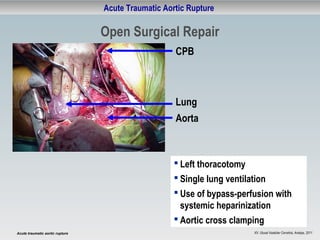
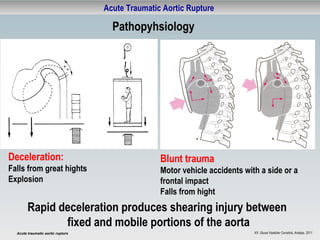
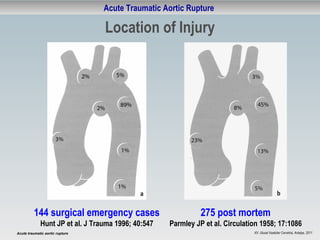
This document discusses acute traumatic aortic rupture, summarizing that it is a life-threatening surgical emergency caused by blunt trauma from motor vehicle accidents or falls. It can be diagnosed using CT scans or TEE ultrasound and treated either through open surgical repair requiring bypass and clamping, or endovascular stent grafting which avoids thoracotomy. While endovascular repair has advantages of less invasiveness and shorter procedure time, open repair may be necessary for injuries of the ascending aorta and there is limited long-term data on endovascular techniques. Complication and mortality rates were found to be lower for endovascular repair compared to open surgery in studies of patients at the Deutsches Herzzentrum Berlin.




![XV. Ulusal Vasküler Cerrahisi, Antalya, 2011Acute traumatic aortic rupture
Acute Traumatic Aortic Rupture
Without treatment
10-15% of the initial survivors die
in the first hour
20-30% die within 6 hours
30-50% within 1 day
60-70% within 8 days
Many of these can be treated!
Natural Course
0
5
10
15
20
100
[%]
14 d7 d48 h24 h6 h1 h
1/2 h
accident 10
weeks
1 year
Gotzen, Hetzer 1982 (n = 40)
Parmley 1958 (n = 275)
Jahnke 1964 (n = 38)
Hartford 1986 (n = 86)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acutetraumaticaorticrupture-150305030729-conversion-gate01/85/Acute-traumatic-aortic-rupture-7-320.jpg)