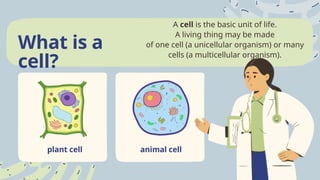
Cells are the basic units of life, with unicellular organisms consisting of one cell and multicellular organisms made up of many cells. The term 'cell' was coined by Robert Hooke in 1665, and the cell theory was later developed by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden, stating that all living organisms are composed of cells which arise from pre-existing cells. The document provides a timeline of significant discoveries related to cell biology, detailing the evolution of cell understanding from 1665 to 2000.