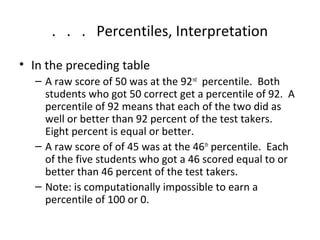
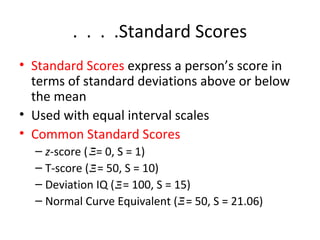
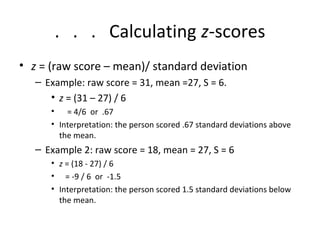
This document discusses different types of scores used to evaluate performance. It describes objective versus subjective scoring and two families of derived scores: scores of relative standing (e.g. percentiles, standard scores) and developmental scores (e.g. age equivalents, grade equivalents). Percentiles express performance as a percentage of others scored lower, while standard scores use deviations from the mean. Developmental scores define performance based on average scores of specific age or grade groups. The document cautions against using developmental scores.