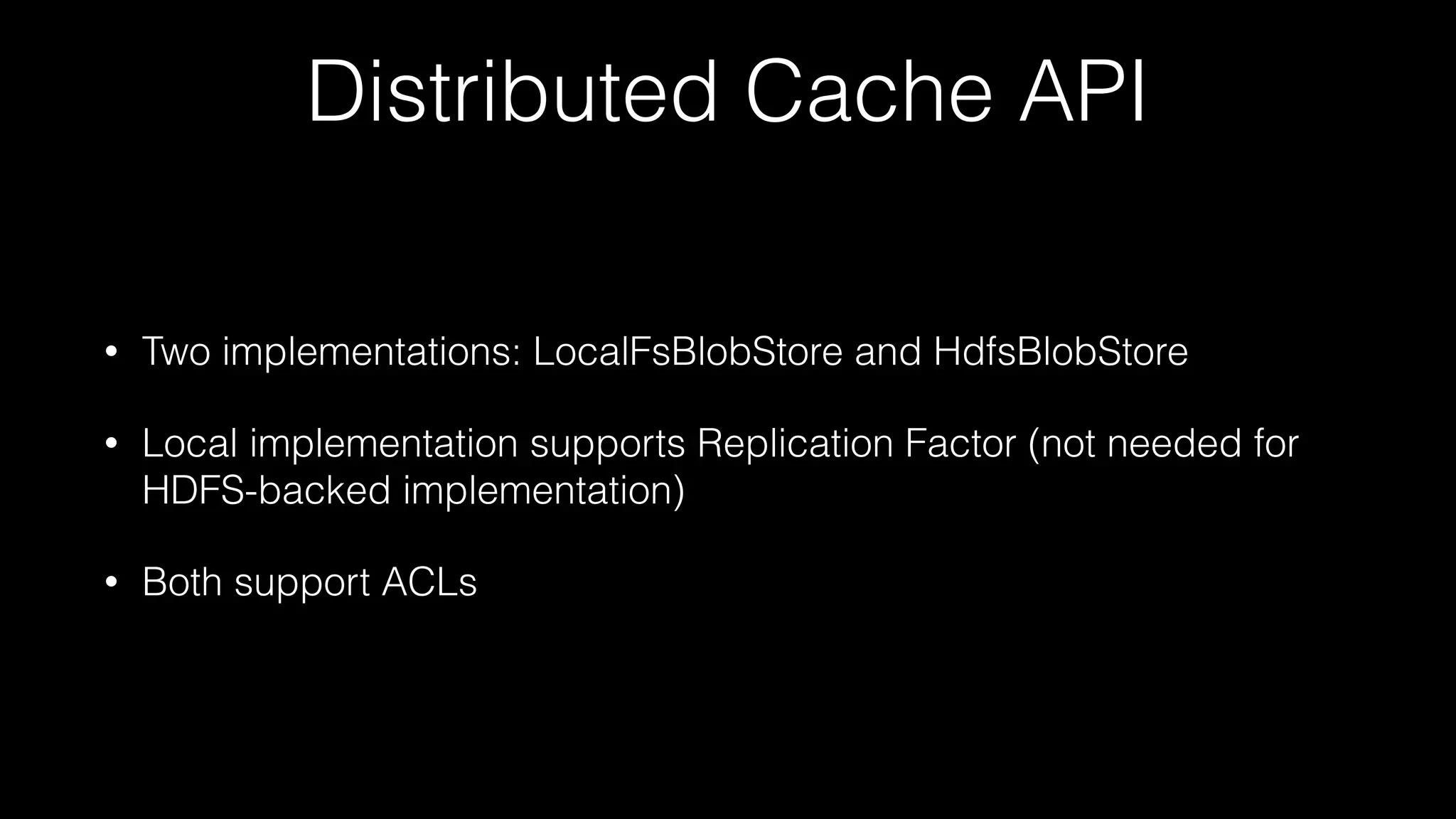
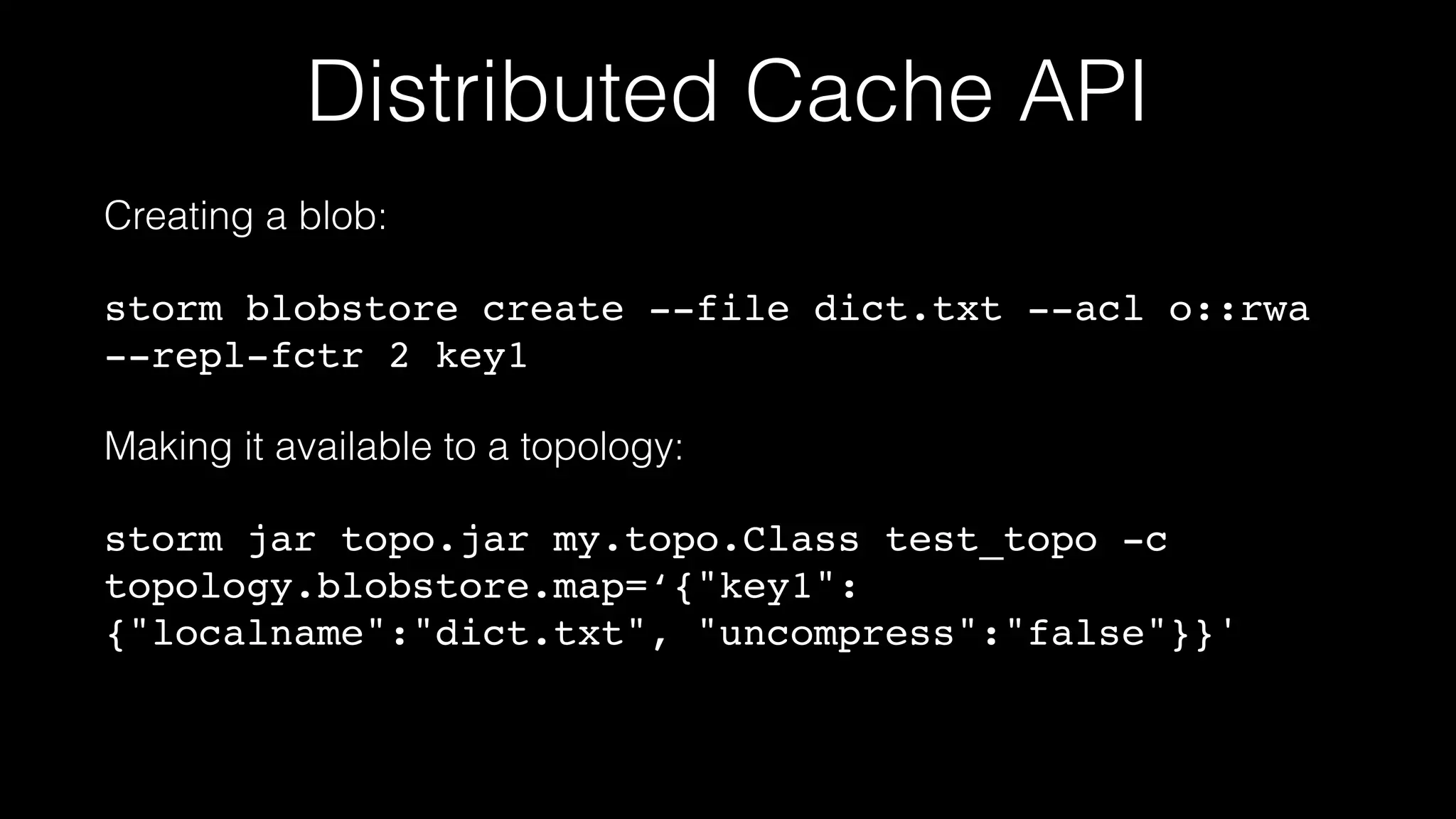
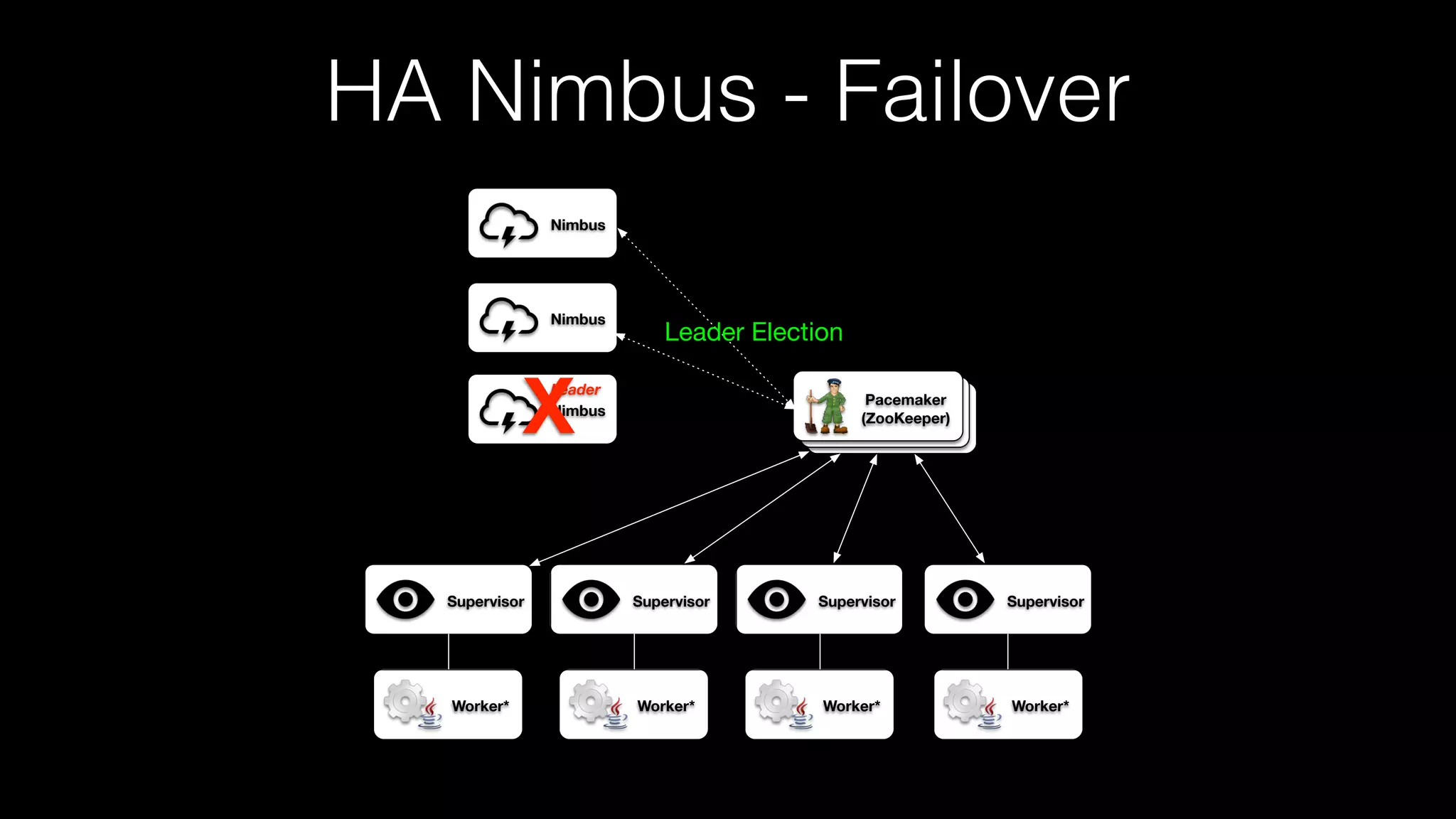
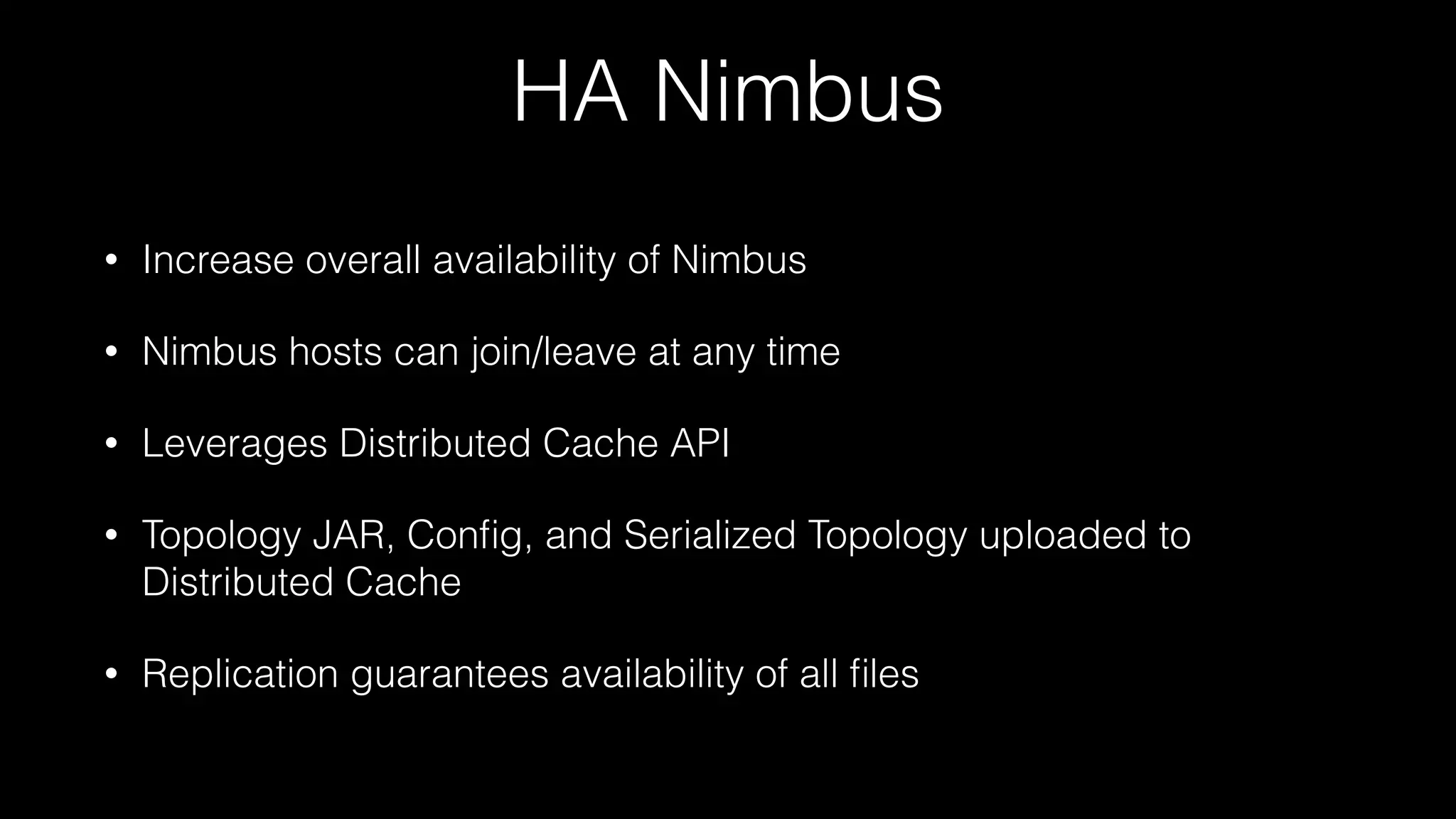
This document summarizes a presentation about the future of Apache Storm given at Hadoop Summit 2016. It discusses recent releases of Storm including 0.9.x, 0.10.x, and 1.0 which focused on areas like enterprise readiness, security, and performance improvements. It also outlines new features in Storm 1.0 like Pacemaker replacing Zookeeper, the distributed cache API, and high availability Nimbus. The presentation concludes by discussing planned improvements in Storm 1.1 like enhanced metrics and looks ahead to the future of Storm including migrating from Clojure to Java and integrating streaming SQL.




















