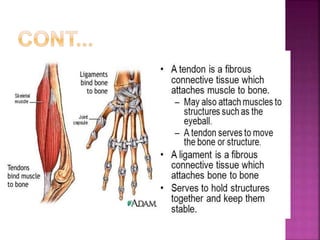
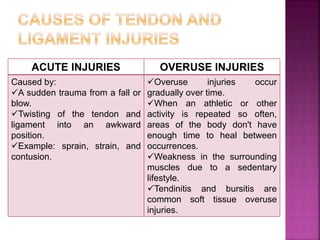
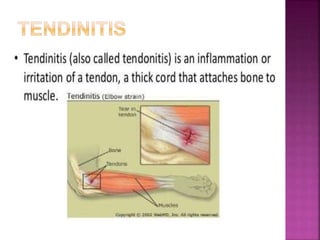
1) Tendons connect muscle to bone and ligaments connect bone to bone. They are both susceptible to acute injuries from trauma or overuse injuries from repetitive stress.
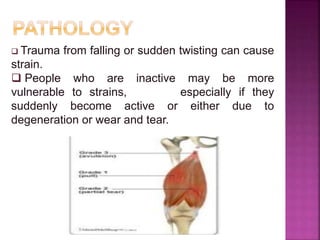
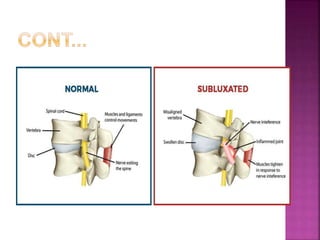
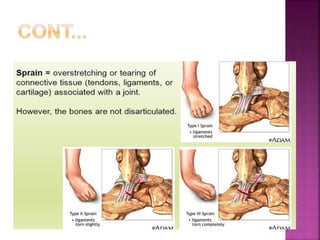
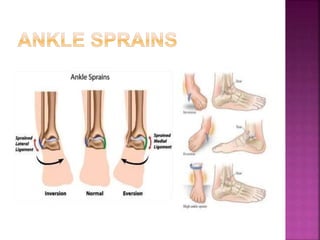
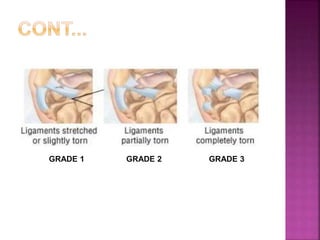
2) Common tendon and ligament injuries include strains, tendinitis, tendinosis, subluxation, ruptures, and sprains. Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and loss of motion.
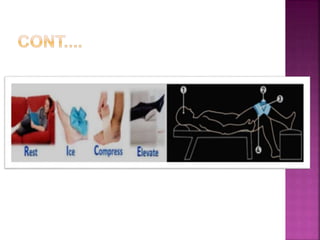
3) Treatment depends on severity but generally involves RICE (rest, ice, compression, and elevation), bracing, physical therapy, or sometimes surgery. Prevention focuses on strength training, wearing proper protective equipment, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.