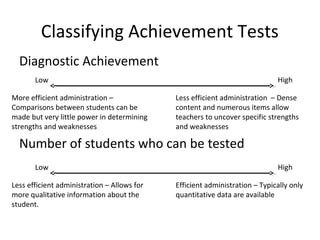
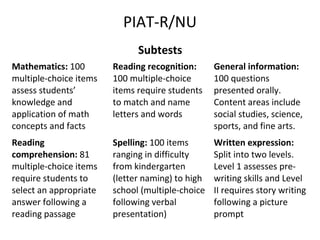
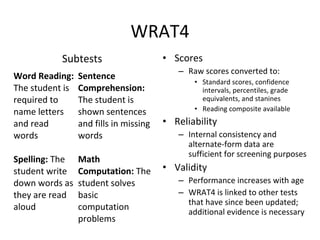
This document discusses achievement tests and provides information on three specific achievement tests: the PIAT-R/NU, WRAT4, and WIAT-III. It summarizes key features of each test including subtests, scores, norms, reliability, and validity. The PIAT-R/NU provides norm-referenced scores across academic areas but has outdated norms and validity data. The WRAT4 is a brief, individually administered test with adequate reliability for screening but could benefit from additional validity evidence. The WIAT-III is a diagnostic, norm-referenced test with strong reliability and validity evidence across multiple academic domains.