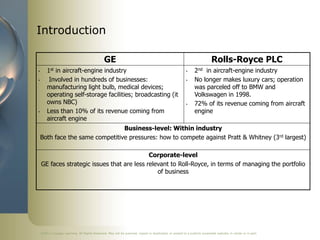
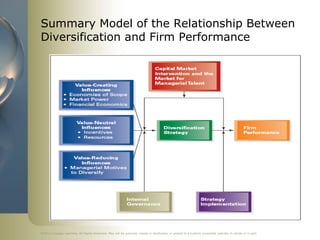
The document summarizes a chapter on corporate-level strategy from a strategic management textbook. It discusses seven key topics: (1) the definition of corporate-level strategy and different levels of diversification, (2) the three primary reasons firms diversify, (3) how related diversification can create value, (4) how unrelated diversification can also create value, (5) incentives and resources that encourage value-neutral diversification, (6) management motives that can encourage overdiversification and reduce value, and (7) a summary model of the relationship between diversification and firm performance.