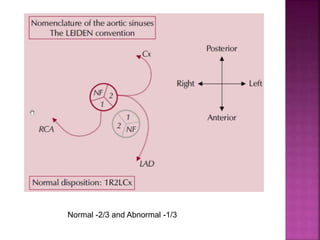
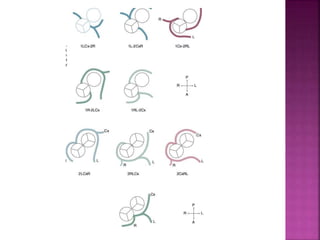
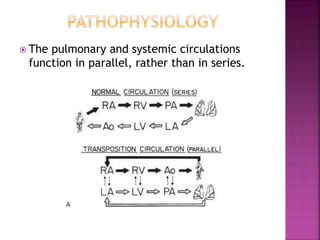
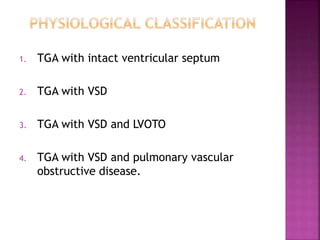
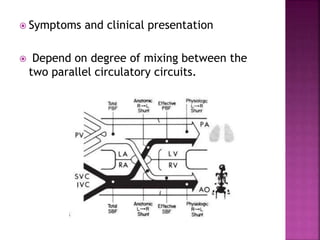
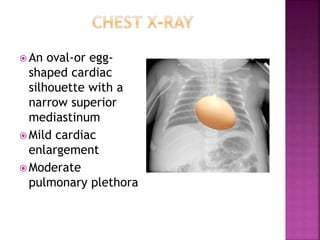
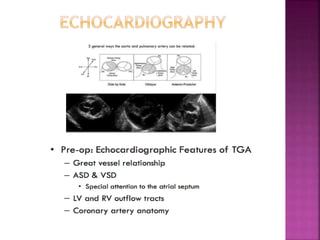
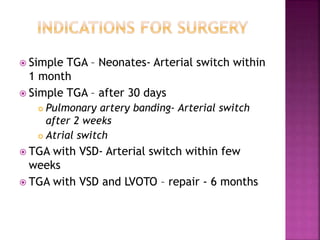
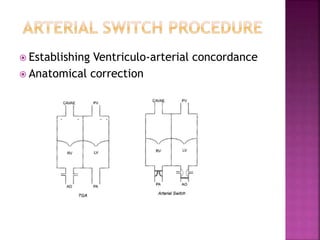
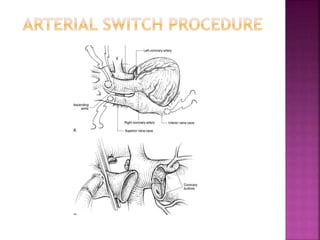
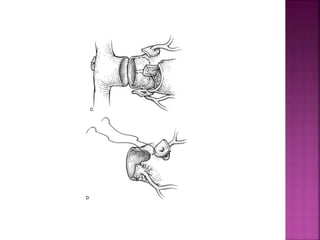
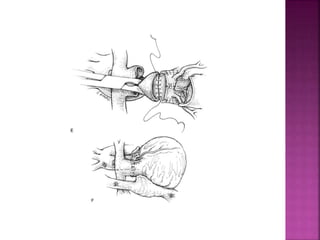
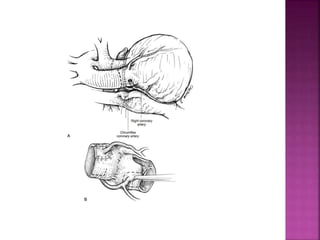
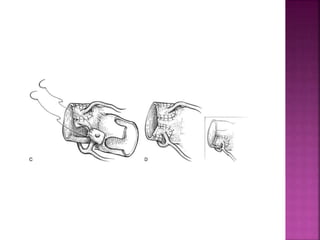
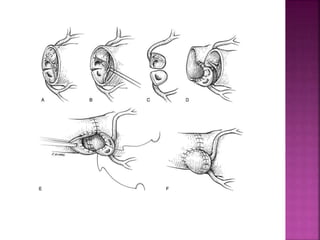
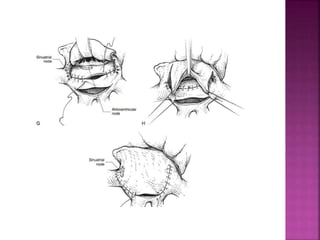
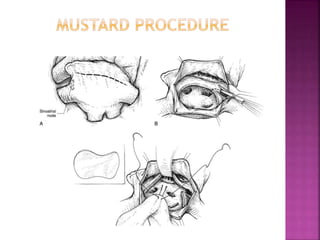
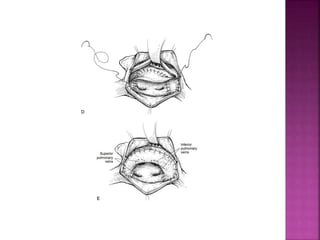
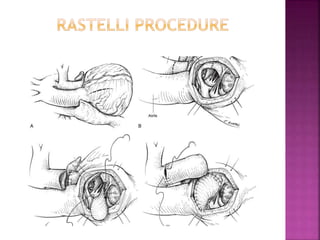
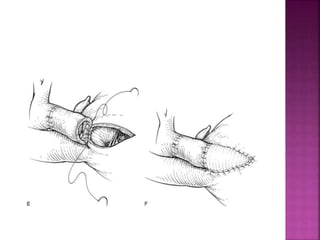
This document discusses the history, diagnosis, and treatment of transposition of the great arteries (TGA). It notes that TGA is a congenital heart defect where the aorta arises from the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery from the left ventricle. The document outlines the key developments in the surgical treatment of TGA, from early septostomies and shunts to the arterial switch procedure. It also describes the clinical presentation and management of different variations of TGA.