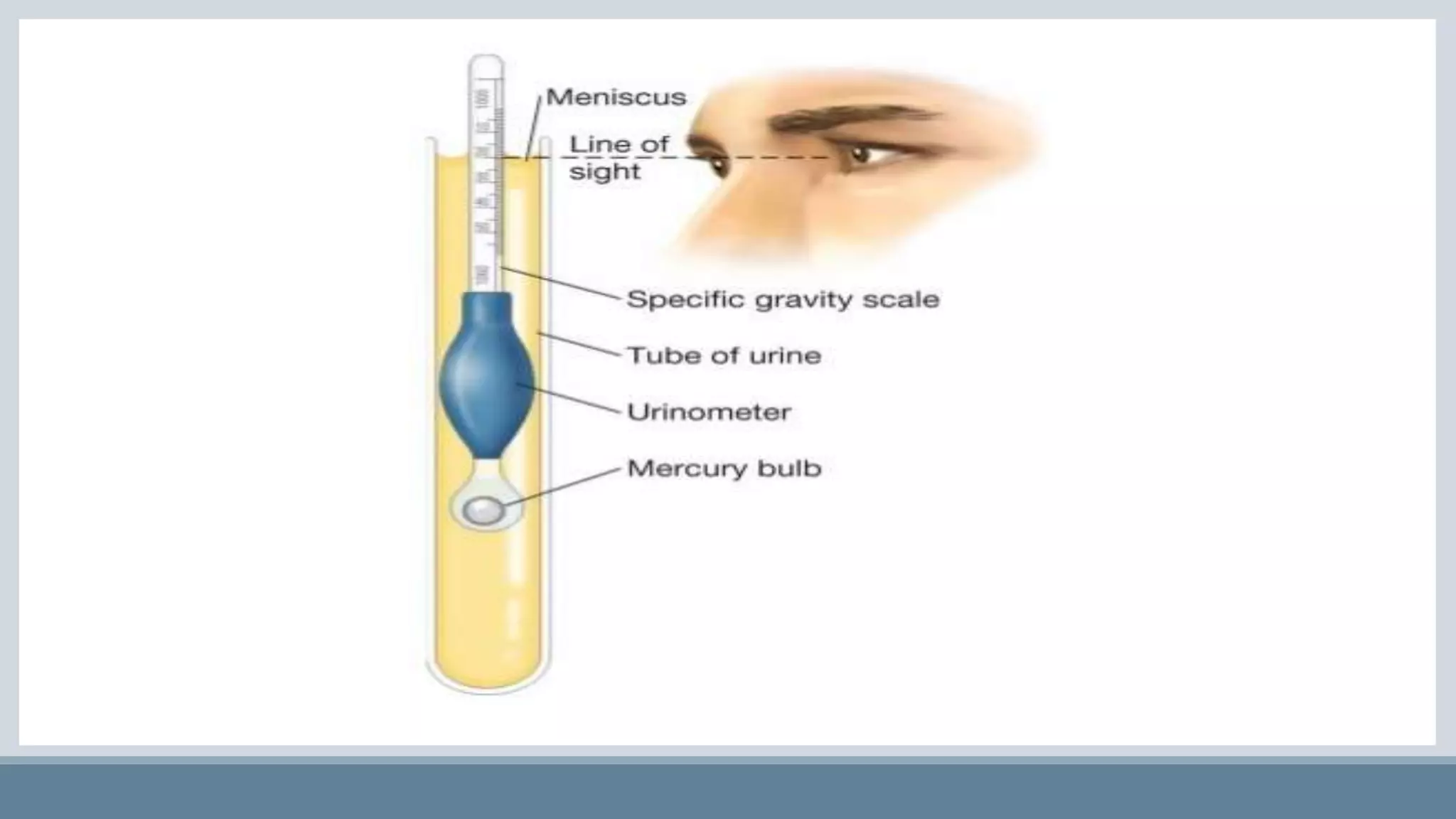
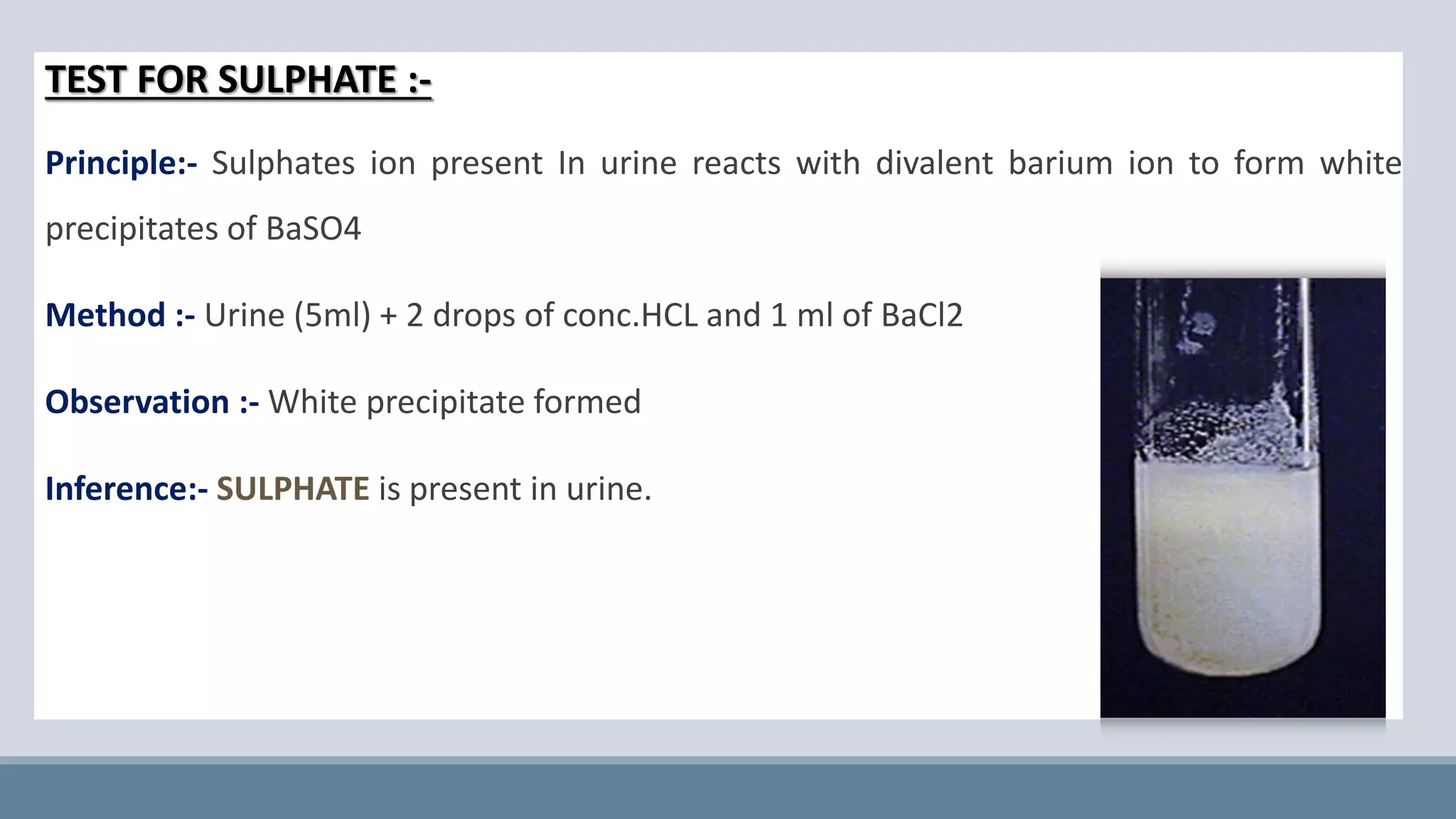
This document provides information on normal urine tests. It discusses the physical characteristics of normal urine like volume, color, odor and pH. It then describes several chemical tests done on urine to detect the presence of urea, uric acid, creatinine, ammonia, chlorides, sulphates and phosphates. Elevated or decreased levels of these substances can provide diagnostic information about conditions affecting the kidneys, liver, muscles and other physiological processes in the body. Urine analysis is a convenient way to obtain health information.