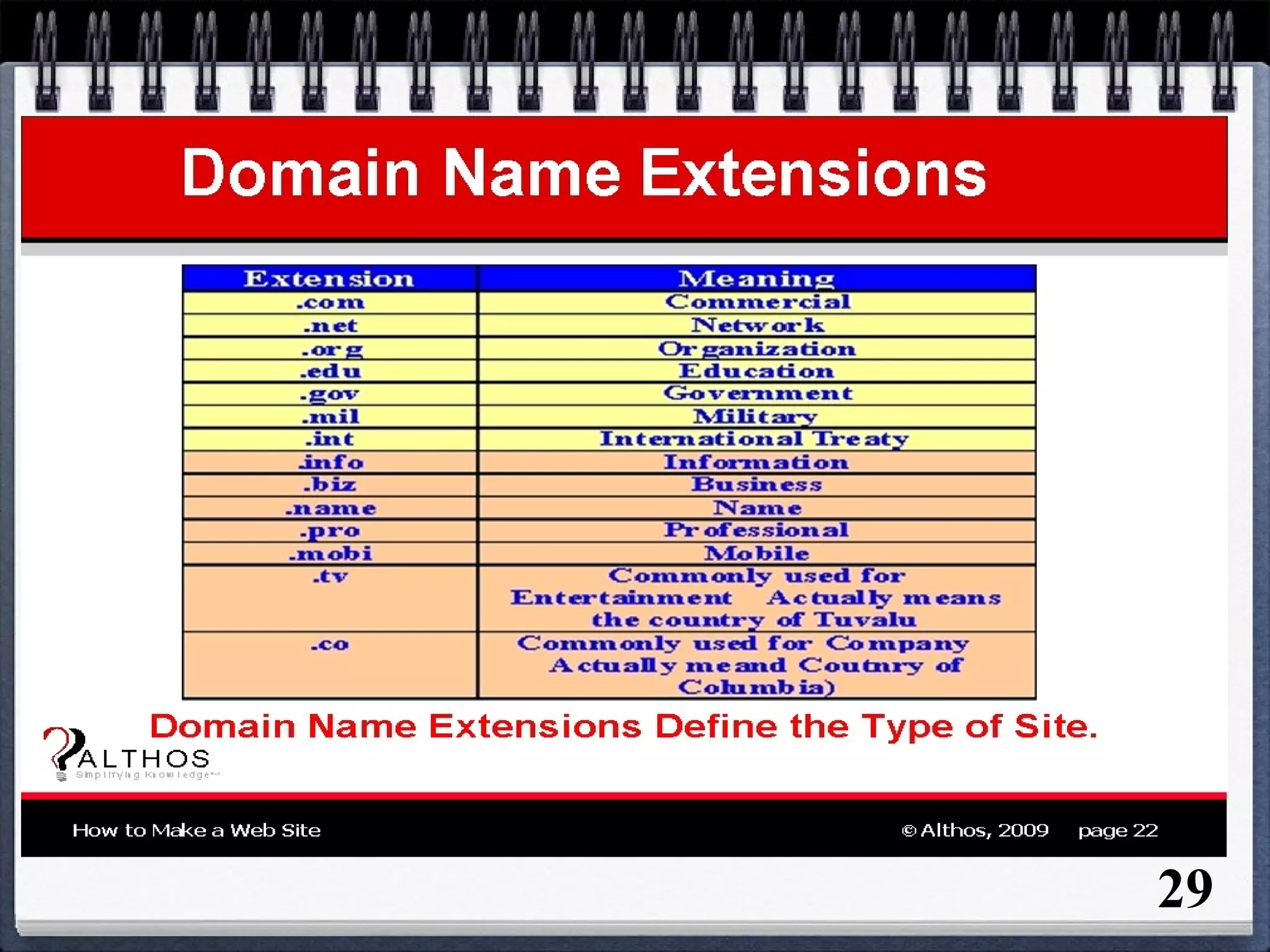
The document provides an overview of the history and development of the Internet and World Wide Web (WWW). It discusses how the Internet originated in the 1960s and evolved with developments like email, file transfer protocol, and domain name servers. It then explains how Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web in 1989 while working at CERN. The document defines key terms related to the Internet and WWW like websites, web servers, HTML, URLs, IP addresses, browsers, and protocols. It provides examples and diagrams to illustrate concepts like client-server structure, domain name systems, and URL structure.