1. Psychosis is common in epilepsy patients, occurring in 1-35% of cases and being 8 times more prevalent than in the general population.
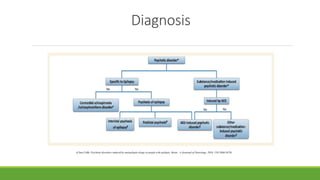
2. Psychosis in epilepsy is classified as ictal, inter-ictal, post-ictal, or antiepileptic drug induced.
3. Diagnosis requires distinguishing psychosis in epilepsy from schizophrenia based on symptoms and personality features, and treatment involves careful use of antiepileptic and antipsychotic drugs due to interactions.