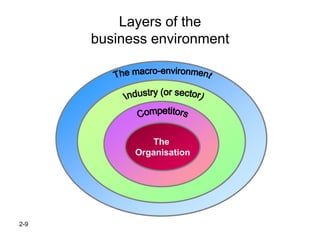
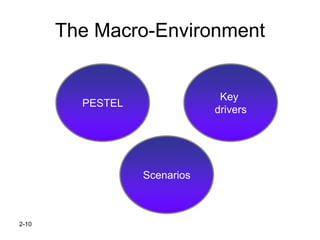
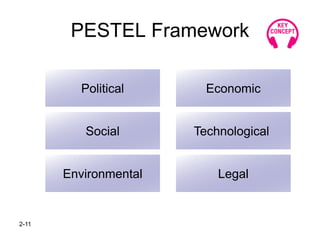
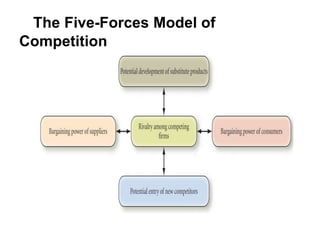
The document discusses strategic management concepts, focusing on the external environment's impact on organizations through frameworks like PESTEL and the five forces analysis. It emphasizes the importance of macro-environment evaluation, scenario planning, and understanding demographic, economic, political, sociocultural, and technological influences on industry dynamics. Additionally, it examines barriers to entry, competitive rivalry, and the significance of strategic groups in market segmentation for effective strategy formulation.