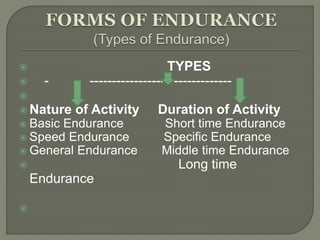
This document discusses different types of endurance and training methods to build endurance. It defines endurance as the ability to resist fatigue during physical activity. There are four main types of endurance defined by the duration and nature of the activity: basic endurance for under 45 seconds, speed endurance from 45 seconds to 2 minutes, general endurance from 2 minutes to 11 minutes, and long time endurance over 11 minutes. The document also outlines several continuous, interval, repetition, and competition training methods that can be used at different intensities and durations to progressively improve endurance over time.