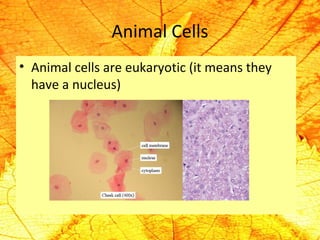
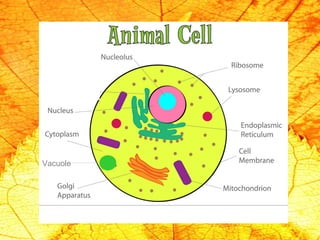
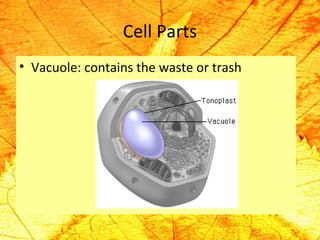
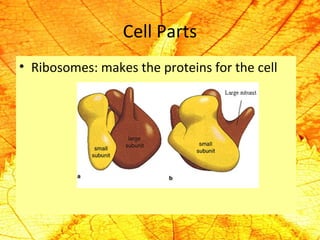
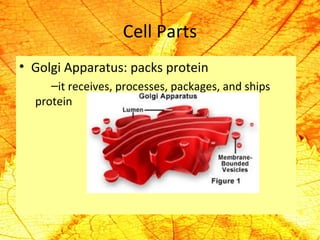
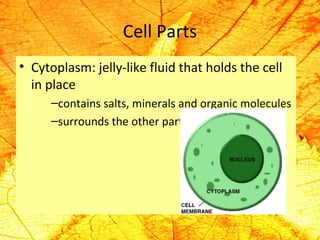
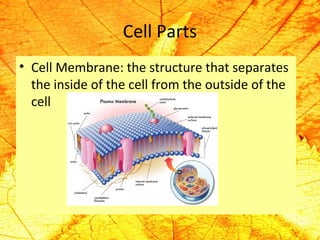
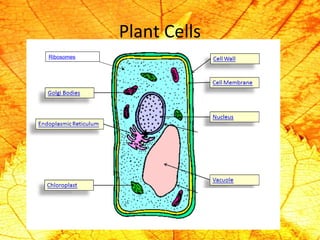
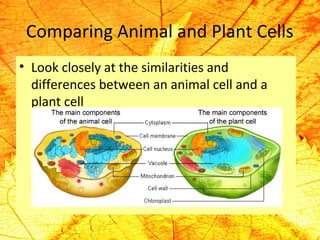
Cells are the basic building blocks of living organisms. They are too small to see with the naked eye and need to be viewed with a microscope. The main purpose of cells is to organize the different parts of an organism and hold the biological equipment necessary to sustain life. There are many types of cells that can differ in shape and size, including animal and plant cells. Animal cells are eukaryotic with internal structures like a nucleus, mitochondria, and vacuoles, while plant cells have additional cell walls and chloroplasts.