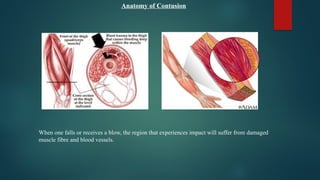
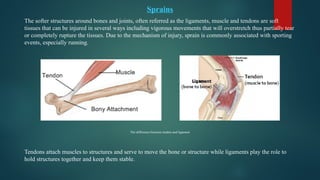
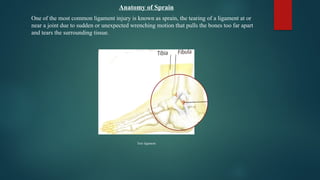
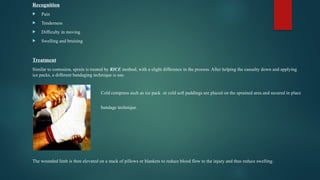
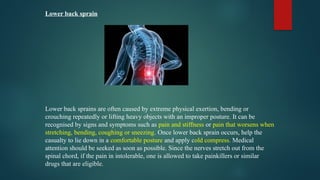
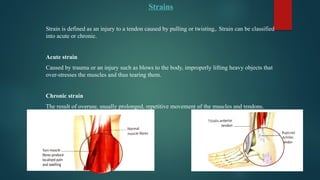
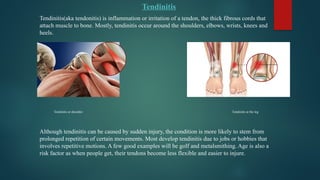
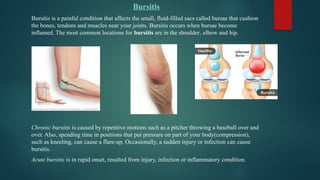
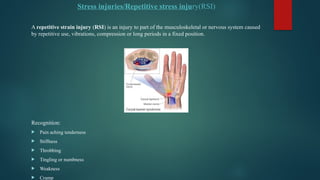
The document details various types of soft tissue injuries, including contusions, sprains, strains, tendinitis, bursitis, and stress injuries, along with their definitions and treatment methods, primarily following the RICE method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation). It highlights the causes, symptoms, and the importance of proper recognition and treatment for each injury type, emphasizing preventative measures and caution against certain harmful practices. The document also provides guidance on makeshift treatments when professional medical help is not immediately available.