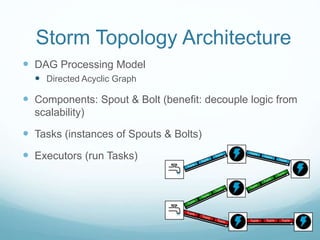
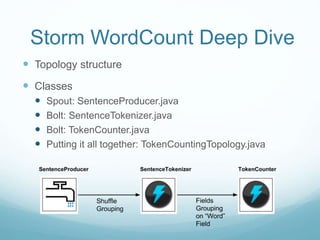
The document provides an introduction to Apache Storm for streaming distributed processing, highlighting its capabilities in real-time data analytics compared to traditional batch processing systems. It includes a detailed overview of Storm's architecture, components, and a practical 'wordcount' demonstration, illustrating how to set it up and use it effectively. Additionally, it discusses various use cases and patterns for Storm in the context of real-time applications.