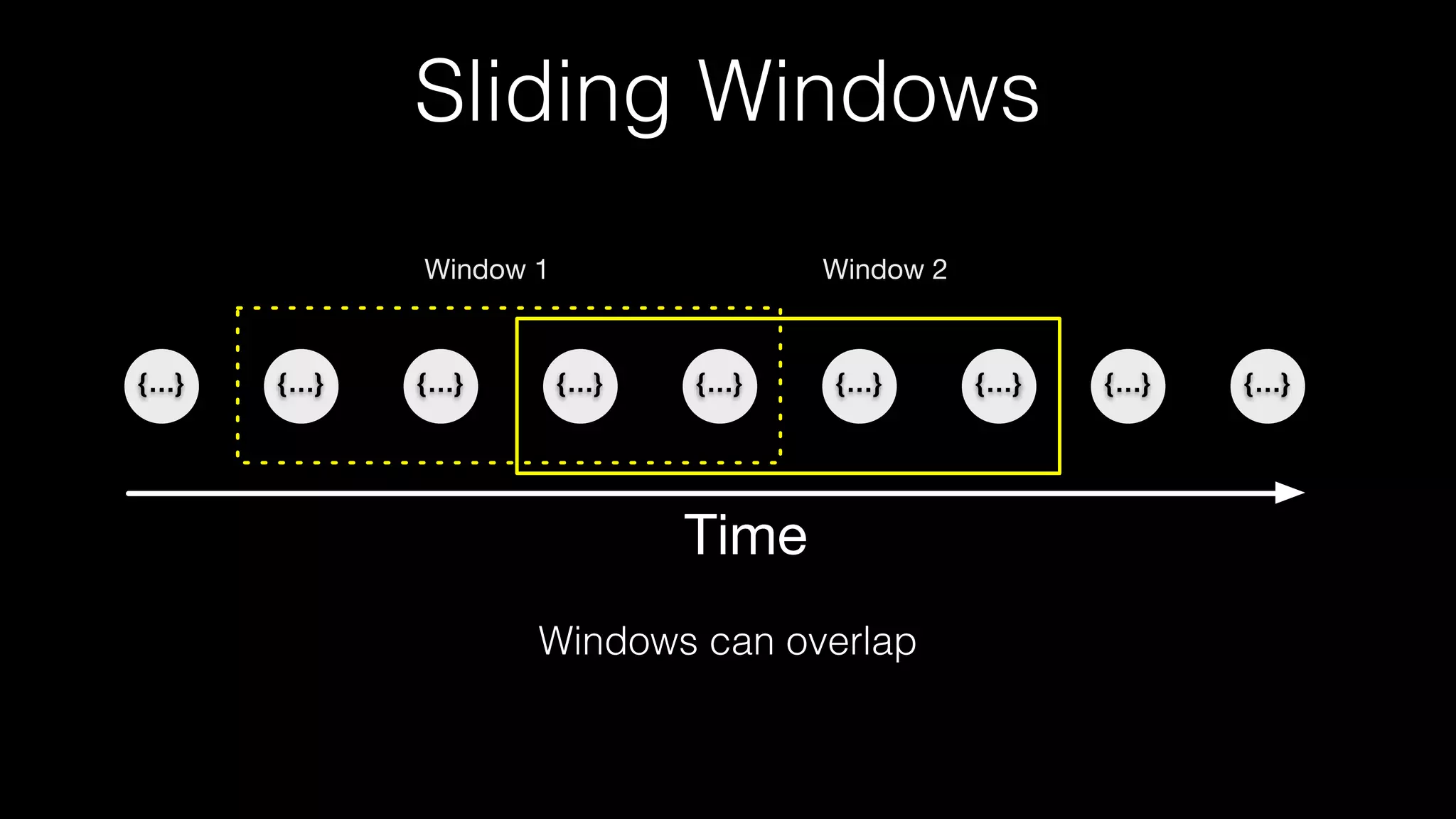








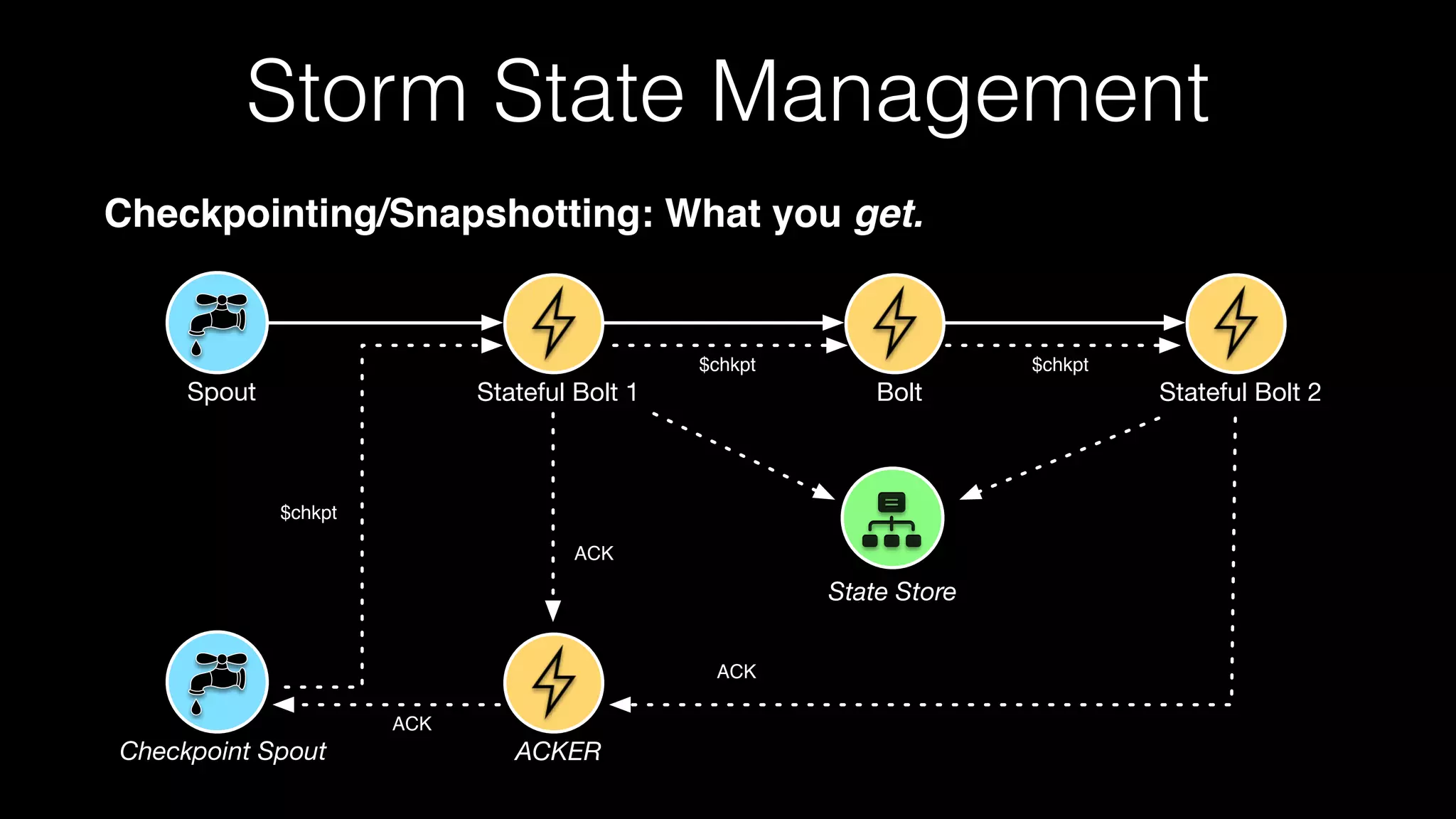
![Checkpointing/Snapshotting
• Asynchronous Barrier Snapshotting (ABS) algorithm [1]
• Chandy-Lamport Algorithm [2]
[1] http://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.08603v1.pdf
[2] http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/people/lamport/pubs/chandy.pdf
State Management](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/june301130hortonworksgoetz-160711181546/75/The-Future-of-Apache-Storm-34-2048.jpg)











![Dynamic Log Levels
Via Storm CLI:
./bin/storm set_log_level [topology name] -l
[logger_name]=[LEVEL]:[TIMEOUT]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/june301130hortonworksgoetz-160711181546/75/The-Future-of-Apache-Storm-48-2048.jpg)























