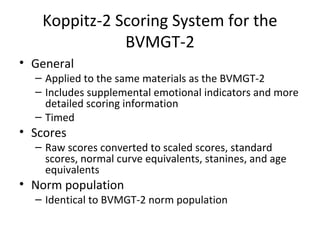
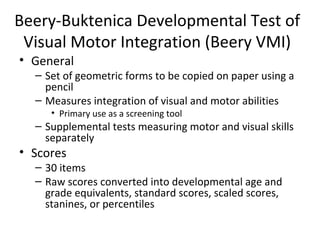
This document discusses measures of perceptual and perceptual-motor skills. It provides an overview of three specific tests: the Bender Visual-Motor Gestalt Test, Second Edition (BVMGT-2), the Koppitz-2 Scoring System for the BVMGT-2, and the Beery-Buktenica Developmental Test of Visual Motor Integration (Beery VMI). For each test, it describes the purpose, administration, scoring, norms, reliability, and validity. The tests are used to screen for and assess perceptual-motor deficits in students, for eligibility decisions, and as part of comprehensive assessments related to brain injury or emotional disturbance.