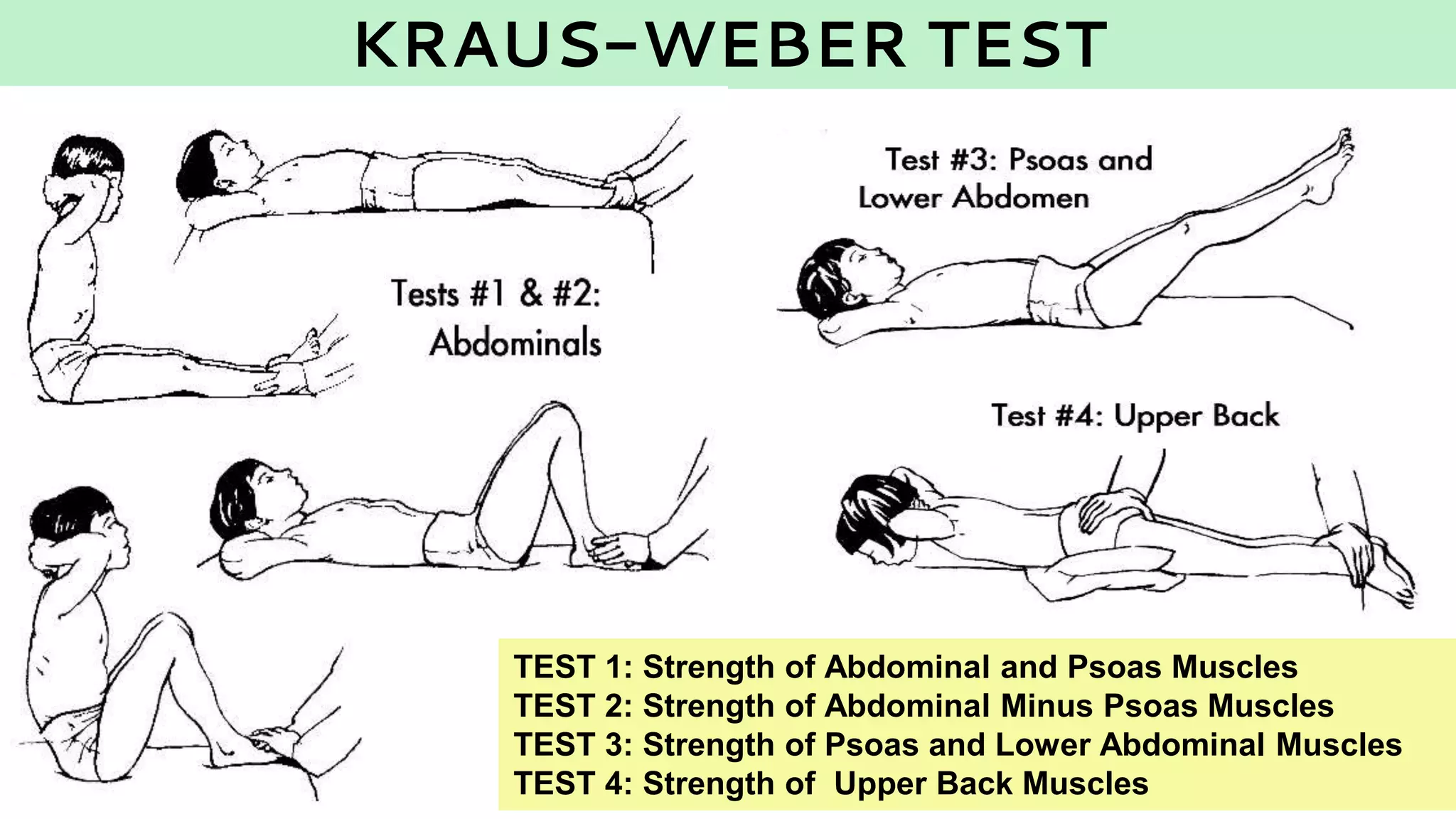
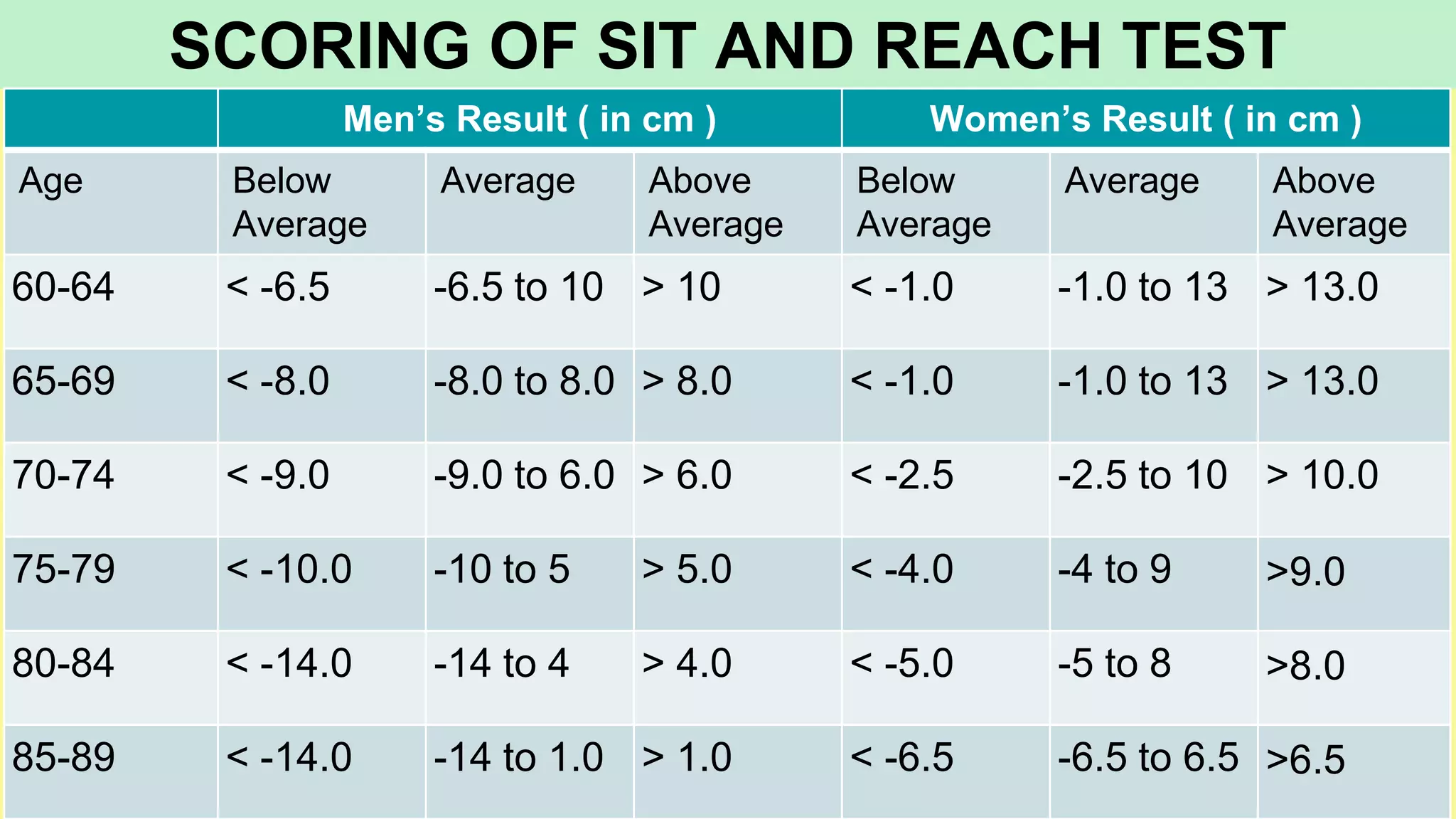
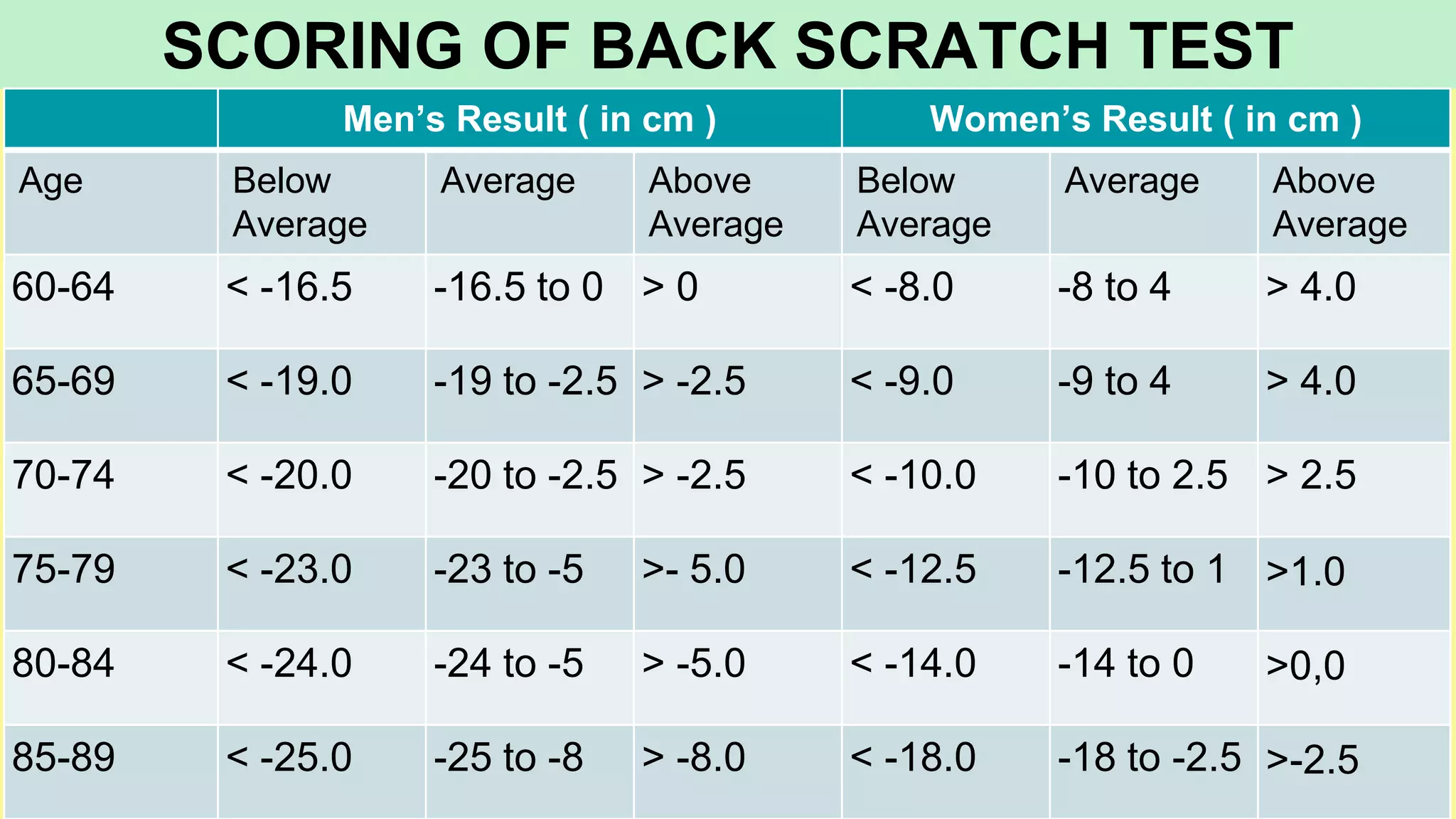
The document summarizes various tests used to measure different components of fitness in sports. It describes the Kraus-Weber test to measure muscular strength, the AAPHER motor fitness test, the Harvard step test and Rockport test to measure cardiovascular fitness, the sit-and-reach test for flexibility, and the Rikli and Jones senior fitness test for older adults. Each test is explained along with the procedures, scoring, and interpretation of results.