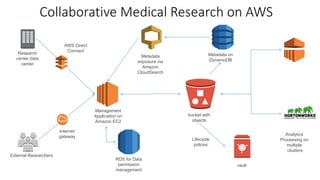
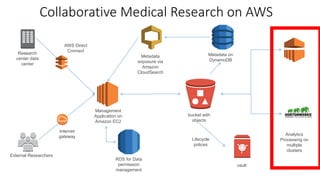
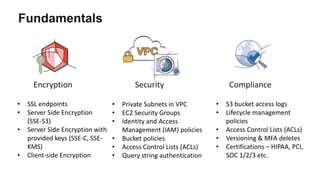
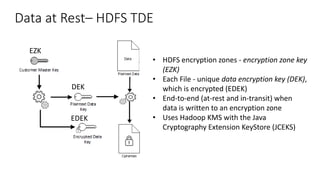
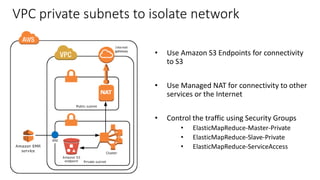
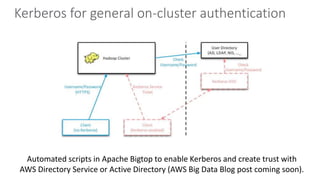
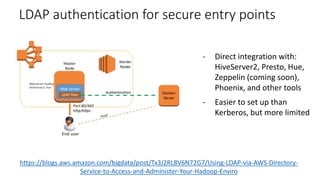
This document discusses HIPAA compliance in the cloud and using Amazon Web Services (AWS) for collaborative medical research. It provides an overview of how AWS services like S3, EC2, DynamoDB, and EMR can be used in a HIPAA-compliant manner. It also discusses challenges of ensuring HIPAA compliance for Hadoop and how tools like encryption, access controls, monitoring, and auditing help address those challenges. The document concludes that security is critical, AWS has tools to make HIPAA compliance easier, and users can move fast while staying safe on AWS.